Question
Question: Which one of the following complexes will show optical activity? A. \[trans - {[Co{(N{H_3})_4}C{l_...
Which one of the following complexes will show optical activity?
A. trans−[Co(NH3)4Cl2]+
B. [Cr(H2O)6]3+
C. cis−[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+
D. trans−[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+
Solution
A coordinate compound is called optically active if the compound has optical isomers. Optical isomers do not have symmetry and do not give identical mirror images. For example, the square shape, when cut in any direction, gives the same images.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Optical activity is the ability of a compound to rotate the plane polarized light which is produced by passing ordinary light through a Nicol prism, when placed in their own solution. Such compounds are known as optically active compounds. A French scientist Jean-Baptiste Biot detected it for the first time.
We can determine optical isomers by two ways.
1.Using mirror images: if we are able to rotate a mirror in such a way that it looks identical to the original molecule, then the molecule is said to be superimposable with no optical isomers.
On the other side, if the mirror image does not give identical original image on rotation, then it is not superimposable and the molecule has optical isomers.
For example, those molecules which have octahedral geometry such as [Cr(H2O)6]3+ and trans−[Co(NH3)4Cl2]+ will have superimposable mirror images.
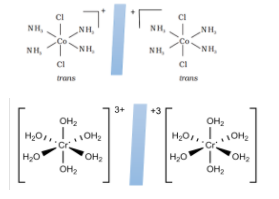
2.Using plane of symmetry: there exists a plane which when cut through any particular coordinate axis produces two exact same images or divides the image into two equal halves. If such a plane of symmetry exists, then no optical isomers are found. Whereas if there is no such symmetry, then the compound has optical isomers.
If a plane of symmetry exists around a central atom, the molecule is achiral and if not, it is a chiral molecule with a chiral centre.
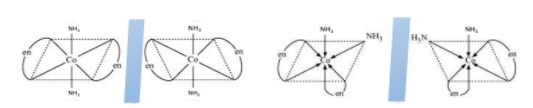
For example, trans−[Co(NH3)4Cl2]+ and trans−[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+ , there exists a plane of symmetry in both which makes them optically inactive. While cis−[Co(NH3)2(en)2]3+ ha no plane of symmetry or any identical mirror image, therefore, it is optically active.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note: For a coordination compound to be optically active, it should have two ambidentate ligands at the minimum and if it shows geometrical isomerism, then it should be cis-isomer. Also, the compound must be chiral i.e. no superimposable mirror image exists.
