Question
Question: Which one of the following carries extranuclear genetic material? (a) Plastid (b) Plasmid (c)...
Which one of the following carries extranuclear genetic material?
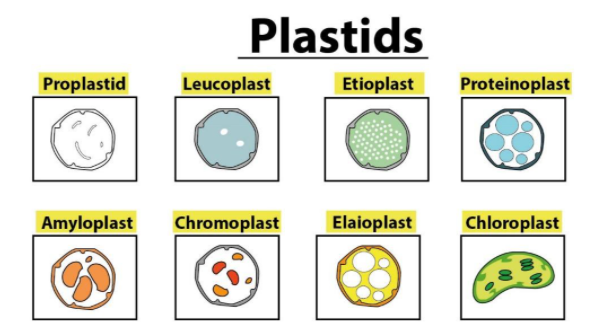
(a) Plastid
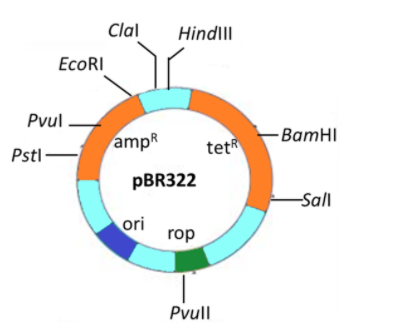
(b) Plasmid
(c) Golgi complex
(d) Both A and B
Solution
Any DNA that is located outside of a cell's nucleus is extrachromosomal. It is often referred to as cytoplasmic DNA or extranuclear DNA. Extranuclear DNA is present in cells of plants, algae, and many other eukaryotic species in a membrane-bound organelle and is often most commonly found in bacteria as small spherical, double-stranded DNA molecules.
Complete answer:
Nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is mainly found in plasmids in prokaryotes, while extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes is mainly found in organelles such as plastids.
Additional Information: A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal molecule of DNA inside a cell that can replicate independently and is physically isolated from chromosomal DNA. Archaea and eukaryotic species also produce plasmids. In nature, plasmids also bear genes that support the body's survival and confer a selective advantage, such as resistance to antibiotics. Although chromosomes are large and contain all the necessary genetic information for normal living conditions, plasmids are typically very small and contain only additional genes that may be useful in certain circumstances or conditions.
The plastid also contains pigments used in photosynthesis, and the color of the cell is determined by the types of pigments in the plastid. They have a similar evolutionary origin and, like the circular chromosome of prokaryotic cells, have a circular double-stranded DNA molecule. Chlorophyll-containing plastids can carry out photosynthesis and are called chloroplasts. Plastids can also store materials such as starch and can synthesize fatty acids and terpenes that can be used for energy production and the synthesis of other molecules as raw material. For example, the components of the plant cuticle and its epicuticular wax are synthesized from palmitic acid by the epidermal cells, which are synthesized in the mesophyll tissue chloroplasts.
So, the answer is, “Both A and B.”
Note: -The principal source of this extrachromosomal DNA is mitochondrial DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in replication research because it is simple to recognize and isolate. In prokaryotes, extrachromosomal DNA exists as circular or linear plasmids outside the nucleoid region.
-Artificial plasmids are commonly used in molecular cloning as vectors, helping to drive the replication inside host species of recombinant DNA sequences. In the laboratory, by transformation, plasmids may be inserted into a cell.
-All plastids are derived from proplastids that are present in the plant's meristematic regions. Proplastids and young chloroplasts are usually divided by binary fission, but this capacity is also available for more mature chloroplasts.