Question
Question: Which one of the following carbocation is most stable? A. \({(C{H_3})_3}C\mathop C\limits^ + {H_2}...
Which one of the following carbocation is most stable?
A. (CH3)3CC+H2
B. (CH3)3C+
C. CH3CH2C+CH2
D. CH3C+HCH2CH3
Solution
Chemical species bearing a positive charge on carbon and carrying six electrons in its valence shell are called carbocations. The stability of carbocations follows the order:
3∘>2∘>1∘
Complete step by step answer: The order of stability of carbocations can be explained based on the following factors:
Inductive effect: The stability of the carbocation directly proportional to +I effect of the alkyl group.
Resonance effect: carbocations in which +vely charged carbon is attached to a double bond or a benzene ring are stabilized by resonance.
Hyperconjugation: effect: The relative stability of carbocations can be explained as more will be the ∝ hydrogen, more will be hyperconjugative structure and more will be stability.
For the case of the above options
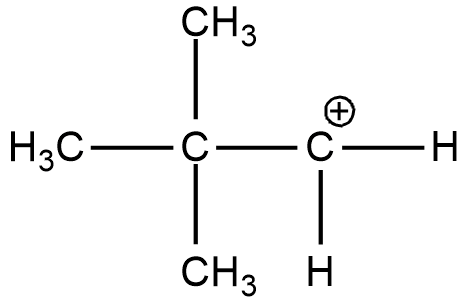(A)
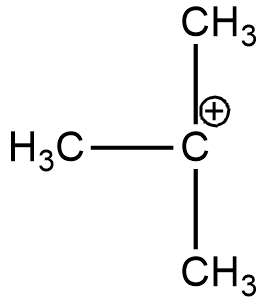 (B)
(B)
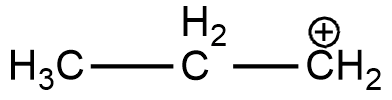 (C)
(C)
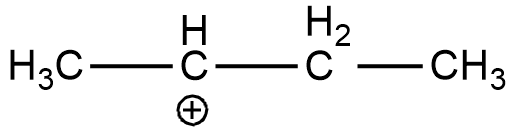 (D)
(D)
In the case of option A, there is only one alkyl group attached to the carbon-containing + charge. In option B there are 3 alkyl groups and in the case of options C and D, there are 1 and 2 alkyl groups respectively. As more will be the alkyl group more will be the electron-donating effect i.e. +I effect which stabilizes the dispersal of + charge on carbocation. Hence option B is more stable. And if we talk about the resonance it exists only in the case of benzene and double-bonded carbocation.
And according to the hyperconjugation effect in the case of option B, there is maximum ∝hydrogen so maximum hyperconjugative structures are there. Hence the maximum will be stability.
Hence the correct option is B.
Note: ∝-hydrogen is that hydrogen that is attached to the carbon bonded with the carbocation. carbocations are highly reactive species and reactivity order is just the opposite of stability order.
