Question
Question: Which one of the following alkenes when treated with HCl yields majorly an anti Markovnikov product?...
Which one of the following alkenes when treated with HCl yields majorly an anti Markovnikov product?
(a) F3C−CH=CH2
(b) Cl−CH=CH2
(c) CH3−CH=CH2
(d) H2N−CH=CH2
Solution
- Hint: The group which has the most electron-withdrawing power attached to the carbon chain will yield majorly anti-Markovnikov products when they are treated with HCl.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Let us understand more about Markovnikov and anti-Markovnikov rule.
-An alkene is a group of organic compounds which has a double bond in it. A double bond contains an extra bond which is known as pi-bond and the electrons in the pi-bond is known as pi-electrons.
-The pi-electron cloud is susceptible to electrophilic attack. An electrophile is an attacking group or ion which has a dearth of electrons. So they love attacking electron-rich areas of a compound and since alkenes have pi-electron clouds, they become an easy target.
-When HCl is added to alkenes, the H+ ion acts as an electrophile and it attacks the pi-bond and breaks the bond and gets attached to one of the carbon atoms. The pi-bond breaks and a positive charge is formed on the other carbon atom. The mechanism is shown below.
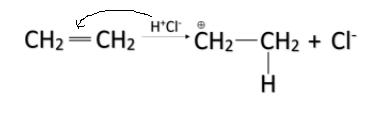
-The partial positive charge formed on the other carbon atom is attacked by the Cl− ion. In this way, the HCl is added in the alkene and the entire reaction is called addition reaction.
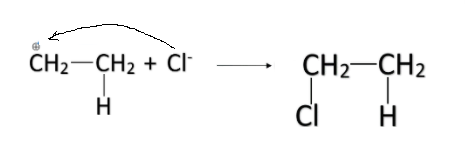
-When the number of carbon atoms in the alkene is more than two, there are two possibilities for the addition. For example, let us consider propene. The formula of propene is CH3−CH=CH2
-In propene, when the H+ ion is added, there are two carbon atoms where the positive charge can form, i.e., in first carbon or the second one. Here comes the Markovnikov rule which governs this type of additions.
-According to this rule, the H+ gets attached to the carbon having more hydrogen substitutes while the halide will add to the carbon having fewer substitutes. This is to ensure that the positive charge formed during the intermediate becomes more stable.
-The methyl groups ( CH3− ) present in the alkene tend to push the electron cloud away from the group. This is known as the positive inductive effect (+I). The pushing of electron clouds away from the group towards the positive charge will help the positive charge to stabilize.
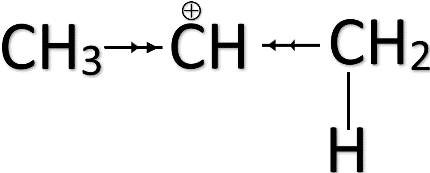
-Anti Markovnikov rule applies when there is a group present in the alkene which has an electron-withdrawing effect due to its higher electronegativity. This is known as the negative inductive effect (-I). These kinds of groups withdraw the electron cloud towards itself thus making the positive charge unstable.
-In an anti-Markovnikov addition reaction, the H+ gets attached to the carbon having fewer hydrogen substitutes and the positive charge is formed on the other carbon and thus the halide ion adds to that carbon.
-Among the given options, the alkene in option A has three fluorine groups attached to it. Fluorine has the highest electronegativity and thus has the most electron-withdrawing power i.e., -I effect. So, that alkene will majorly yield anti-Markovnikov product on treating it with HCl.
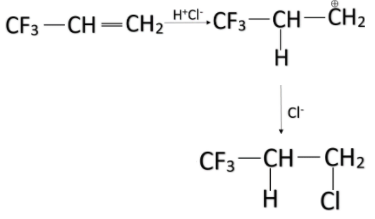
Note: Always remember, the Markovnikov product is formed mostly when there is a group that has +I effect while anti-Markovnikov product is formed mostly when there is a group that has –I effect. Don’t confuse between them.
