Question
Question: Which one amongst of the following isomerism is shown by \(\left[ {{\text{Pt}}{{\left( {{\text{N}}{{...
Which one amongst of the following isomerism is shown by [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] ?
A. Structural
B. Geometrical
C. Optical
D. Conformational
Solution
The compound [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] forms two isomers. In one both the same groups are on the same side and in second, both same groups are on a different side.
Complete step by step answer:
The compounds having the same chemical formula but a different arrangement of atoms is known as isomers.
The compounds that have the same number of atoms but different bonding are known as structural isomerism. In both isomers of [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] bonding remains the same so, option (A) is incorrect.
Geometrical isomerism is shown by the compounds that have the same chemical formula but the different spatial arrangement of atoms. Both the isomers of [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] differ in the spatial arrangement so, option (B) is correct.
Geometrical isomerism in [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] is shown as follows:
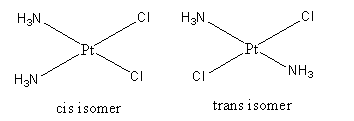
The [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] is a square planar complex. In which two ammine and two chloro ligands are present.
Cis isomer is the isomer that has the same priority group on the same side of the metal.
Trans isomer is the isomer that has the same priority groups on different sides of the metal.
Optical isomerism is shown by the optically active compounds. The isomers are known as enantiomers. Enantiomers are the non-superimposable mirror image. Both of the isomers of [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] have plane so, none of the isomers is optical active so, option (C) is incorrect.
The isomers that can be interconverted into each other by rotation around a single bond by rotation are known as conformational isomers. Both of the isomers of [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] cannot be converted into each other by rotation so, option (D) is incorrect.
Thus the correct option is (B).
Note: Square planar complexes do not show optical isomerism because square planar complexes always have a plane of symmetry. Geometrical and optical isomerism is part of stereoisomerism. In both isomerism, the spatial arrangement differs.
