Question
Question: Which of the following would give Hoffmann alkene? This question has multiple correct options. A) ...
Which of the following would give Hoffmann alkene? This question has multiple correct options.
A) 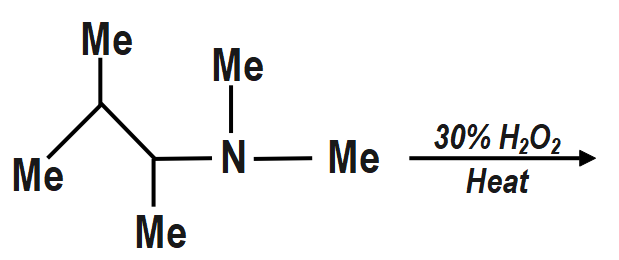
B) 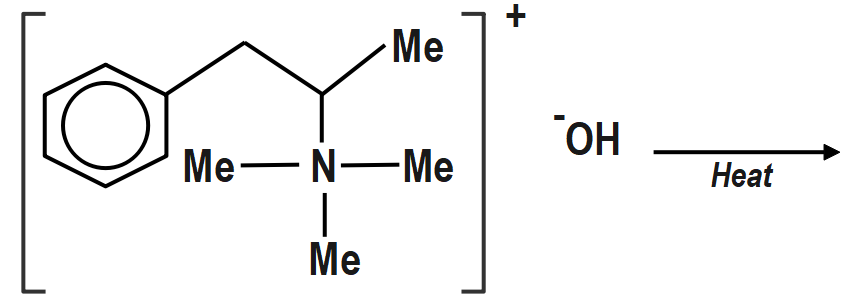
C) 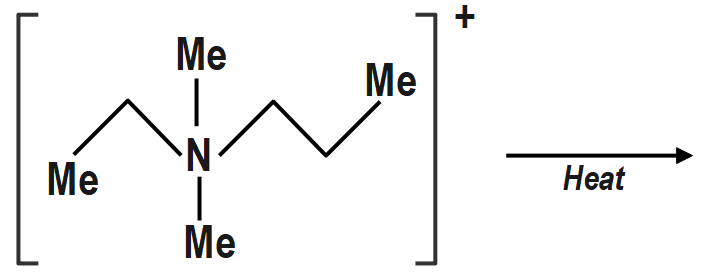
D) 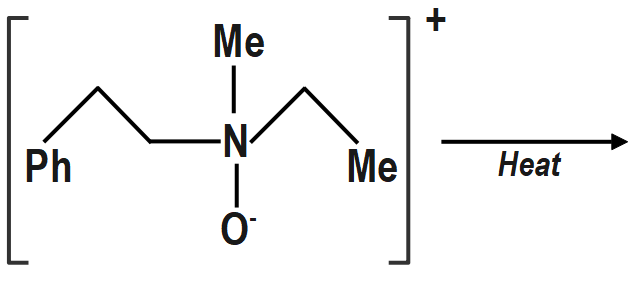
Solution
Alkenes are the one with at least one carbon-carbon double bond. They are very important for the chemical industry as they are produced due to the cracking of alkanes. They also burn in air and form carbon dioxide and water. Ethene in oxygen reacts explosively so it is not much good as a fuel. They can be used in the chemical industry too where they are used to produce plastics and many other chemicals which are to be used as fuels.
Complete step by step solution:
It does not have beta hydrogens present which is why methyl iodide is used in excess which thus cannot complete elimination. If there are two different sets of beta hydrogen present in the alkyl group then the alkene isomer having less substituted double bond is made as the major product of the reaction.
The Hofmann rule states that the major alkene product is the least substituted and least stable product when it comes to asymmetrical amines. The Hofmann elimination can be illustrated as follows:
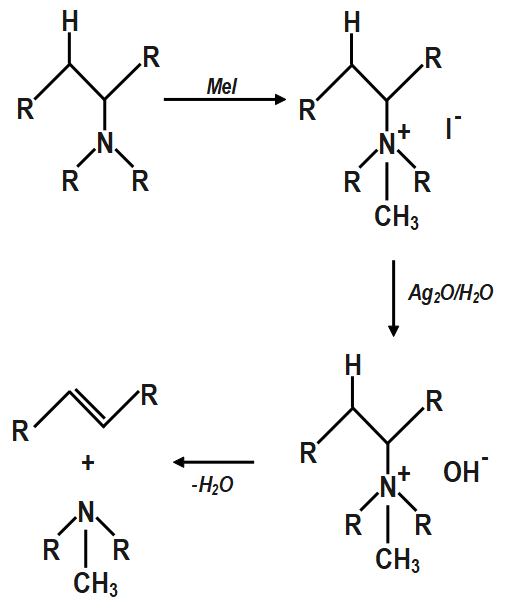
The products which are made is an alkene and a tertiary amine. With addition of silver oxide and water to quaternary ammonium iodide salt and heating of mixture results in the formation of elimination reactions which result in required products.
Thus we know,
(a,c)
a. The oxidation of 3 amine to amine oxide followed by Cope reaction on heating gives Hofmann alkene (less substituted).
b. (II) will not give Hofmann alkene. Benzylic Hydrogen atom is more acidic due to
(−I) effect ofPh.
c. (III) will give Hofmann alkene CH2=CH2
d. (IV) will not give Hofmann alkene (Cope reaction). Same explanation as in (b) above.
Note:
They are mostly gases from two or four carbon atoms, from five to seventeen they are liquids and from eighteen onwards they are solids at room temperature. They are lighter than water and are insoluble in the same. They are soluble in organic solvents. The replacement of the iodine by a hydroxyl anion is followed by an elimination reaction to form the alkene as well.
