Question
Question: Which of the following will not undergo nucleophilic aromatic substitution? I.
II.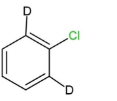
III.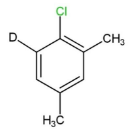
IV.
A.I,II and III
B.II and IV
C. III and IV
D. only IV
Solution
Nucleophilic substitution is a type of reaction, where a nucleophile takes the place of a leaving group in any organic compound. When a group is removed from the aromatic ring, and the nucleophile gets attached, the reaction is called a nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Complete step-by-step answer: Any aromatic compound has the activating positions of ortho and para. These ortho and para positions contain a beta- hydrogen that makes them activating. These positions are activated for the incoming nucleophile, and the nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction occurs. If any group takes the place at ortho and para position and replaces the beta- hydrogen, then the nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction is not supported in that compound.
We can see that compounds,I,IIand III contain beta- hydrogen, or the deuterium ion, which is an isotope of hydrogen, at the ortho and para positions. So these compounds will easily undergo nucleophilic aromatic substitution.
While we can see that compound IVcontains methyl groups at all the free ortho and para positions, which is attached by replacing a beta- hydrogen. So, this compound will not undergo nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Hence, only IVwill not show nucleophilic aromatic substitution, so option D is correct.
Note: Nucleophilic substitution reactions are of 2 types, nucleophilic substitution 1, SN1 and nucleophilic substitution 2, SN2. Which happens in 2 steps and 1 step respectively. SN2reactions happen with inversion of configuration.
