Question
Question: Which of the following will give unsymmetrical di-substituted urea after reactions with \(C{H_3}N{H_...
Which of the following will give unsymmetrical di-substituted urea after reactions with CH3NH3?
- CoCl2
2)CH3CH2NCS - CH3CH2NCO
- All of these.
Solution
We know that Urea, additionally called carbamide, the diamide of carbonic corrosiveness. Its equation is H2NCONH2 . Urea has significant utilizations as a compost and feed supplement, just as a beginning material for the assembling of plastics and medications. It is a vapid, glasslike substance that melts at 132.7∘C(271∘F) and deteriorates prior to bubbling.
Complete answer:
Urea serves a significant part in the digestion of nitrogen-containing compounds by creatures and is the primary nitrogen-containing substance in the pee of vertebrates. It is a drab, scentless strong, profoundly solvent in water and for all intents and purposes non-harmful. The body utilizes it in numerous cycles, most eminently nitrogen discharge. The liver structures it by consolidating two alkali atoms (NH3 ) with a carbon dioxide (CO2 ) particle in the urea cycle. Urea is broadly utilized in composts as a wellspring of nitrogen (N) and is a significant crude material for the synthetic business.
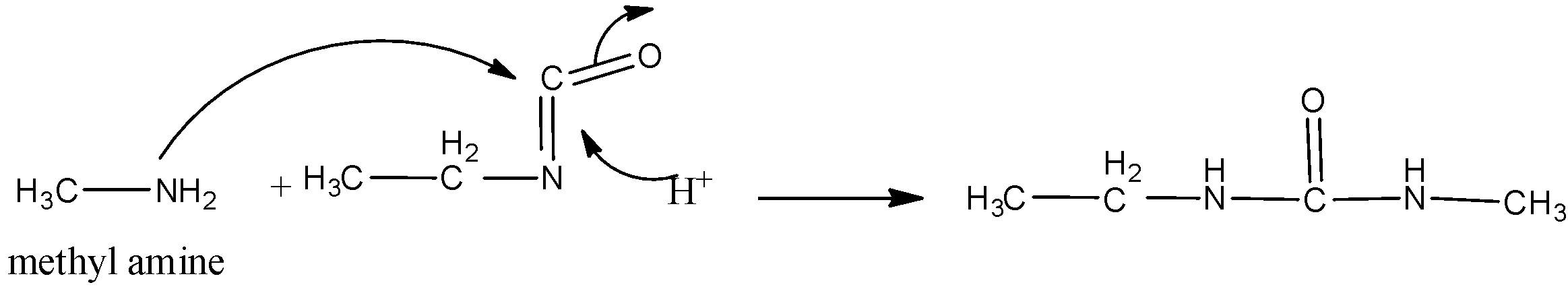
Hence option C is correct.
Note:
Over 90% of world modern creation of urea is bound for use as a nitrogen-discharge fertilizer. Urea has the most noteworthy nitrogen substance of all strong nitrogenous manures in like manner. Along these lines, it has a low transportation cost for every unit of nitrogen supplement. The most widely recognized contamination of engineered urea is biuret, which weakens plant development. Urea separates in the dirt to give ammonium. The ammonium is taken up by the plant. In certain dirts, the ammonium is oxidized by microbes to give nitrate, which is likewise a plant supplement. The deficiency of nitrogenous mixtures to the climate and overflow is both inefficient and naturally harming. Consequently, urea is in some cases pretreated or adjusted to upgrade the productivity of its rural use. One such innovation is controlled-discharge manures, which contain urea exemplified in an inactive sealant. Another innovation is the change of urea into subordinates, for example, with formaldehyde, which debase into smelling salts at a speed coordinating with plants' healthful prerequisites.
