Question
Question: Which of the following structures is L-arabinose? A. 
B. 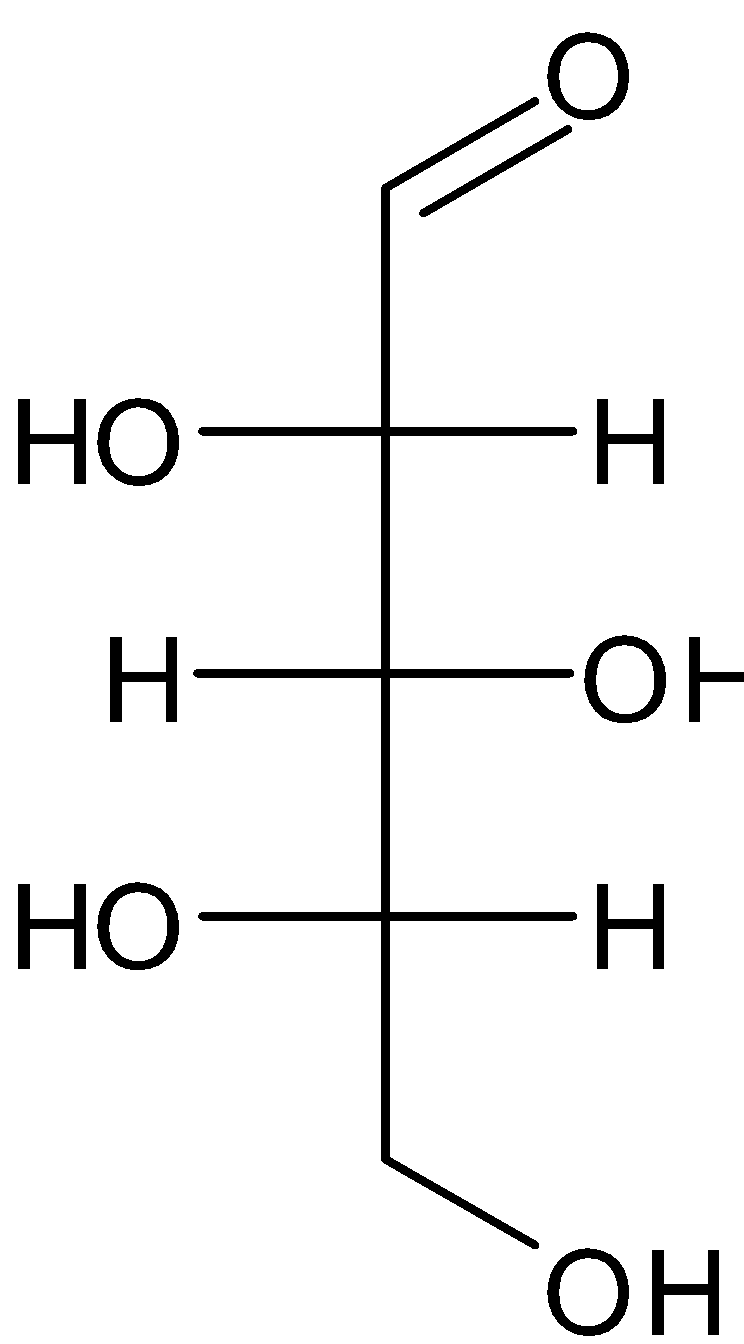
C. 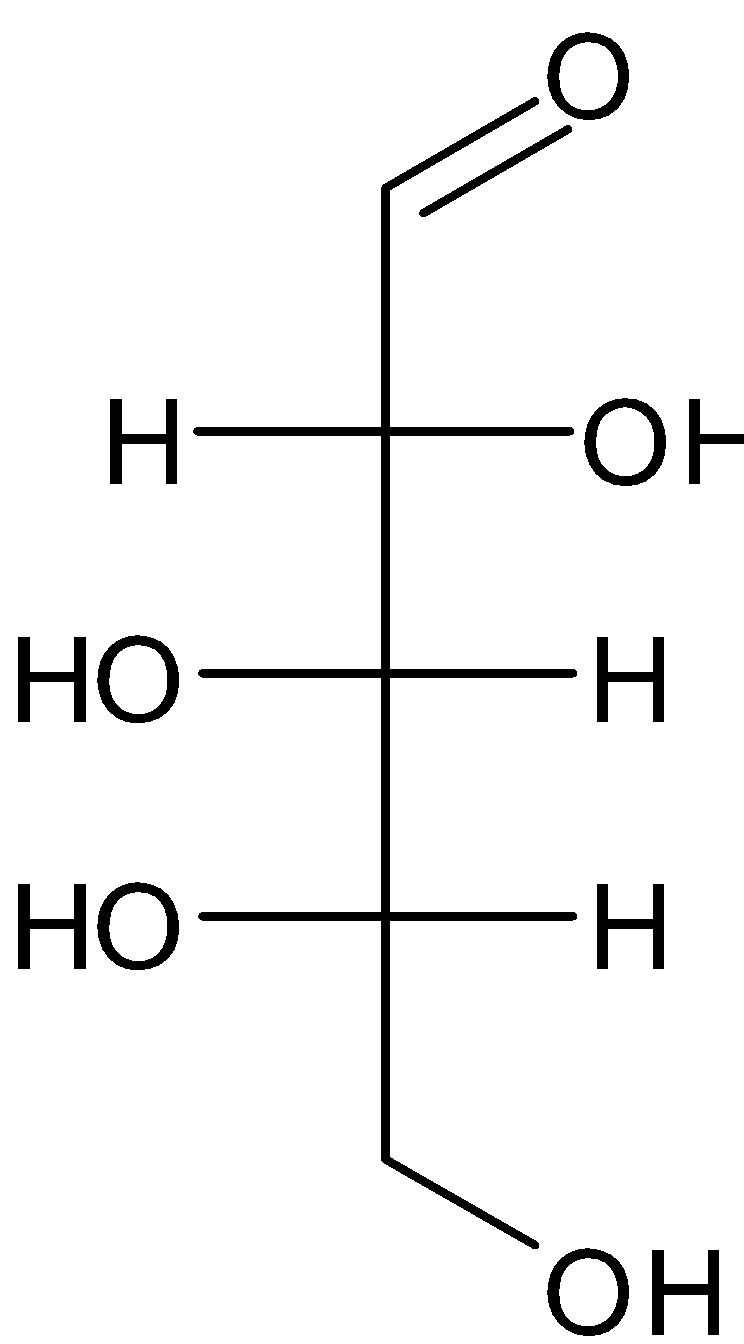
D. 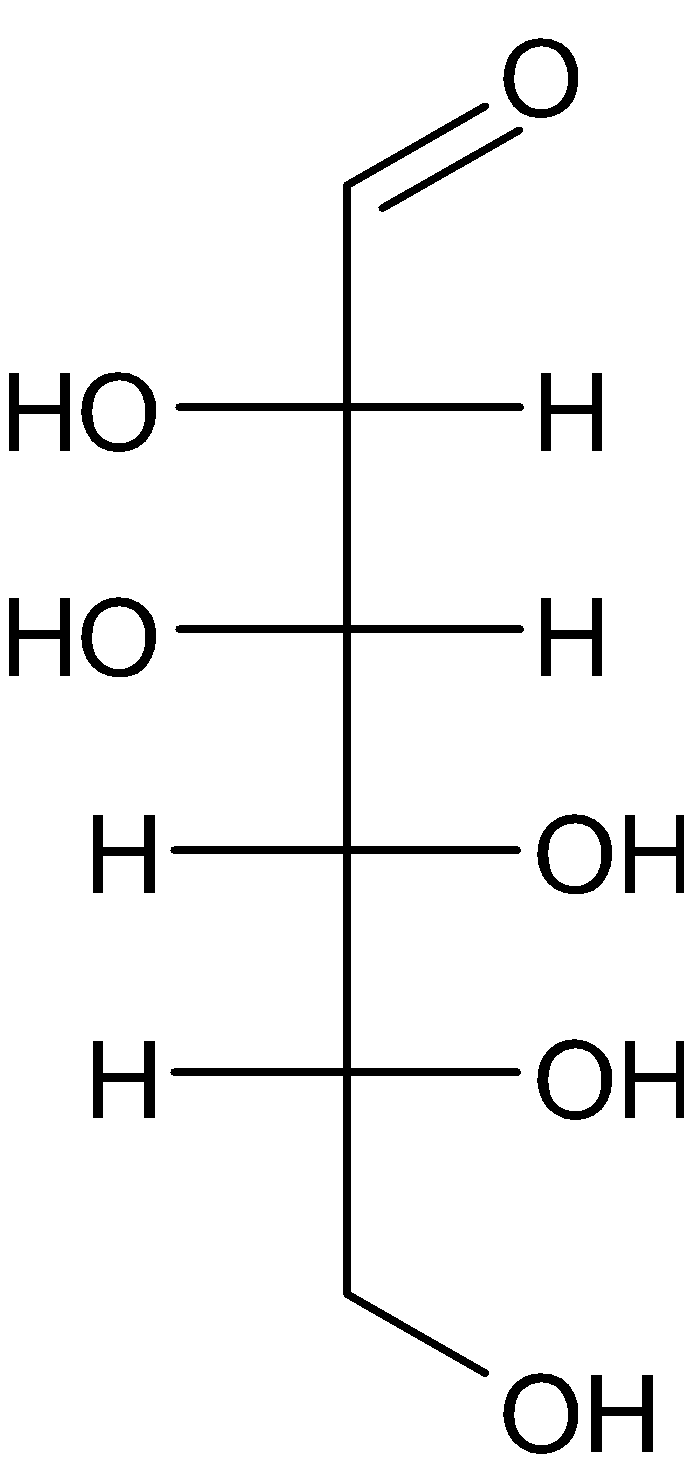
Solution
Carbohydrates are monosaccharides, disaccharide and polysaccharides. Usually simple sugars are monosaccharide. Arabinose is a simple sugar. It is an aldopentose, i.e., it has five carbon atoms in it and the functional group is aldehyde.
Complete step by step answer:
Arabinose is an aldopentose i.e., it is a monosaccharide containing five carbon atoms and it has aldehyde (CHO) functional group.
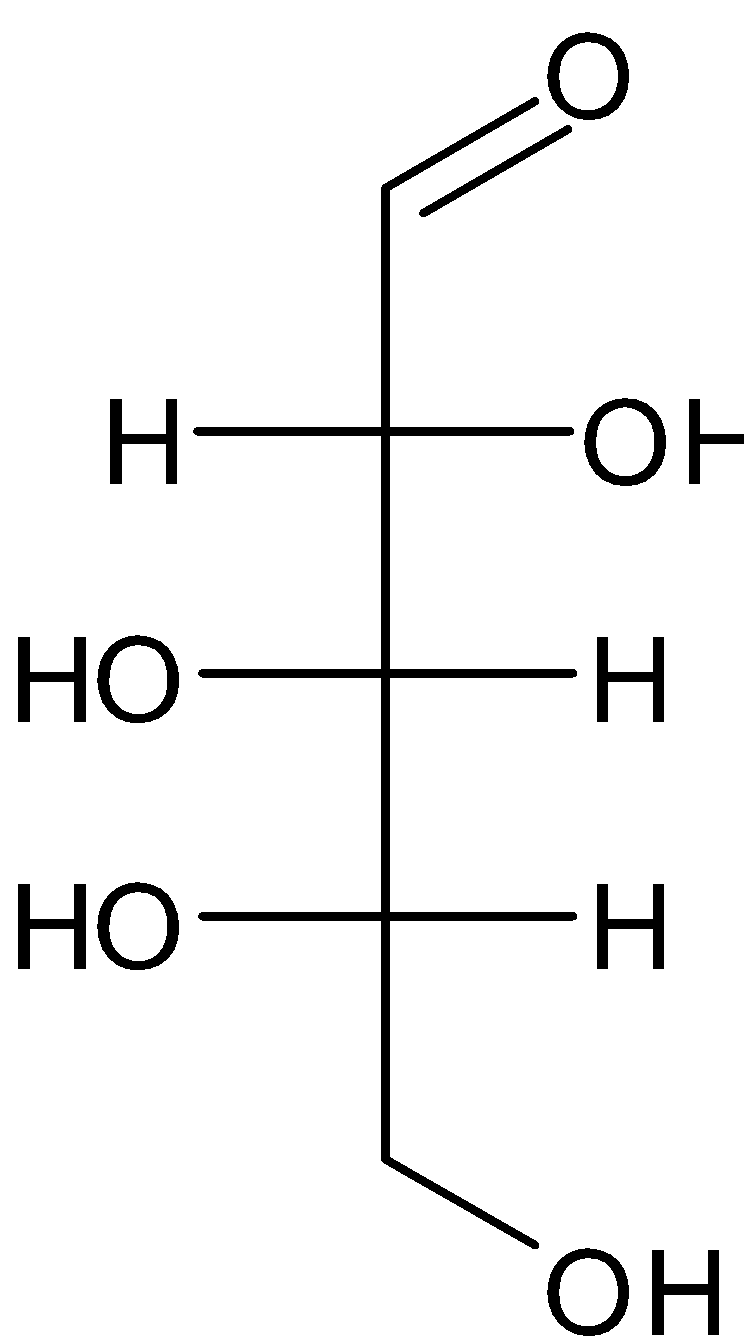
Due to biosynthetic reasons, most of the saccharides are abundant in nature as the "D"-form which is structurally analogous to D-glyceraldehyde. But, L-arabinose is more common than D-arabinose in nature as it is formed as a natural component of biopolymers like hemicellulose and pectin. The use of arabinose in synthetic biology, is as a one-way or reversible switch for protein expression under the promoter in E. coli.
It finds an application as a commercial as a sweetener, also it is an inhibitor of sucrase, which is the enzyme that breaks down sucrose as glucose and fructose in the small intestine.
The classic method for the organic synthesis of arabinose from glucose is by the Wohl degradation.
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Additional information:
Monosaccharides are the building blocks of carbohydrates. They can be said as polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing five, six, seven, or eight membered carbon atoms. They are classified as pentoses, hexoses, heptoses, and octaves, respectively. They can more specifically be expressed by the kind of carbonyl compound present, such as aldohexose or ketohexose.
Note: The most common hexoses are D-glucose, D-fructose, D-galactose, and D-mannose. These all are aldohexoses, except D-fructose, it is a ketohexose. For example, a five membered carbon sugar with aldehyde as carbonyl group is an aldopentose and a six membered carbon sugar with a ketone as carbonyl group is a ketohexose.
