Question
Question: Which of the following shows the \(SN{\,^1}\) reaction most readily? A. 
B. 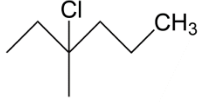
C. 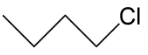
D. 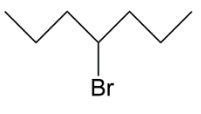
Solution
SN1 represents the unimolecular nucleophilic reaction where you have to see the reactivity order for compounds and then only you can solve this above question. In the SN1 reaction, in the first step a carbocation is formed after the leaving group leaves and that carbocation is responsible for the rate. The more stable the carbocation formed faster will be the reaction.
Complete step-by-step answer: In the SN1 reaction there are two steps involved in the step 1 the leaving group leaves the carbon atom and creates a positive charge there, the carbocation will formed which must be stable. Hence, the stability of carbocation is somewhere responsible for reaction rate. So, we can write the order of reaction as 3∘>2∘>1∘
In the above order we place the tertiary carbocation as first because if in the unimolecular nucleophilic reaction tertiary carbocation will form the speed will be faster. Our aim is to differentiate the above option as 3∘,2∘and1∘
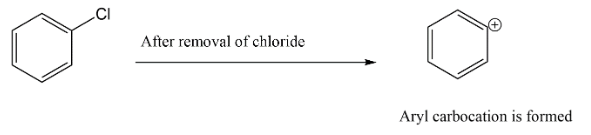
Let’s start with option A. we have chlorobenzene, which will have a partial double bond character on carbon to chlorine bond hence, there is less chances that this substrate will give SN1 faster.
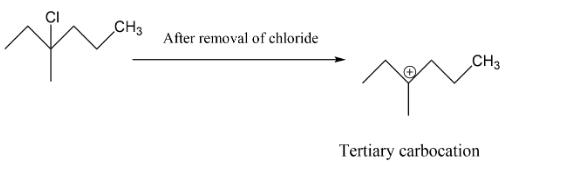
In the next option B we have a tertiary carbocation, we get to know about this as per after the chlorine group will leave the carbocation which will form is tertiary carbocation hence this may be our answer.
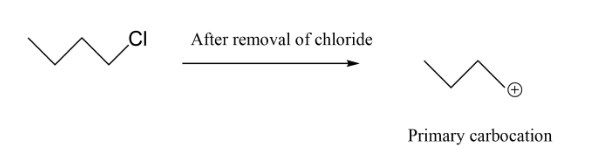
In option C, we have primary carbocation which is least when we see the order hence this cannot be our answer to this question. Lastly we have, secondary carbocation because on removal of bromine as ion it will leave a positive charge which is connected to 2 alkyl groups.
So, the correct option is B.
Note: If you are confused in any option, try to figure out the type of carbocation which will form when halogen leaves from that side. There are many cases like option A where the halogen group will be attached to a sp2 hybridized carbon in that case the removal of any leaving group will be hard because of the double bond character generated at that site and also it will be a vinyl site.
