Question
Question: Which of the following shows the laboratory synthesis of Fluorobenzene \(({{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}F)\)? ...
Which of the following shows the laboratory synthesis of Fluorobenzene (C6H5F)?
A) By heating phenol with HF and KF
B) From aniline by diazotization followed by heating the diazonium salt with HBF4
C) By direct fluorination of benzene with F2 gas
D) By reacting PhBr withNaFsolution
Solution
The answer is based on the concept of reaction mechanism of organic chemistry and also it reacts with the compound where the fluorine can attract the electrons as fluorine is the electronegative element.
Complete step-by-step answer: In the classes of organic chemistry, we have come across various named reactions and also some of the basic reactions like halogenations, addition reactions, substitution reactions and also the oxidation and reduction reactions.
Let us now see each of these options given one by one by reacting it with phenol and deduce the correct answer.
- In option A) When we heat phenol with fluorobenzene, we get the products which is as shown below,
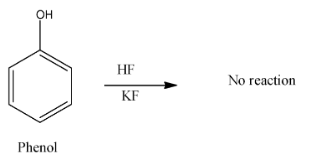
- Here, since the fluoride ion is highly electronegative and it needs a group which is able to donate its electron and only then fluorine attaches to this compound.
- Here, even the acidity factor plays its role where acidity is measured based on the donation of electron and here since inHF, the more electronegative fluorine atom attracts the electron strongly from hydrogen, it does not donate the proton easily asHFis weak acid.
Thus, the reaction does not take place.
- In case of option B) The reaction is given a name Baltz-Schiemann reaction and it takes place as shown below:
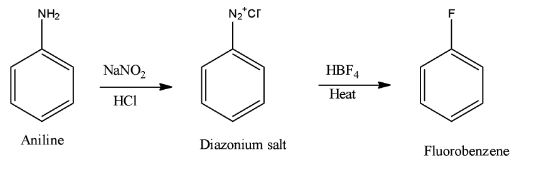
The reaction of diazonium salt withHBF4yields fluorobenzene and this option is correct answer.
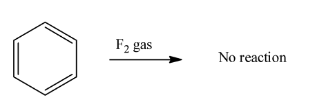
Now in option C) The fluorine atom is highly electronegative and for the homolytic division of fluorine gas that isF2needs higher energy and the stability of the reaction condition gets lower and therefore, the reaction is not possible. Therefore, this option is ruled out.
In case of option D) Treating of bromobenzene withNaFdoes not produce fluorobenzene as according to the Finkelstein reaction which is used for the halogen exchange reaction and since fluorine is highly electronegative than bromine, the reaction does not take place.
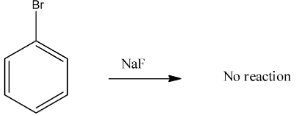
Therefore, the correct answer is option B).
Note: Note that Finkelstein reaction involves the exchange of the halogens that is alkyl or aryl bromide and also chloride with the sodium iodide solution and brominated compounds are more reactive than chlorinated compounds because the order of reactivity is iodide > bromides > chlorides > fluorides and therefore fluorides are not exchanged much here.
