Question
Question: Which of the following remains unaffected on heating? A. Malonic acid B. Maleic acid C. Fumari...
Which of the following remains unaffected on heating?
A. Malonic acid
B. Maleic acid
C. Fumaric acid
D. Succinic acid
Solution
The acid which undergoes heating produces carbon dioxide in the product. This process is kind of a decarboxylation process. Thus, only those acids will respond to heating which can release carbon dioxide from their carboxylic acid group. The cis form of an acid can easily release carbon dioxide from its carboxylic acid group.
Complete answer:
Let us explain each of the given options separately.
A. Malonic acid: The structure of malonic acid is:
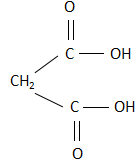
As it is clearly visible, the structure is a cis structure and there exists a dipole moment. Due to this, when malonic acid is heated, it releases carbon dioxide as a product.
B. Maleic acid: The structure of maleic acid is:
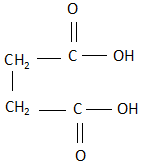
As it is clearly visible, the structure is a cis structure and there exists a dipole moment. Due to this, when maleic acid is heated, it releases carbon dioxide as a product.
C. Fumaric acid: The structure of fumaric acid is:
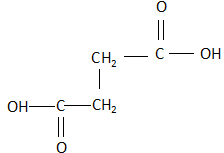
As it is clearly visible, the structure is a trans structure and the dipole moment of the compound is zero as the two carboxylic acid groups oppose the dipole moments of each other and completely neutralize each other. Due to this, when fumaric acid is strongly heated, it shows no response. There is no release of carbon dioxide.
D. Succinic acid: The structure of succinic acid is:
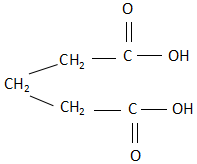
As it is clearly visible, the structure is a cis structure and there exists a dipole moment. Due to this, when succinic acid is heated, it releases carbon dioxide as a product.
Thus, the correct option is C. Fumaric acid.
Note:
Fumaric acid is used as an acid regulator in the food additives and is commonly used in baking powder and beverages where the requirement is the purity of the compound. It is also used as an acid in the leavening process.
