Question
Question: Which of the following reactions will not result in the production of ethylene glycol: 1.\({C_2}{H...
Which of the following reactions will not result in the production of ethylene glycol:
1.C2H4OH3O+Heat
2.ClCH2CH2ClOH−Heat
3.CH2=CH2(i)CH3COOOH(ii)H3O+
4.CH2=CH2alk.KMnO4
Solution
One of the reactions above is a polymerization reaction which results in the formation of polyethylene, and hence does not form ethylene glycol. We know that ethylene glycol is generally formed by the substitution reaction, Beyer’s reaction and acid hydrolysis or catalytic oxidation.
Complete step-by-step answer: As we have studied the synthesis methods of ethylene glycol, let us discuss the production of ethylene glycol in the following given reactions.
The first reaction results in formation of ethylene glycol as a result acid (or alkaline) hydrolysis of ethylene oxide. Ethylene oxide is usually produced by catalytic oxidation of ethylene. We can write the chemical reaction in simple words as “Ethylene oxide (C2H4O) undergoes acid hydrolysis in the presence of dilute acid and at high temperatures to produce ethylene glycol (HO−CH2−CH2−OH)”
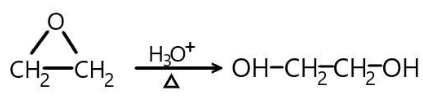
Then we have a second reaction which results in the formation of ethylene glycol by means of substitution reaction. Ethylene glycol forms as both the chloride groups are substituted by hydroxyl groups in the presence of aqueous sodium hydroxide. We can write the chemical reaction as “Dichloroethane undergoes substitution reaction in the presence of aqueous sodium hydroxide solution at higher temperatures to produce ethylene glycol.
ClCH2CH2ClAq.NaOHHeatHO−CH2−CH2−OH+2NaCl
Fourth reaction results in the formation of ethylene glycol with the help of Baeyer’s reagent, which is nothing but a cold and dilute alkaline potassium permanganate solution. It is an additional reaction where the addition of hydroxyl groups (hydroxylation) happens at both carbon atoms. As always, we can write chemical reactions in simple words as “Ethylene undergoes hydroxylation in the presence of cold and dilute alkaline potassium permanganate solution to produce ethylene glycol.”
CH2=CH2alk.KMnO4HO−CH2−CH2−OH
And lastly, reaction 3 results in the production of polyethylene, which begins by the formation of free radicals. The reaction appears as follows
CH2=CH2(i)CH3COOOH(ii)H3O+−(CH2−CH2)n−
Thus, the correct answer is option (3).
Note: Always remember that the simplest and the easiest way of production of ethylene glycol is by the reaction of ethane or ethylene with water which results in an intermediate that is ethylene oxide which basically reacts with water in the solution to give ethylene glycol.
