Question
Question: Which of the following reactions will best convert nitrobenzene into 2, 4, 6-trichlorobromobenzene? ...
Which of the following reactions will best convert nitrobenzene into 2, 4, 6-trichlorobromobenzene?
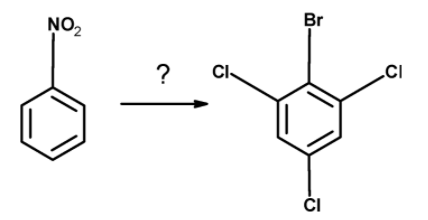
A) SnCl2 / HCl , Cl2−H2O , NaNO2 / HCl −00C , CuBr
B) Cl2 / AlCl3 , SnCl2/HCl , NaNO2 / HCl −00C , CuBr
C) SnCl2 / HCl , Br2−H2O , NaNO2 / HCl −00C , CuCl
D) SnCl2 / HCl , NaNO2 / HCl −00C , H2O , Cl2(aq) , HBr
Solution
The aromatic nitro compounds are reduced by the active metals. The nitro group is reduced to −NH2 groups. The exposure to the excess of halogen results in the 2, 4, 6-tri halo substituted benzene ring. The reaction of the conversion of aromatic primary amines to the diazonium salt ArN2+X− is a diazotization reaction. The diazonium group in the diazonium salts is replaced by the groups to get the desired product.
Complete answer:
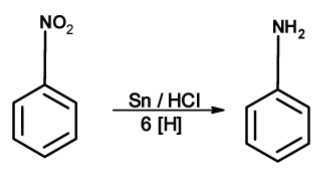
The nitro compounds can be reduced with active metals such as Fe , Sn , Zn , etc. And conc. hydrochloric acid. The mixture of SnCl2 and conc. HCl has been used for the reduction of aromatic nitro compounds.
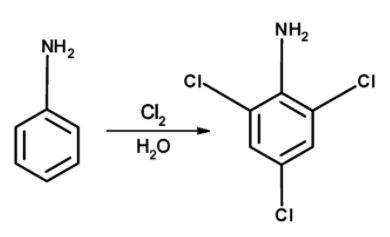
Aniline when reacted with the chlorine molecules, the aniline is converted into 2, 4, 6-trichloroaniline. The reaction of conversion of aniline to the 2, 4, 6-trichloroaniline is as follows,
The diazonium salts have the general formula of ArN2+X− , where X− maybe anion like chloride, bromide, etc. and the group N2+ ( −N ≡ N− ) is called as the diazonium group. These are obtained when the aromatic primary amines react with nitrous acid.
The diazonium salt is prepared by heating the ice-cold solution of aromatic primary amines in excess of the mineral acid like HCl or H2SO4 with the ice-cold solution of sodium nitrite dissolved in water. The temperature is maintained between the 273 K −278 K because most of the diazonium salts decompose at a higher temperature.
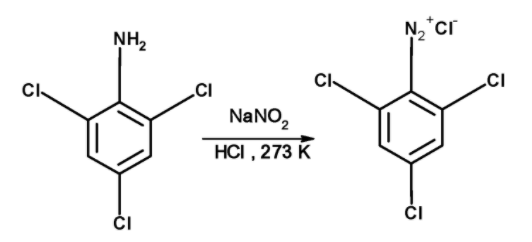
The benzene diazonium chloride of The 2, 4, 6-trichloroaniline is prepared by treating an ice-cold solution of aniline in hydrochloric acid with an ice-cold solution of sodium nitrite at about 00C . The reaction of converting aromatic primary amine to diazonium salt is called diazotization. The 2, 4, 6-trichloroaniline is converted into diazonium salt as follows,
NaNO2 + HCl → NaCl + HONO
The diazonium salt of The 2, 4, 6-trichloroaniline when warmed with the cuprous bromide CuBr in hydrochloric acid the corresponding bromide is formed. The resultant compound is 2, 4, 6-trichlorobromobenzene. The diazonium salt is converted to the halide group. The reaction is as follows,
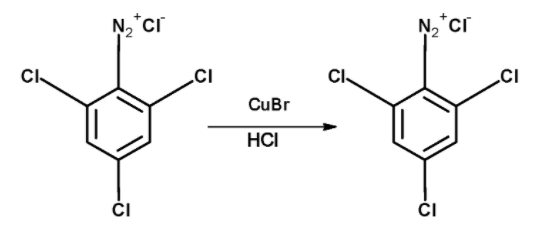
Thus, the nitrobenzene is converted into the 2, 4, 6-trichlorobromobenzene by the action of the following reagent : SnCl2 / HCl , Cl2−H2O , NaNO2 / HCl −00C , CuBr
Hence, (A) is the correct option.
Note:
Note that the preparation of aryl halide from diazonium salt is a good method and has many advantages. Aryl chlorides and bromides when obtained by direct halogenation of aromatic compounds give a mixture of products that are difficult to separate. However, in the diazonium salt replacement method, a pure single product is formed. This also provides a good synthetic route for the preparation of aryl iodides and fluorides which are not obtained by direct halogenation.
