Question
Question: Which of the following reactions is/are feasible? a) \[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COO...
Which of the following reactions is/are feasible?
a) CH3COOH+HCOONa→
b) HC≡C−Na+H2O→
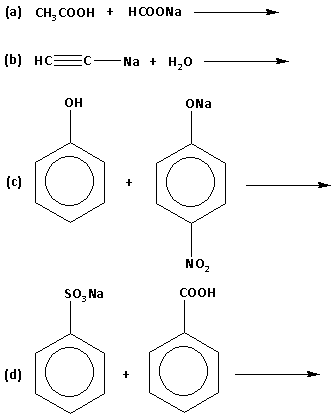
Solution
We know that the given reactions are acid-base reactions. The feasibility of an acid-base reaction depends on the strength of the acids. Strong acids favour the reaction in the forward direction whereas weak acids do not favour the reaction. Thus, the reactions in which weak acids are on the reactant side are not feasible.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that the feasibility of an acid-base reaction depends on the strength of the acids. A strong acid dissociates and forms a conjugate base. If there is strong acid on the reactant side then it will dissociate easily and react with another reactant which is a base.
Thus, the reactions in which the strong acid is on the reactant side are feasible.
And the reactions in which strong acid is on the product side are not feasible.
We are given reaction (a) as follows:
CH3COOH+HCOONa→
In the reaction, acetic acid reacts with sodium formate. The products of the reaction are formic acid and sodium acetate. The complete reaction is as follows:
CH3COOH+HCOONa→HCOOH+CH3COONa
In the reaction, formic acid is stronger than acetic acid. Thus, stronger acid is present on the product side.
Thus, reaction (a) is not feasible. Thus, option (a) is not correct.
We are given reaction (b) as follows:
HC≡C−Na+H2O→
In the reaction, sodium acetyide reacts with water. The products of the reaction are acetylene and sodium hydroxide. The complete reaction is as follows:
HC≡C−Na+H2O→HC≡CH+NaOH
In the reaction, water is stronger than acetylene. Thus, stronger acid is present on the reactant side.
Thus, reaction (b) is feasible. Thus, option (b) is correct.
We are given reaction (c) as follows:
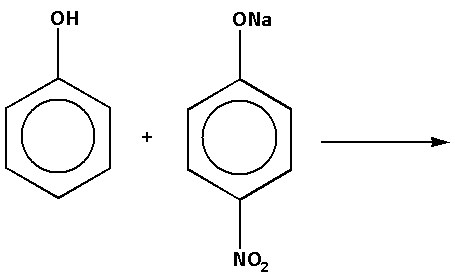
In the reaction, phenol reacts with sodium nitrophenolate. The products of the reaction are nitrophenol and sodium phenoxide. The complete reaction is as follows:
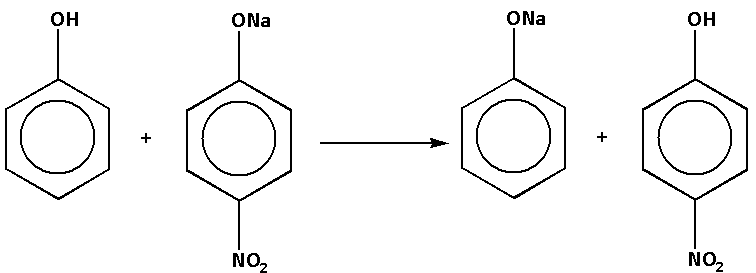
In the reaction, nitrophenol is stronger than phenol. Thus, stronger acid is present on the product side.
Thus, reaction (c) is not feasible. Thus, option (c) is not correct.
We are given reaction (d) as follows:
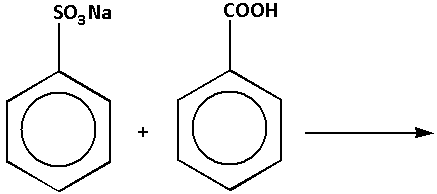
In the reaction, sodium benzene sulphonate reacts with benzoic acid. The products of the reaction are benzene sulphonic acid and sodium benzoate. The complete reaction is as follows:
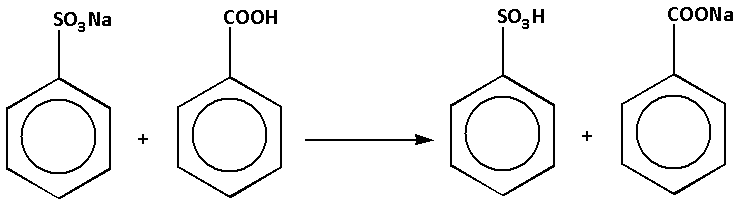
In the reaction, benzene sulphonic acid is stronger than benzoic acid. Thus, stronger acid is present on the product side. Thus, reaction (d) is not feasible. Thus, option (d) is not correct.
Thus, the feasible reaction is reaction (b). Thus, the correct option is (b).
Note: The feasibility of an acid-base reaction is compared on the basis of the strength of the acids only and not on the strength of the bases. The strength of an acid depends on the pKa value of the acid. Higher the pKa value lower is the strength of the acid.
