Question
Question: Which of the following primary amine is not prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis: A.\[C{H_3} ...
Which of the following primary amine is not prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis:
A.CH3−CH2−NH2
B.CH3−NH2
C.Ph−NH2
D.Ph−CH2−NH2
Solution
The Gabriel synthesis is a chemical reaction that transforms primary alkyl halides into primary amines. Traditionally, the reaction uses potassium phthalimide and, therefore, is also called Gabriel phthalimide synthesis. It uses a nucleophilic substitution reaction to form primary amines from alkyl halide.
Complete answer:
In Gabriel phthalimide synthesis, a base abstract proton from phthalimide gives a nucleophile phthalimide ion which attacks on the unhindered primary alkyl halide. The base hydrolysis of alkylated phthalimide gives the primary unhindered amine and phthalimide ion. Phthalimide ion itself is a bulky ion, so it prefers attack on hindered alkyl halide.
Gabriel phthalimide synthesis can be understood through the following mechanism:
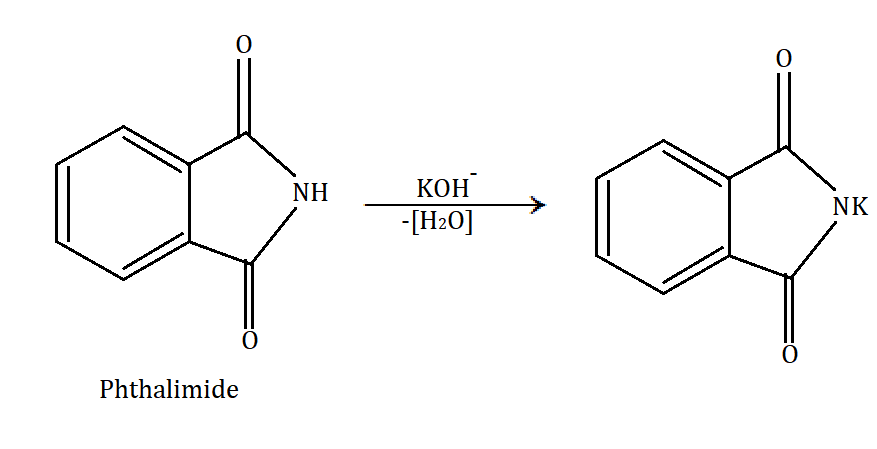
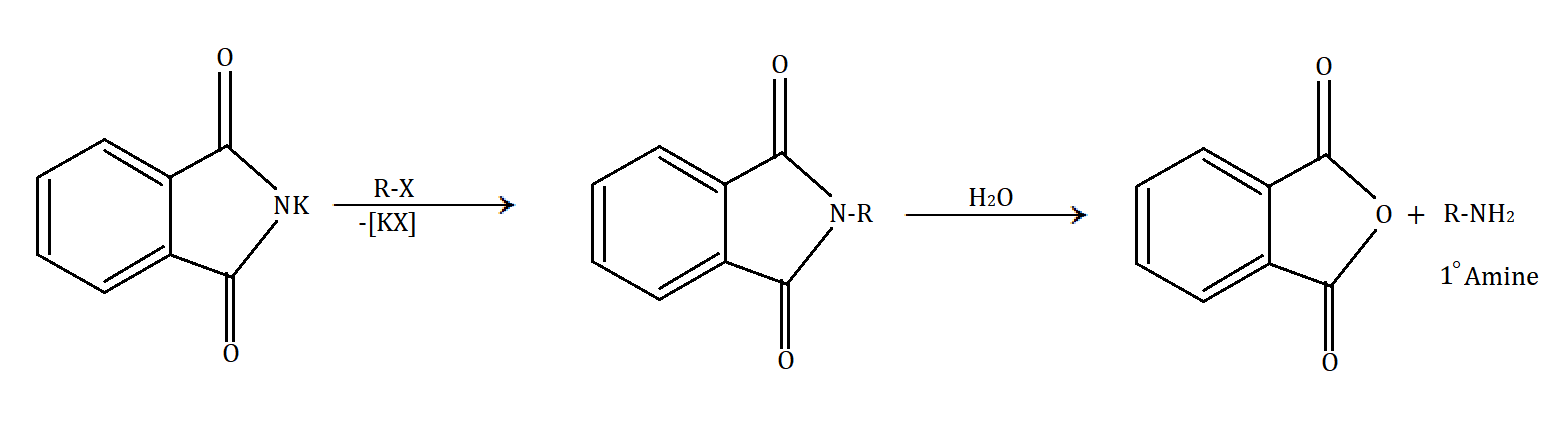
In the given options, CH3−CH2−NH2 (ethyl amine), CH3−NH2 (methyl amine) and Ph−CH2−NH2 (1−phenyl methanamine) are the compounds which can be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis. Ethylamine and methylamine are simple aliphatic compounds. While in 1−phenyl methanamine, the amine part is at the methyl part and phenyl is acting as a functional group and hence should be considered an aliphatic amine.
Hence, Ph−NH2 (aniline) is the only compound that cannot be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis.
Therefore, the correct option is C.
Note:
Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is only used for primary amines as steric hindrances do not allow the reaction for secondary and tertiary aliphatic amines. It is also not applicable for 1∘ aromatic compounds, aryl halide does not undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction. Aromatic compounds usually show electrophilic substitution reactions. Nucleophilic substitution destabilizes the resonance of aromatic compounds.
