Question
Question: Which of the following potential energy diagrams represents the \({{S}_{N}}1\) reaction? (A) 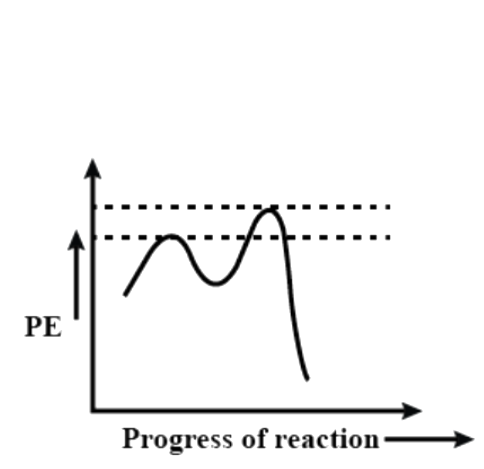
(B) 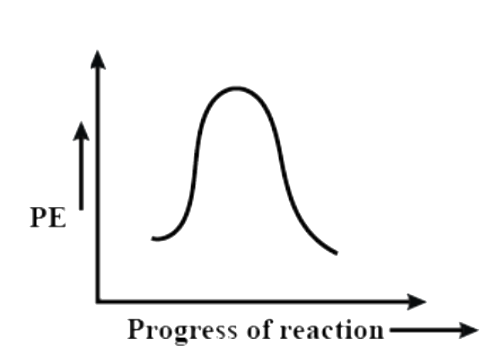
(C) 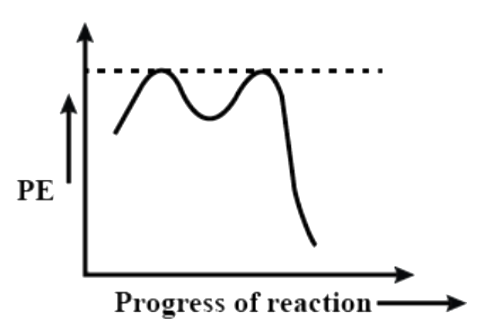
(D) 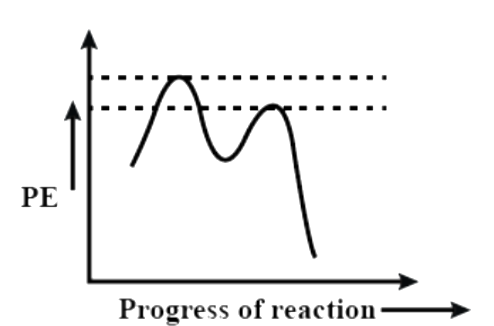
Solution
HINT: To solve this, remember that SN1 is an abbreviation for substitution nucleophilic unimolecular reaction. It is not a concerted mechanism and it takes place in two differentiable steps. Removal of the leaving group and addition of nucleophiles are the main steps.
COMPLETE STEP BY STEP SOLUTION: Before answering this question, let us discuss what SN1 reaction is and also its mechanism. We know that SN1 mechanism is nucleophilic substitution unimolecular reaction. In SN1 reaction, SN basically stands for nucleophilic substitution and 1 stands for unimolecular. In SN1 , the first step i.e. leaving of the leaving group and formation of the carbocation is the slow step and thus the rate determining step and the second step i.e. the attack of the nucleophile is the fast step. Now, let us see the reaction mechanism by taking an example. In the first step of the mechanism, the leaving group leaves the substrate and this leads to the formation of a carbocation. We can write the reaction as-
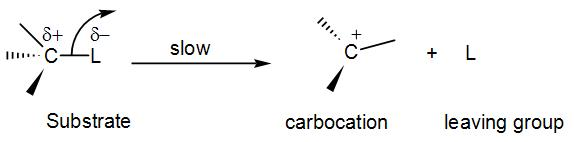
Then, the nucleophile (Nu) attacks the carbocation and gives us the product.
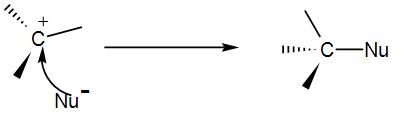
As we can see from the above example, this is a two-step process. The reactivity of compounds undergoing SN1 depends upon 2 factors.
- The first factor is the effectiveness of the removal of the leaving group.
- The second factor is whether or not the carbocation formed is stable.
Now let us see the potential energy diagram of the reaction. We can see from the above example that a carbocation intermediate is formed during the course of the reaction. So, basically the reaction proceeds from reactant to a transition state to intermediate to a second transition state and then product. So, there are two peaks (as we can already understand it is a 2 step reaction). The first transition state includes the bond cleavage of C – X and the second transition state is the formation of C – Nu bond. The intermediate is the carbocation that is formed upon removal of the leaving group. The first transition state peak is higher than the second because it involves the breaking of a C – X bond that is the stable.
So, among the given options, the correct answer is option – (D).
NOTE: Like the nucleophilic substitution we discussed above, there are more substitution reactions. Electrophilic substitution is a reaction where the leaving group is substituted by an electrophile and nucleophilic substitution is a substitution reaction where the leaving group is replaced by the nucleophile by attacking on the positively charged atom to which the leaving group is attached. SN2 mechanism is known as nucleophilic substitution bimolecular. Here, 2 stands for bi-molecular and SN stands for nucleophilic substitution as usual. This mechanism is concerted i.e. the removal of the leaving group and addition of the nucleophile takes place in a single step and the reaction passes through a transition state.
