Question
Question: Which of the following plot represents the graph of pH against volume of alkali added in the titrati...
Which of the following plot represents the graph of pH against volume of alkali added in the titration of NaOH and HCl
A.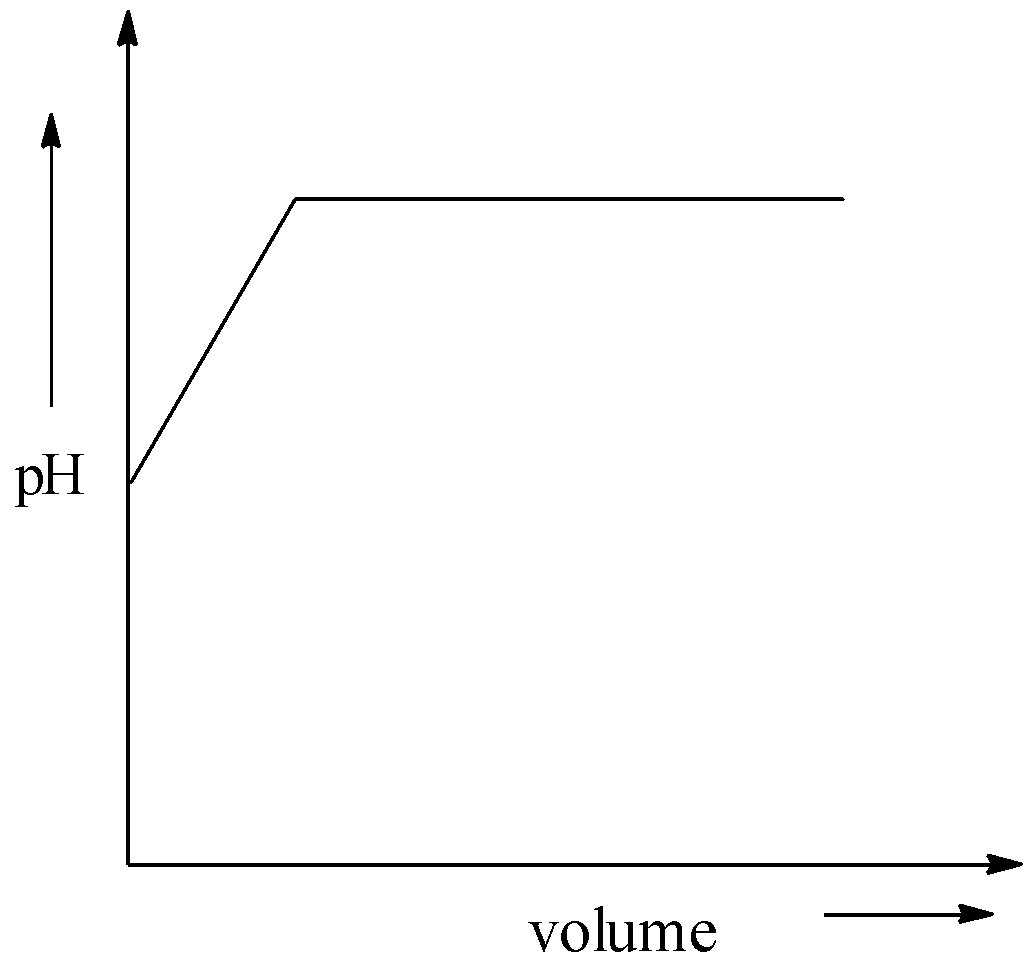
B.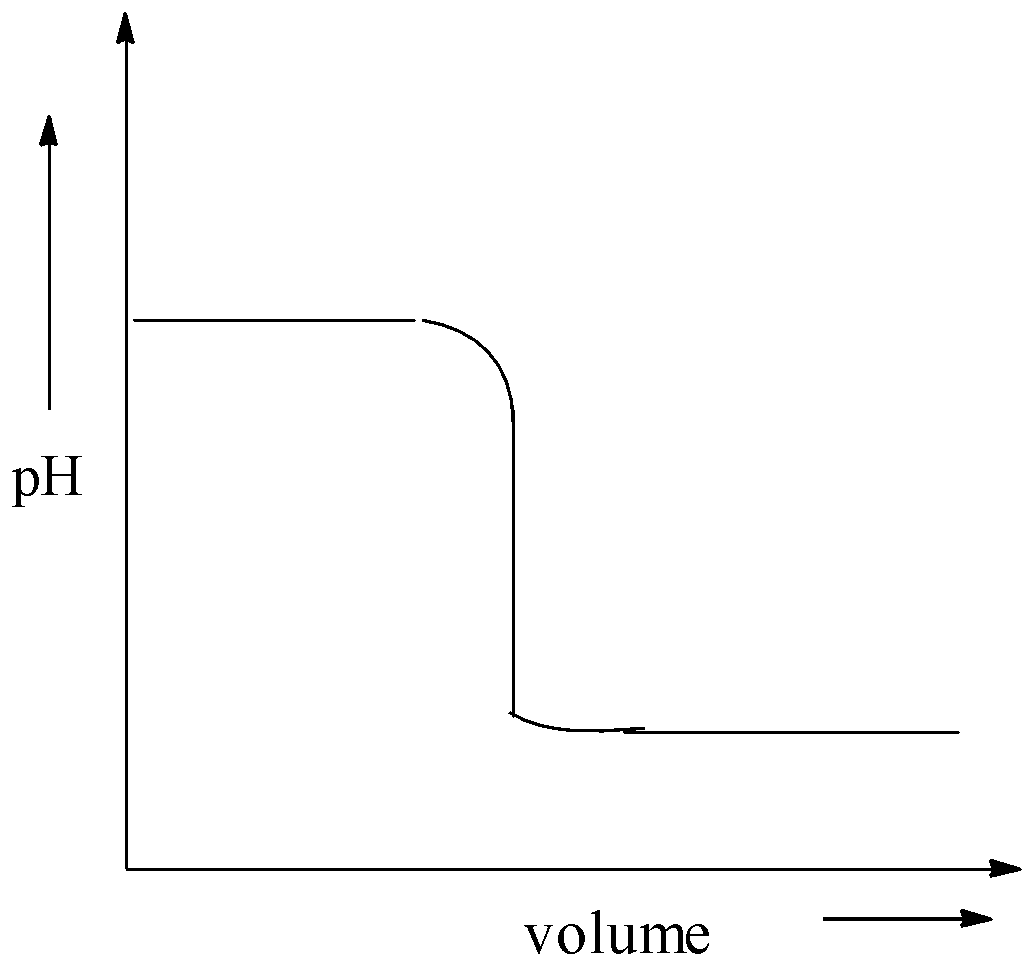
C.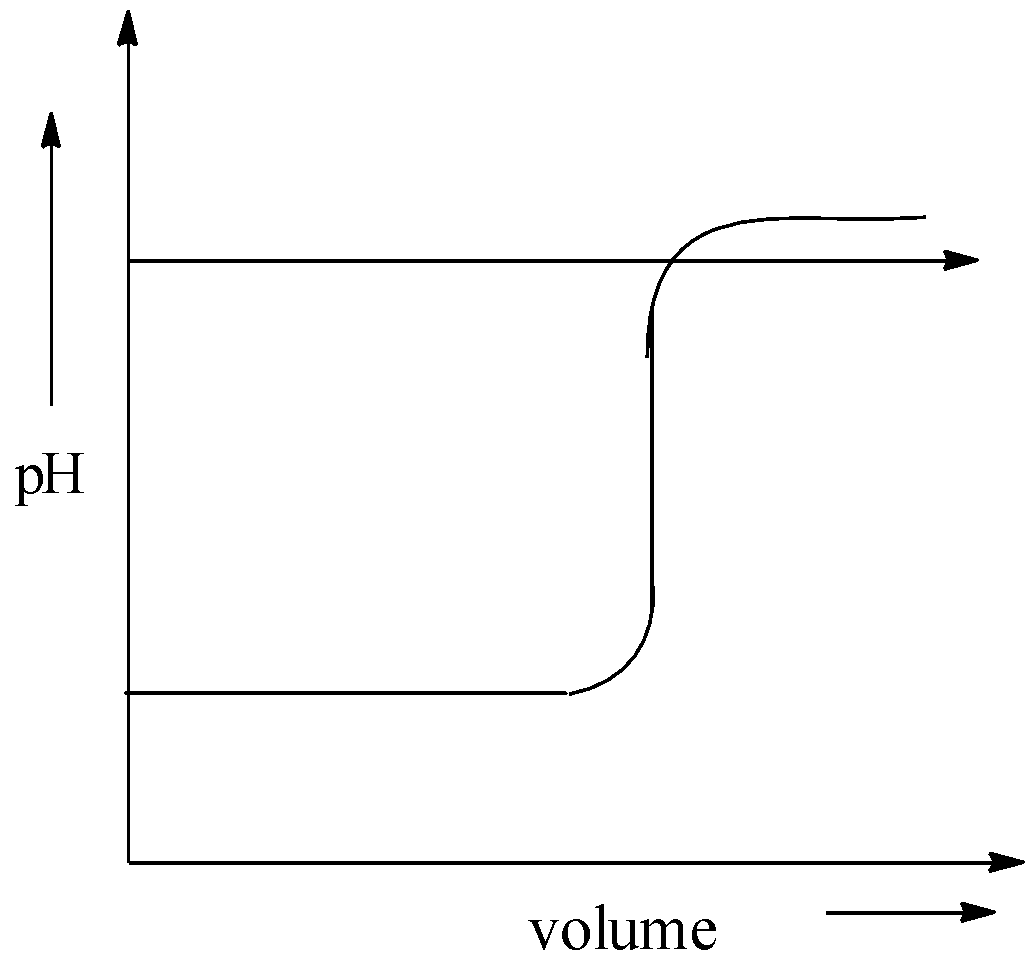
D.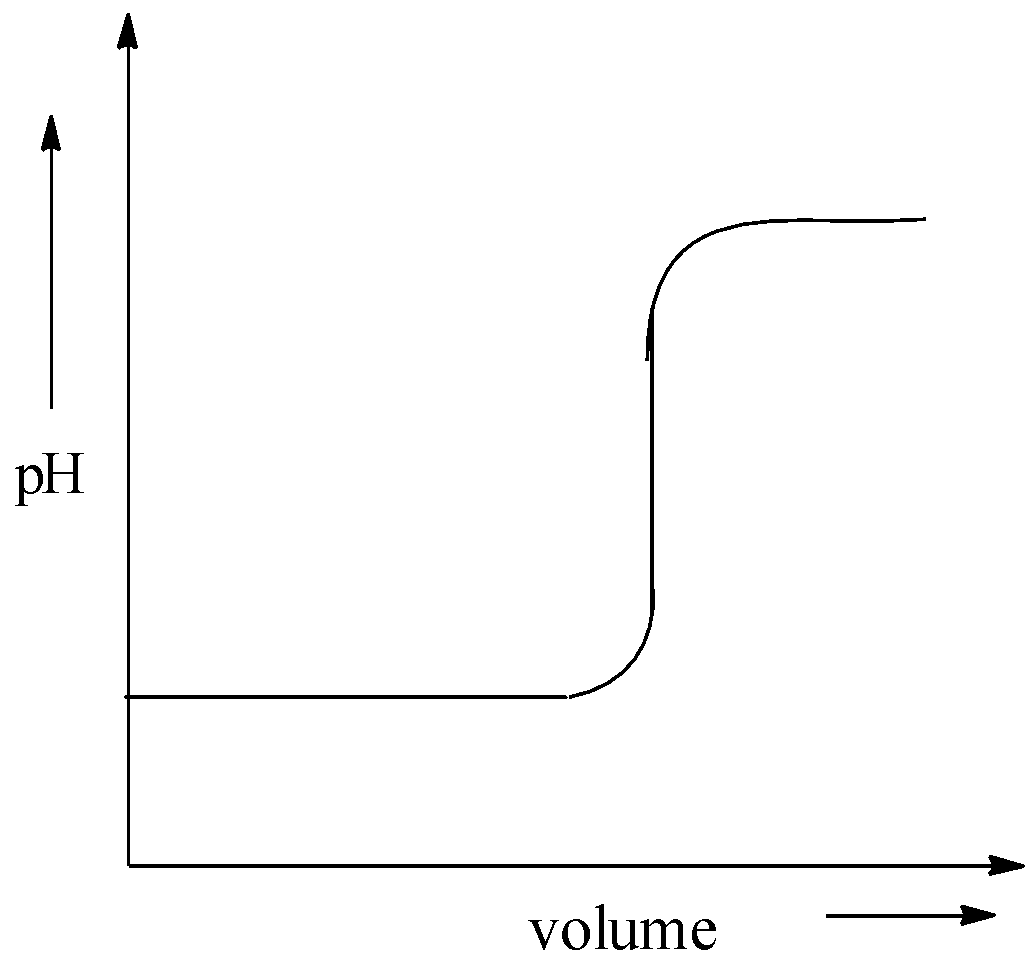
Solution
We need to know that pH is mainly used to find out the solution which is acidic, basic or neutral. And the range of pH from one to 14 . The solution is neutral if the pH is 7 . And if it is less than 7 means, the solution is acidic and pH is greater than seven means, the solution is basic. And pH mainly measures the relative amount of free hydrogen which is present in the water.
Complete answer:
While adding alkali to acid, there occurs a change in pH. And the acidity of acid becomes decreasing and the basicity will start to increase. But there is no sudden increase in the pH Hence, option (A) is incorrect.
Here, the base is added to the acid solution. Hence, pHof the solution is low at the initial stage. But, in this graph, the plot of pH starts from its higher range. Hence, option (B) is correct.
When sodium hydroxide is added to hydrochloric acid, pH of the solution remains the same at the initial stage. After that it suddenly increases pH. Then it became almost the same. After that there is no change in the pH. Therefore, the graph of pH against volume of alkali added in the titration of NaOH and HCl is,
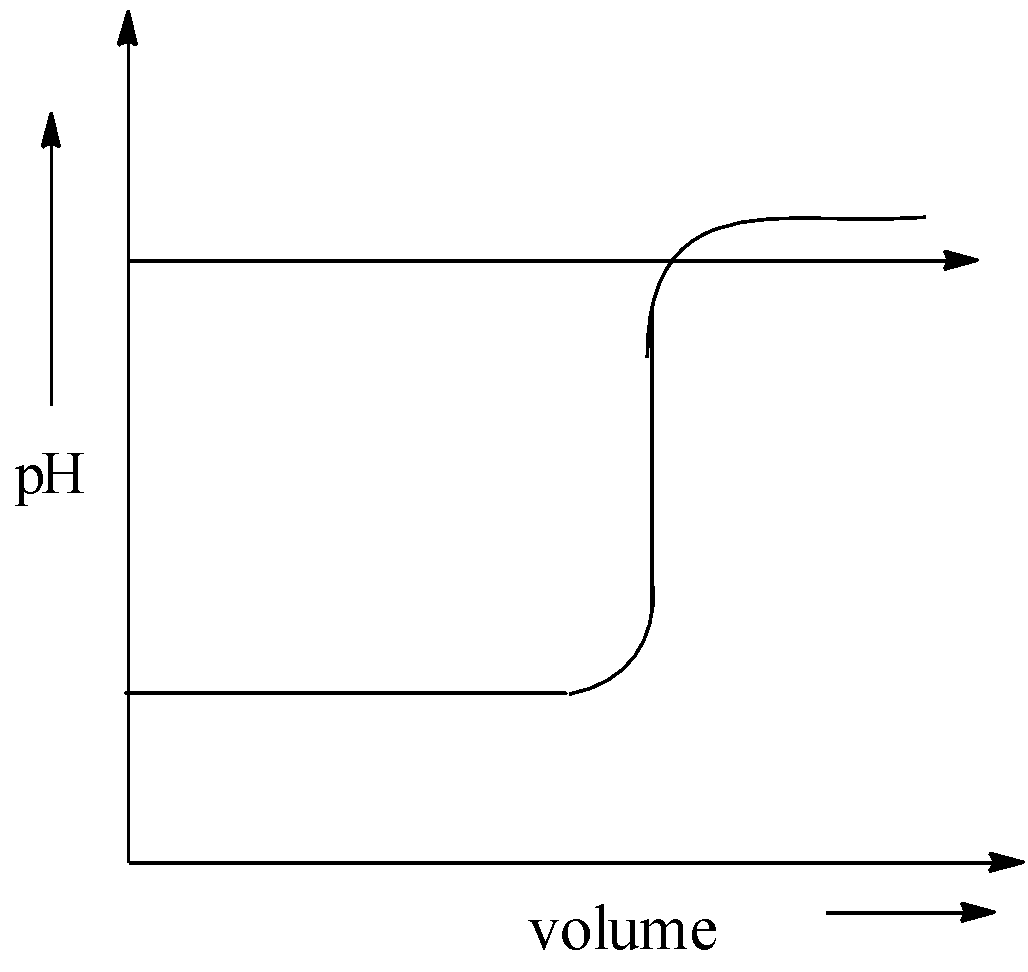
Hence, option (C) is correct.
This is not the correct graphical representation of pH against volume. Hence, the option (D) is incorrect.
Hence, option (C) is correct.
Note:
We need to know that when the alkali and acid are mixing in the right amounts, the reaction is wound up with the formation of a neutral solution. If water or base is added to an acid, the pH of the acid will be increasing. Because, there is a decrease in the acidity and the acid becomes less acidic. If the water is added to an alkali solution, the pH of the base becomes near 7 due to the decrease in the concentration of hydroxide ions.
