Question
Question: Which of the following on oxidation gives ethyl methyl ketone:- (A) \(2 - propanol\) (B) \(1 - b...
Which of the following on oxidation gives ethyl methyl ketone:-
(A) 2−propanol
(B) 1−butanol
(C) 2−butanol
(D) t-butyl alcohol
Solution
Oxidation is a process in which a compound or an element attains its more positive oxidation state. For example- when primary alcohol is converted to the aldehyde. Oxidation reaction takes place due to the oxidising agent present in the reaction. In order to know the products of the oxidation of given compounds we will first need to see their structures and then oxidise them with the help of oxidising agents.
Complete answer:
We know that oxidation reaction takes place when a compound which needs to be oxidised reacts with oxidising agent. Oxidation is a process in which a compound or an element attains its more positive oxidation state. Oxidising agents are the compounds which get reduced and oxidised to another compound.
A primary alcohol gets converted into an aldehyde when it reacts with a mild oxidising agent and if it reacts with a strong oxidising agent, then it forms carboxylic acid.
A secondary alcohol on reacting with a strong or mild oxidising agent, gives ketone as a product. Tertiary alcohol due to its valency does not get oxidised.
Structures of the given compounds are:
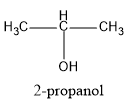
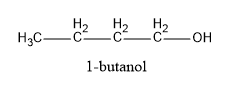
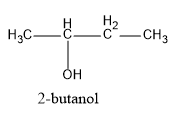
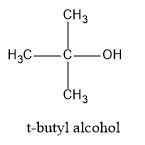
Hence, in the above structures, we can see that 2−propanol and 2−butanol are secondary alcohols and will form ketones on oxidation.
The oxidation reactions of both the alcohols is shown below:
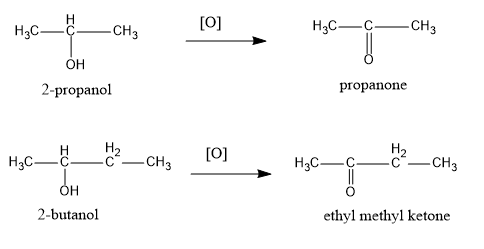
Therefore, we can see that 2−butanol on oxidation gives ethyl methyl ketone.
Hence, the correct option is (C) 2−butanol .
Note:
We should remember that primary and secondary alcohols get oxidised when reacted with oxidising agents but tertiary alcohols do not undergo oxidation because the alcoholic carbon atom does not contain a hydrogen atom and on oxidation, it cannot detach to a bond to form a double bond with the oxygen of alcohol.
