Question
Question: Which of the following molecules is chiral? How is this determined \(3,4-\text{Dimethyl}-1-\text{p...
Which of the following molecules is chiral? How is this determined
3,4−Dimethyl−1−pentene
2− bromo butanamide
2− bromo−1− butanol
Chlorocyclohexane
Cis 1,2− dimethyl cyclobutane
Trans −1,2−dimethyl cyclobutane
1−pentanenitrile
3−pentanamine
2−aminopropanoic acid (common name alanine)
2,3− dibromobutane
Solution
Chiral carbons are these carbons which cannot be superimposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotations and transacts. This property of carbon or molecules is called chirality. An achiral molecule is superimposable with its mirror image. A chiral carbon is that carbon which has all four groups attached are different and asymmetrical.
Complete step by step answer:
To determine whether a molecule is chiral is to examine its symmetry- a plane of symmetry or a mirror plane. If an imaginary line. Passes through the centre of objects and divides the object so that one half is a mirror image of the other half.
Any molecule that has a plane of symmetry is not chiral. If no plane of symmetry is present, then the molecule is chiral.
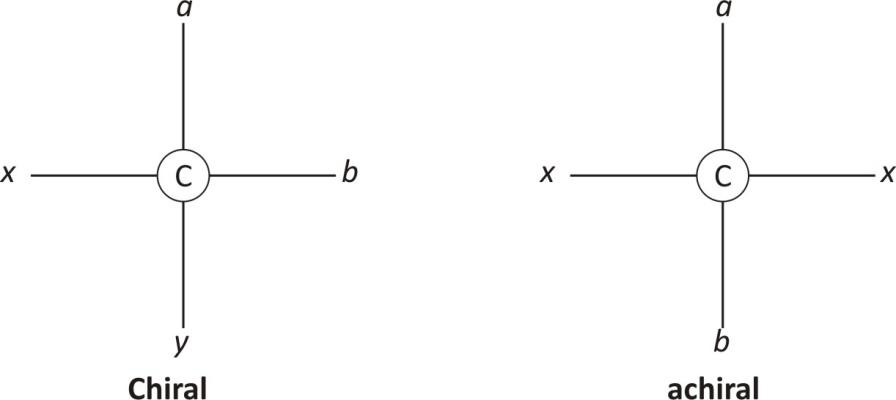
3,4−dimethyl−1− pentene
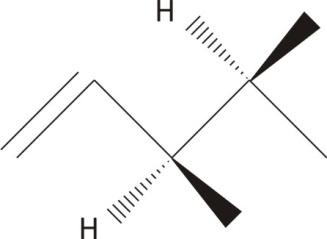
The central carbon are chiral with no plane of symmetry
Ans: Chiral
2−bromo butanamide
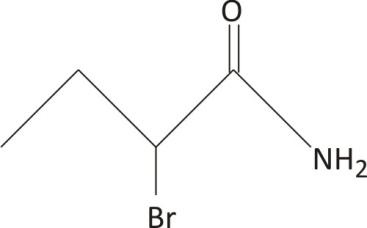
One carbon is chiral, with no plane of symmetry
Ans. Chiral
2− bromo−1−butanol
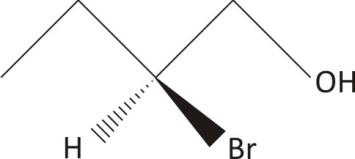
One chiral carbon, no symmetry
Ans. Chiral
Chlorocyclohexane
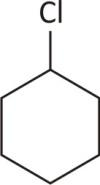
No chiral carbon
Ans Achiral
Cis,−1,2−Dimethycyclobutane
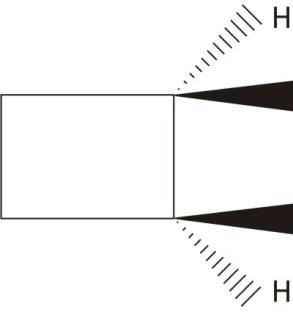
Two carbons are chiral with plane of symmetry
Ans. Achiral
trans−1,2− dimethylcyclobutane
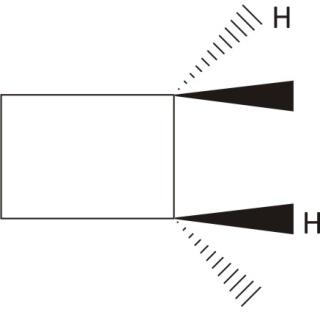
The chiral carbons with no plane of symmetry
Ans. Chiral
1−pentanenitrile

No chiral carbons
Ans. Achiral
3−pentamine
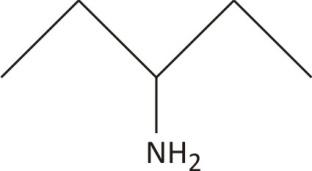
No chiral carbon
Ans. Achiral
2−Aminopropanoic Acid (Alanine)
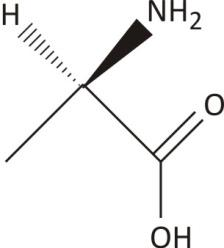
One chiral carbon with no plane of symmetry
Ans. Chiral
2,3− Dibromobutane: Contain both chiral and achiral form
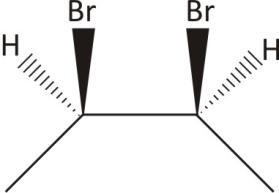
Two carbon and chiral with plane of symmetry
Ans. Achiral
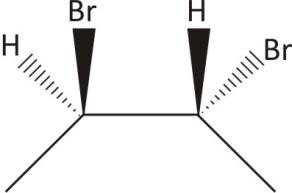
Two chiral carbons and no plane of symmetry
Ans. Chiral
Note: Atoms other than carbon can be chirality centers. When an atom such nitrogen or phosphorus has four different groups or atoms attached to it, it is a chirality centre.
The isomerism that is caused by the non-similar arrangements of atoms or functional groups belonging to an atom in space is called stereoisomers.
