Question
Question: Which of the following leads to bonding? A) 
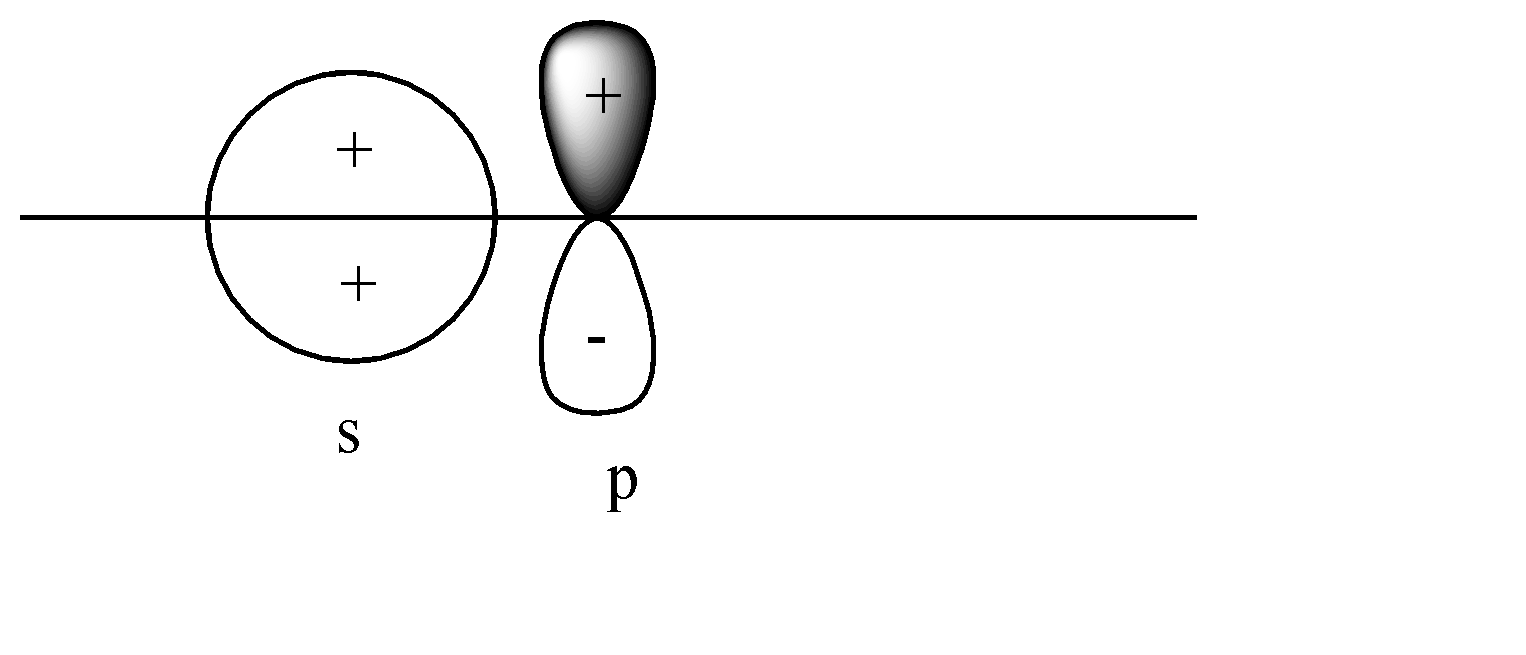
B)
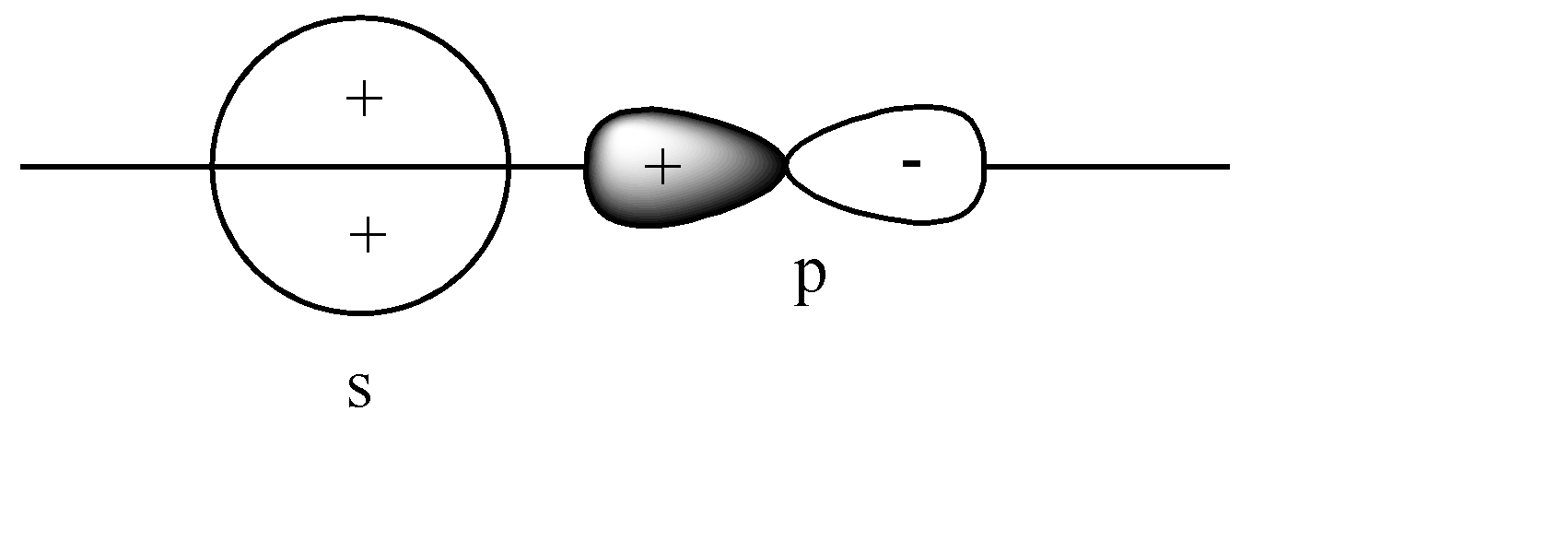
C)
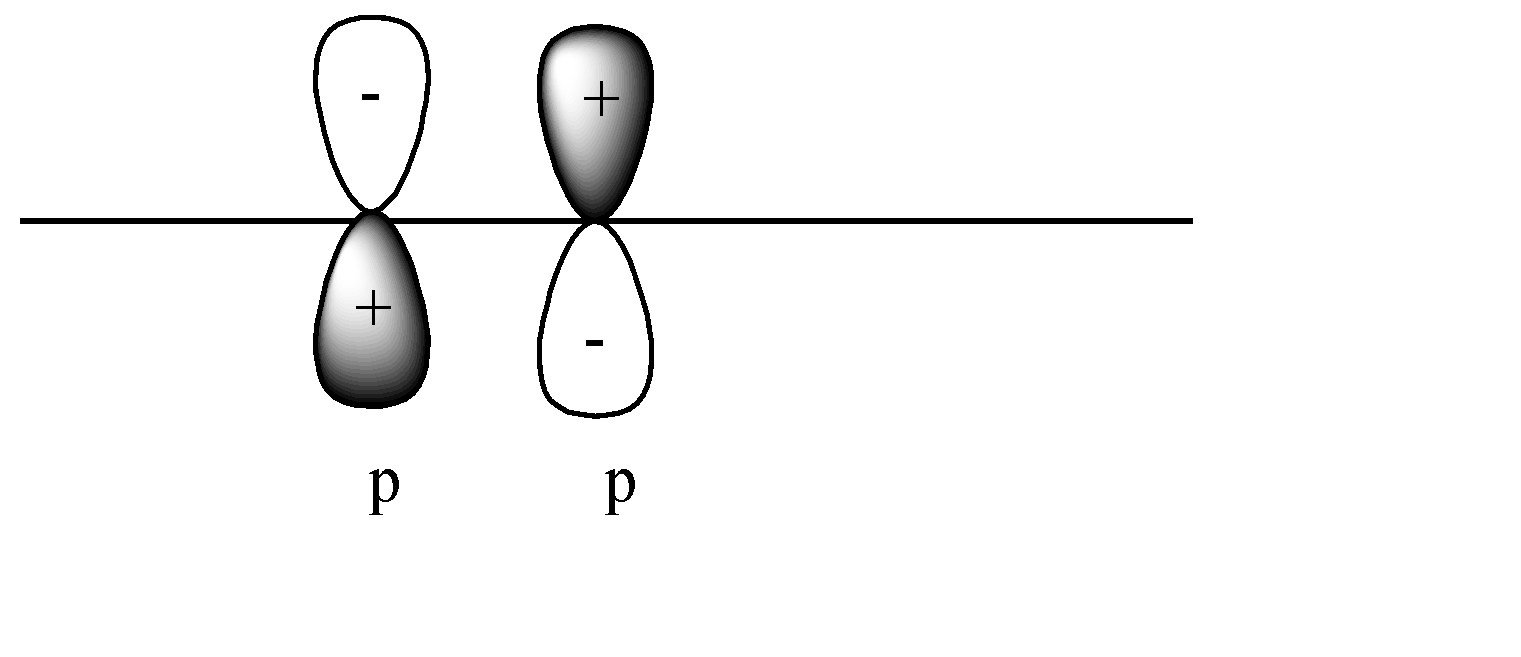
D)
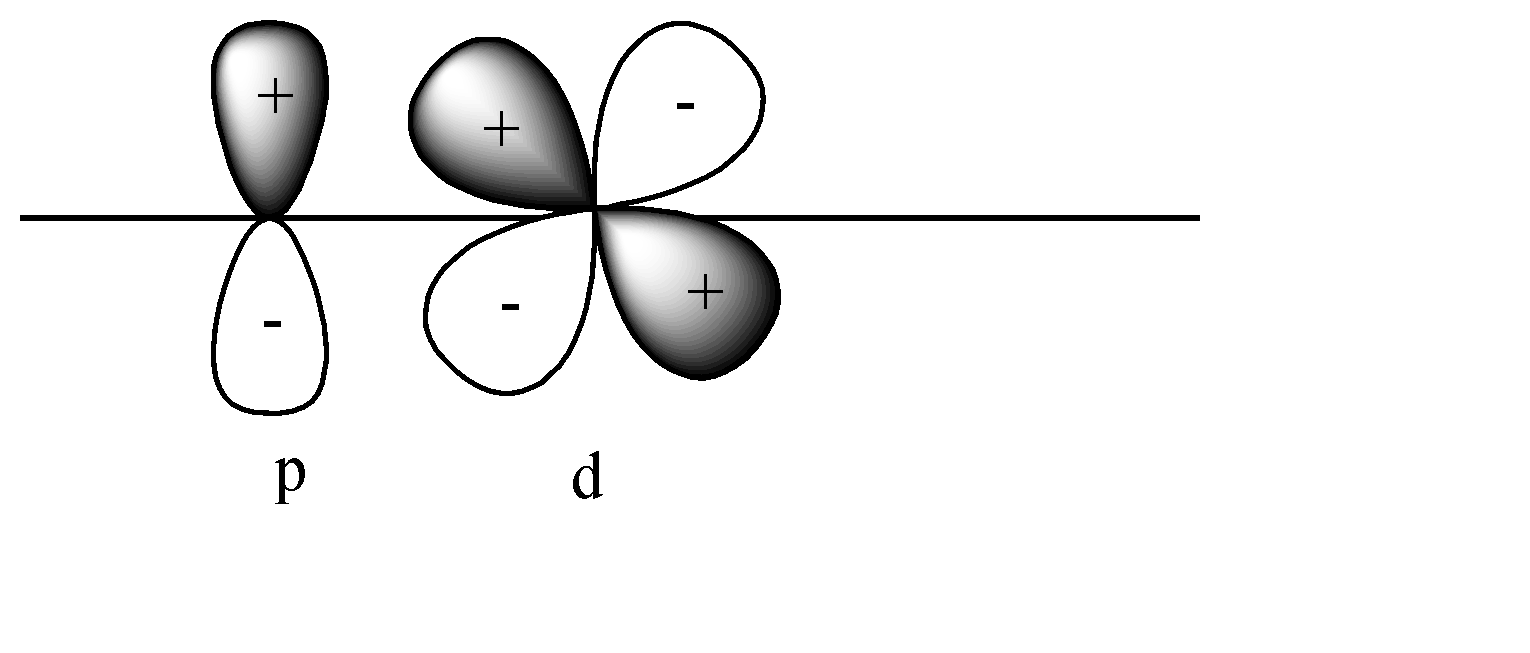
Solution
To answer this question, we have to recall the concept of sigma bond formation by mixing of orbitals. The + and – refers to the electron density dispersion across the orbitals. The formation of covalent bonds happens on collision of orbitals. Some lead to constructive interference and some destructive.
Complete answer:
According to the VSEPR theory there are two types of bonds that can be formed by collision of orbitals:
1. Sigma Bond
2. Pi Bond
The formation of sigma bonds occurs due to head-to-head collision of the orbitals that lie in the same plane or are coaxial/collinear. By definition, a sigma bond is formed by overlapping atomic orbitals that are in line with the internuclear axis. The s-orbital is spherical in shape and is said to be non-directional. P- orbitals have a dumbbell shape, and in order to form a sigma bond, p orbital must lie on the internuclear axis.
Let’s analyze the given options:
A)
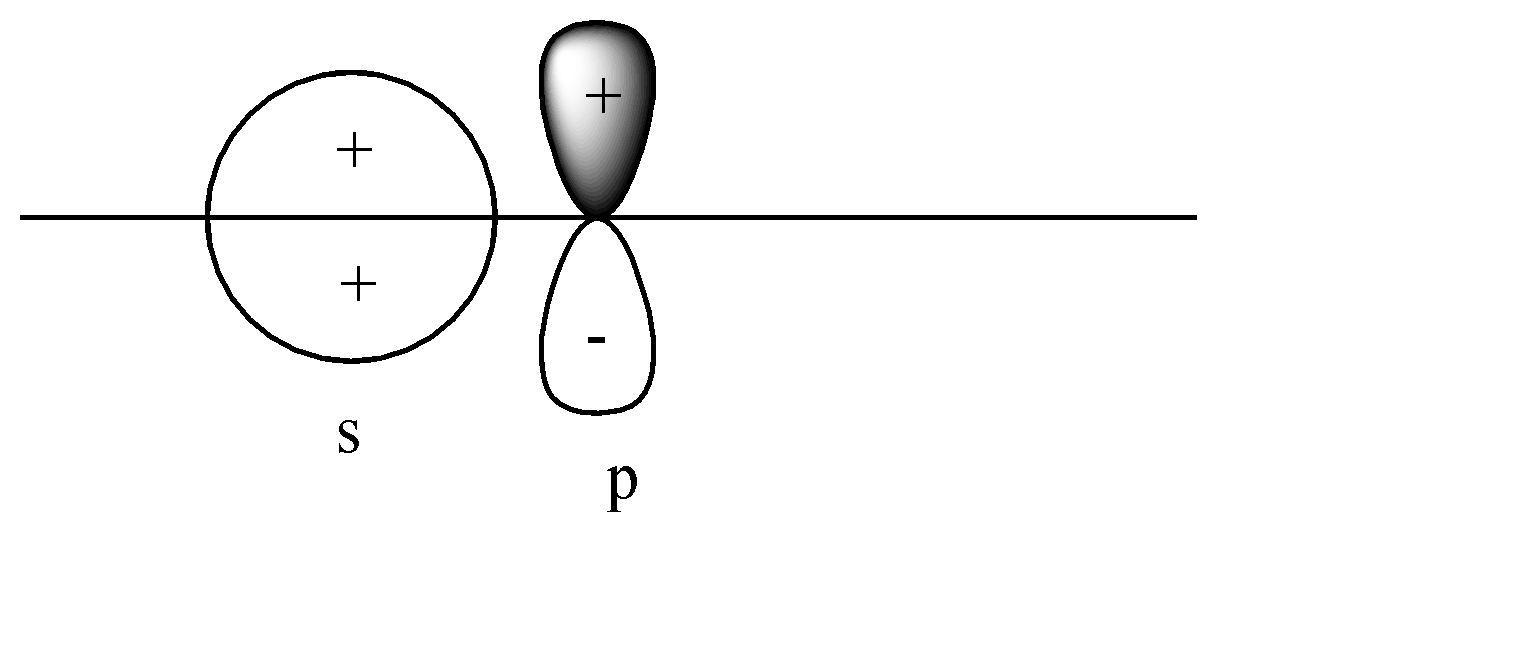
Here the s-orbital is present on the axis, but the p-orbital is perpendicular to the axis. Head-to-head collision is not possible; hence no formation of bond will take place.
B)
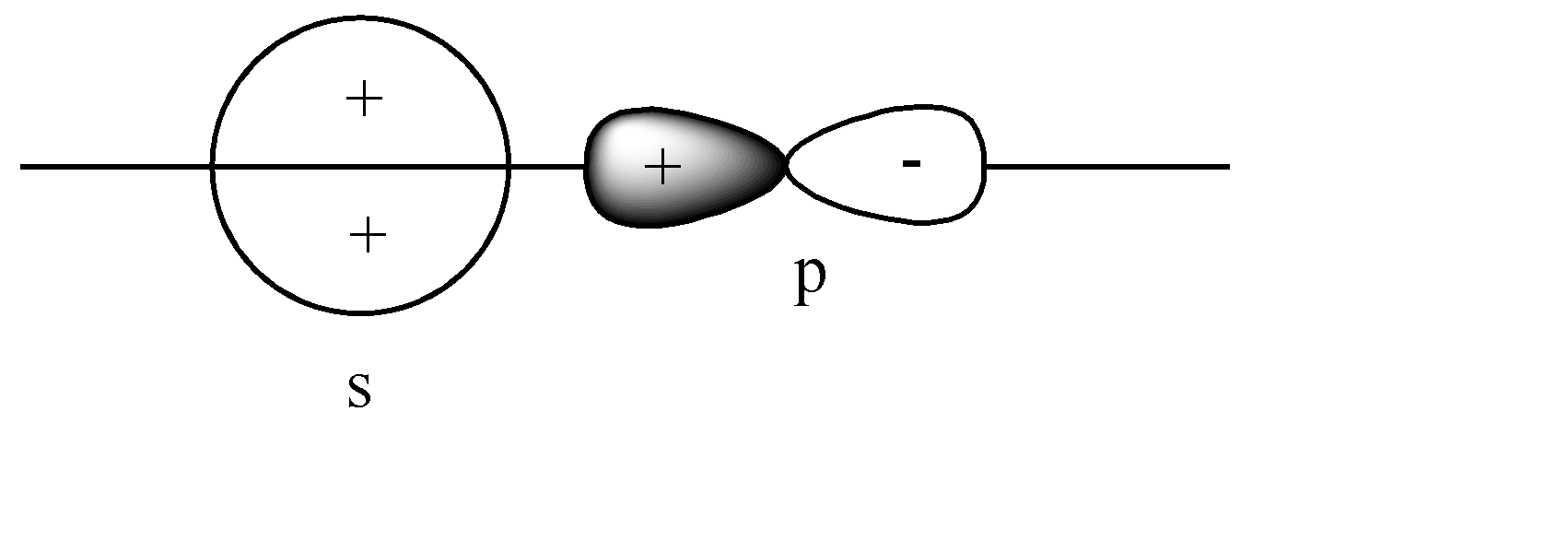
The s-orbital is present on the axis, and the p orbital is also parallel to the axis. Hence head-to-head collision is possible. Since the like charge i.e., ‘+ charge’ overlap, this leads to a constructive overlap, hence forming a Bonding sigma bond. This is the correct answer.
C)
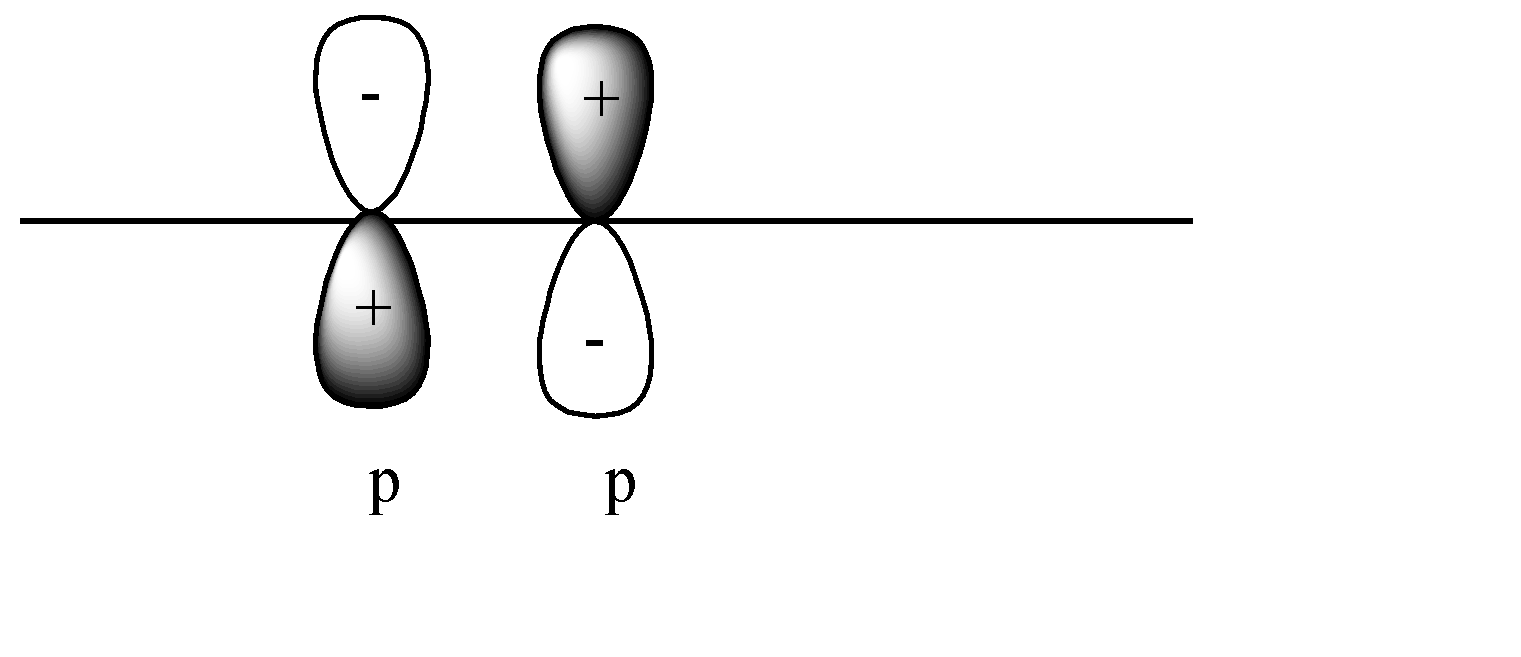
In this case a pi covalent bond will be formed by lateral overlap, or shoulder-to-shoulder overlap. In this case + orbital overlaps with – orbital, and vice versa. This leads to destructive overlap and formation of antibonding pi bonds.
D)
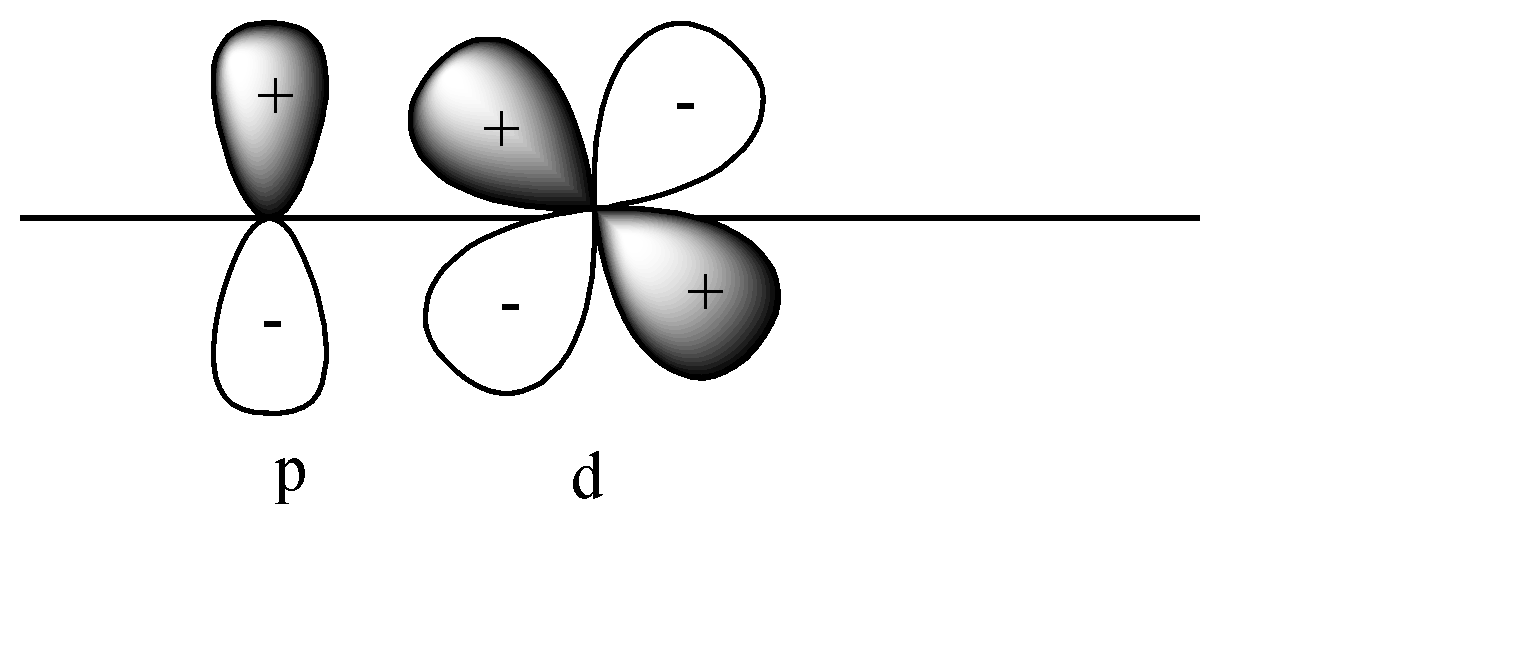
In this case also pi bonds will be formed as both p and d orbitals are perpendicular to the axis. In this case + orbital overlaps with – orbital, and vice versa. This leads to destructive overlap and formation of antibonding pi bonds.
Therefore, we can conclude that option (B) is the correct answer.
Note:
If s orbital combines with a p orbital perpendicular to the plane, no bond formation takes place and this forms a NBMO (non-bonding molecular orbital). Similarly with two p-orbitals, one in axis and one perpendicular to the axis, for example px&py orbitals on x-axis, will lead to a formation of NBMO.
