Question
Question: Which of the following is true for nitrate anion. A.The formal charge on \[N\] is zero B.The bon...
Which of the following is true for nitrate anion.
A.The formal charge on N is zero
B.The bond order of NO bond is 34
C.The average formal charge on oxygen is 31
D.There are 2−π bonds in the ion
Solution
To answer this question, you should recall the concept of formal charge and bond order. It’s a theoretical charge over an individual atom of an ion as the real charge over a polyatomic molecule or ion is distributed on an ion as a whole and not over a single atom.
The formula used: FC=V−N−2B
where V is the no. of valence electron N is the no. of non-bonding electrons and B is the no. of electrons in the covalent bond
Complete Step by step solution:
The bond order shows the number of chemical bonds present between a pair of atoms. For instance, the bond order of diatomic nitrogen N≡N is 3 and bond order between the carbon atoms in H−H≡C−H is also three. The bond order describes the stability of the bond. The molecular orbital provides an easy understanding of the concept of the bond order of a chemical bond. It quantifies the degree of covalent bonds between the atoms. The formal charge of nitrogen can be calculated using: FC=V−N−2B
(V = no. of valence electron N = No. of nonbonding electrons B = No. of electrons in covalent bond)
FC of N in NO3−=0
FC of O in NO3−=−31
The Lewis structure of nitrate ion can be drawn as:
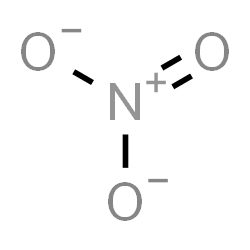
We can see that the total number of bonds = 4.
The number of bond groups between individual atoms = 3 and bond order =34=1.33. There is one pi bond.
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option D.
Note: In most of the compounds, the oxidation number of oxygen is −2 . There are two exceptions here.
Peroxides: Each oxygen atom exhibits an oxidation number of −1 . Example, Na2O2
Superoxide- Every oxygen atom is allocated an oxidation number of −2 1 . Example, KO2
Oxygen is bonded to fluorine- Example, dioxygen difluoride where the oxygen atom is allocated an oxidation number of +1 .
