Question
Question: Which of the following is the primary host of Taenia solium? A) Humans B) Pig C) Sheep D) Sn...
Which of the following is the primary host of Taenia solium?
A) Humans
B) Pig
C) Sheep
D) Snail
Solution
Body of Taenia solium has three regions, namely scolex, neck and strobila. Its body is thin, flat, tape-like and 1.5 to 7.5 long and it exhibits pseudo segmentation.
Complete Answer:
- Taenia solium is popularly known as the pork tapeworm. It is an endoparasitic cestode in the small intestine of man. It is common in those parts of the world where pork is eaten without proper cooking. Its body is divided into three regions, namely scolex, neck and strobila.
- Scolex is the small, pin-head like and mouthless anterior part. It has four cup shaped suckers and a terminal retractile cone, called rostellum. Neck is a very short and unsegmented region, just behind the scolex. Here, body segments are constantly budded off and hence this region is referred to as the budding zone or the zone of proliferation.
- Strobila is the long, ribbon like and segmented posterior part. It is composed of 800-1000 segments, called proglottids.
The life cycle of Taenia solium is completed in two hosts, namely man and pig. Man is the primary or principal host, and pig is the secondary or intermediate host. Copulation, fertilization and early development take place in the human intestine.
- Development starts soon after fertilization. Each fertilized egg develops into a six hooked embryo, called hexacanth embryo. It is enveloped by an embryonic membrane, enclosed by a mantle or embryophore, and protected by a hard shell or capsule. Hexacanth, together with the embryonic membrane, embryophore and the shell, is known as oncosphere. The eggs containing oncosphere are called embryonated eggs. At this stage, the gravid proglottid detaches from the strobila and passes out along with human faeces. In the soil, the proglottid and the uterus disintegrate and the embryonated eggs get dispersed.
So, here the correct answer is A) Humans.
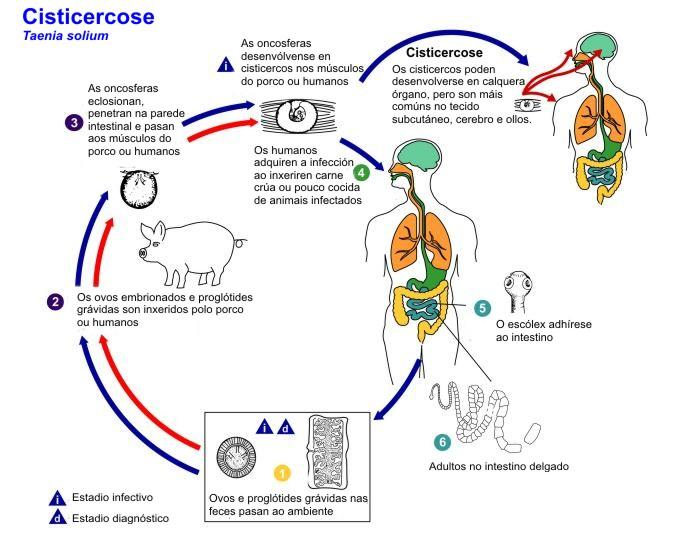
Figure: Life cycle of Taenia solium.
Additional information:
- Taenia solium is an obligatory parasite, morphologically and physiologically adapted for an endoparasitic life.
- Its parasitic adaptations include both degenerations and neoformations.
Note: Transmission to new human hosts occurs through the meat of pig. It occurs when man eats improperly cooked measly pork. During this large number of bladder worms get into the human stomach. In the stomach, the bladder gets dissolved and the uninjured part passes to the small intestine. It clings to the intestinal wall with hooks and suckers. Then it buds off a chain of proglottids and transforms to an adult tapeworm.
