Question
Question: Which of the following is the most stable conformer along the \( 2,3\,C-C \) bond axis of the given ...
Which of the following is the most stable conformer along the 2,3C−C bond axis of the given compound?
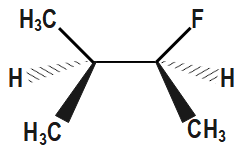
(A)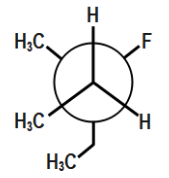
(B)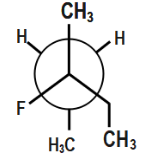
(C)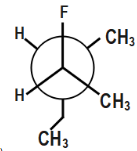
(D)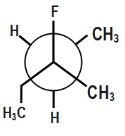
Solution
Hint : In the question we are given a wedge and dash configuration of a compound and in the given options we are given the Newman projections of the entire configuration. For figuring out which is the most stable conformation along 2,3 C−C we will have to look at the bulkiness of the substituents and their repulsion.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Bulky groups are those groups which have many atoms attached in their molecules and they also have high atomic weight. Whenever two bulky groups are present nearby each other or lie in the close proximity of each other there is a repulsion between them. The more the repulsion the more unstable will be the compound.
Therefore, we can say that if more bulky groups are present in the compound the more will be the repulsion and thus less will be the stability of the molecule. So, now we will analyze the solution option by option.
In the first option we can see that the two methyl groups along with one methyl group are located in close proximity of each other or we can say near each other. We know that methyl and ethyl groups are bulky groups and thus we can see that there are three bulky groups. Therefore, there will be a great repulsion. Hence this compound will be unstable. In the second option though methyl and ethyl are far from each other, but we can see that ethyl and methyl are in close proximity of each other and hence the compound will be unstable due to repulsion between ethyl and methyl bulky groups.
In the third option if you observe carefully ethyl group is completely oriented at a different orientation. Now, if there is a repulsion between the methyl groups, we can also see that H and H will show no repulsion. Though methyl groups will show repulsion to some extent, a larger proportion of compounds is not showing repulsion.
Also, hydrogen bonding will easily occur between hydrogen and the fluorine as shown.
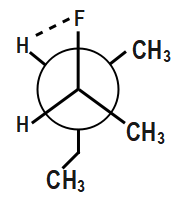
This hydrogen bonding provides additional stability. Therefore, this compound will be most stable.
Thus, this option is correct.
In option fourth, there will be repulsion between ethyl and methyl groups. Thus, this compound will also not be stable.
Hence, the correct option is option C.
Note :
Remember that alkanes due to rotation around the C−C single bonds can have infinite number of conformations. However, rotation around the C−C single bond is not completely free. It is hindered by a small energy barrier of 1−20kJ due to weak repulsive interaction between the adjacent atoms. Such a type of repulsive interaction is called torsional strain.
