Question
Question: Which of the following is polar? (a) \(N{F_3}\) (b) \(B{F_3}\) (c) \(S{F_4}\) (d) \(Si{F_...
Which of the following is polar?
(a) NF3
(b) BF3
(c) SF4
(d) SiF4
Solution
For this we have to first know about the polarity, polar molecule, which molecules attract other molecules towards itself and on which factors the polarity of any molecules effect and then we have to compare the polarity of the molecules.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s start with the definition of the polar molecules,
Polar Molecules: A diatomic molecule which is bounded by a polar covalent bond are called polar molecules.
But the question is what we meant by polar?
Polar means the compounds are having magnetic poles between the elements, due the electrical charges within the molecule.
Polarity: The formation of poles between the elements of a molecule is called Polarity.
Factors which affects polarity:
(a) Presence of lone pair.
(b) Presence of electron withdrawing group.
(a) Presence of lone pair: When there is a presence of lone pairs in the molecule, the molecule generates poles, due to larger electron density on the lone pairs. So, the polarity develops and the electron density is higher on the lone pair side.
(b) Presence of electron withdrawing group: When there is a presence of electron withdrawing group in the molecule, the molecule generates poles, due to larger ability to attract electrons of the electron withdrawing group. So, the polarity develops and the electron density is higher on the electron withdrawing group side.
Polarity is a vector quantity, if the molecules have geometrical symmetry in the structure then they will cancel each other’s polarity and become non-polar and if the molecule is asymmetrical, it will be polar.
So, now take the examples which are in the options and try to find out the correct option.
(a) NF3 : The structure of the compound is given as
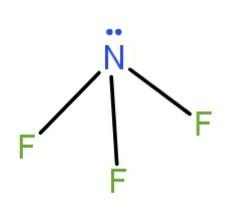
In this, we see that, in the opposite sides there are electron withdrawing groups and a lone pair. So, they will not cancel each other’s polarity because of unsymmetrical geometry and the molecule becomes polar.
(b) BF3 : The structure of the compound is given as
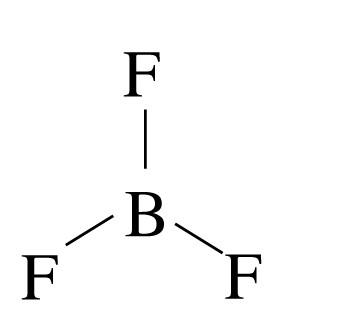
In this case, the boron has no lone pair and the molecule has symmetry. So, the molecule becomes non-polar.
(c) SF4 : The structure of the compound is given as
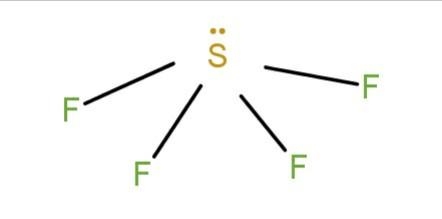
In this, we see that, in the opposite sides there are electron withdrawing groups and a lone pair. So, they will not cancel each other’s polarity because of unsymmetrical geometry and the molecule becomes polar.
(d) SiF4: The structure of the compound is given as
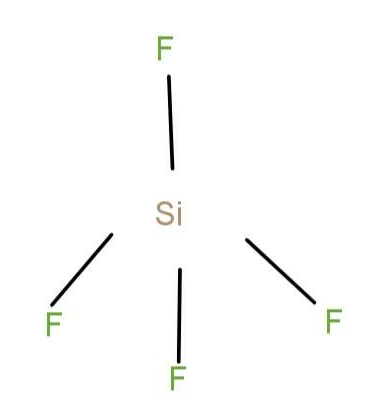
In this case, as in the boron has no lone pair and the molecule has symmetry. Silicon also has no lone pair and the molecules have symmetry. So, the molecule becomes non-polar.So, the molecule becomes non-polar.
Hence, this question has multiple correct options, the correct options are (a) and (c).
Note: While finding, the molecule has polarity or not we have to think about the geometry of the molecule and if we have to compare the polarity of two molecules, we have to keep in mind the lone pairs and electron withdrawing groups both.
