Question
Question: Which of the following is paramagnetic? A. \(CO\) B. \({{O}_{2}}^{-}\) C. \(C{{N}^{-}}\) D. ...
Which of the following is paramagnetic?
A. CO
B. O2−
C. CN−
D. NO+
Solution
A molecule having one or more unpaired electrons in their valence shell is paramagnetic or having an odd electron system is paramagnetic. As an example, the answer compound has 15 electrons and encompasses a bond order of two. 5 and has 1 unpaired electron in π∗ antibonding orbitals. Therefore could be a paramagnetic molecule. we'd like to grasp about molecular orbital theory in detail for further clarification.
Complete step by step answer:
- There are 3 types of magnetic substances: paramagnetic, diamagnetic, ferromagnetic substances. Paramagnetic substances are weakly attracted by magnets, diamagnetic substances are repelled by magnets and ferromagnetic substances are strongly attracted by magnets.
- Molecular orbitals are obtained by combining the atomic orbitals on the atoms within the molecule. Consider the molecule NO2, for instance. one amongst the molecular orbitals during this molecule is built by adding the mathematical functions for both the 1s atomic orbitals that move to create this molecule. Another orbital is created by subtracting one in every of these functions from the opposite.
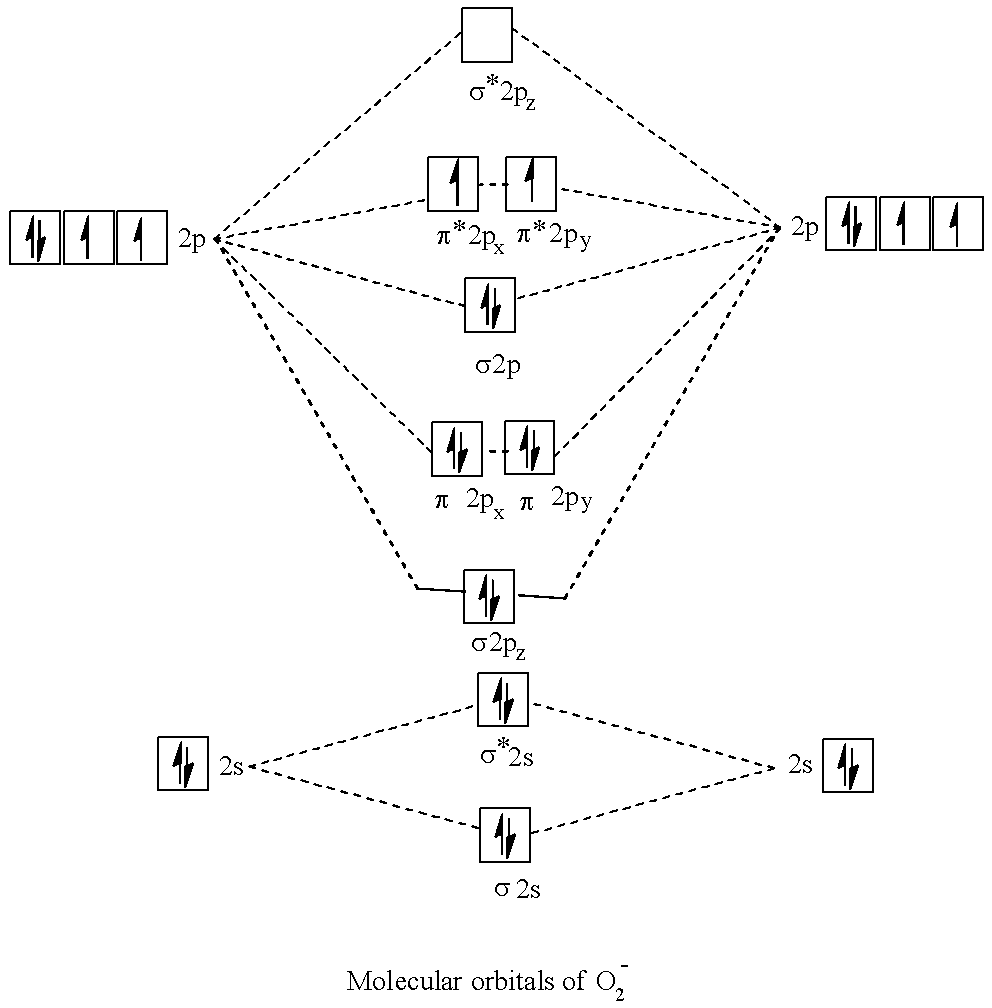
- Molecular orbital (MO) theory describes the behavior of electrons in an exceedingly large molecule in terms of combinations of the atomic wave functions. Materials with unpaired electrons or odd numbered electrons are paramagnetic and drawn to a magnetic field, while those with all-paired electrons that's even no of electrons are diamagnetic and repelled by a magnetic force field. Now let's come to the answer part.
- CO,CN− and NO+ are isoelectronic with 14 electrons each and there's no unpaired electrons present within the MO configuration of those species. So these are diamagnetic. NO+ is paramagnetic in nature thanks to the presence of 1 unpaired electron within the valence shell.
So the correct answer is “B”:
Note: A simple rule of thumb is employed in chemistry to work out whether a particle (atom, ion, or molecule) is paramagnetic or diamagnetic in nature. If all the electrons within the particle are paired, then the substance product of this particle is diamagnetic, If it's unpaired electrons, then the substance is paramagnetic in nature.
