Question
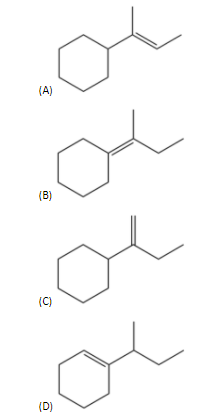
Question: Which of the following is not the product of dehydration of: 
Solution
There is a dehydration reaction taking place for a compound given in the question. Think about what kind of reaction is dehydration and what changes will take place in the compound when dehydration is completely carried out. Try to draw all the possible products in this reaction and then choose the product which is not formed in this reaction as an answer.
Complete step by step solution:
- Dehydration reaction is a process in which water molecules are removed from the reactant to give product.
- Here, the given compound is an alcohol. We know, alcohols undergo dehydration in the presence of a strong dehydrating agent like sulphuric acid or phosphoric acid to form alkenes.
- So, dehydration is an elimination reaction. This reaction is also known as !!α!! , !!β!! -elimination reaction because one hydroxyl (-OH) group which at !!α!! -carbon and one hydrogen atom (-H) which is at adjacent !!β!! -carbon is eliminated in the form of water to give an alkene.
- A general reaction can be represented as,
CH3−CH2−OHH2SO4CH2=CH2+H2O
- Now, let’s write the reaction of the given compound.
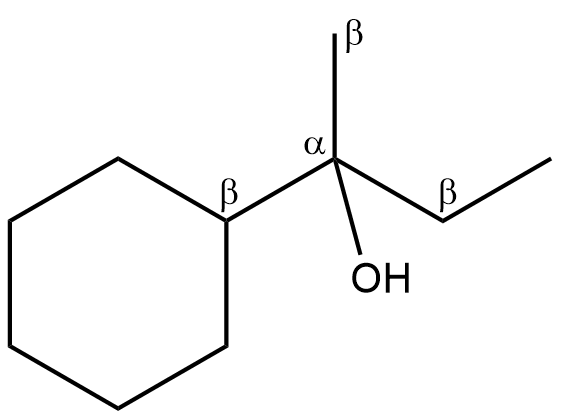
- The double bond will be formed in between the !!α!! -carbon and the !!β!! -carbon atoms which are losing a water molecule. So, the given alcohol molecule has three !!β!! -hydrogen atoms and therefore, three elimination products are possible.
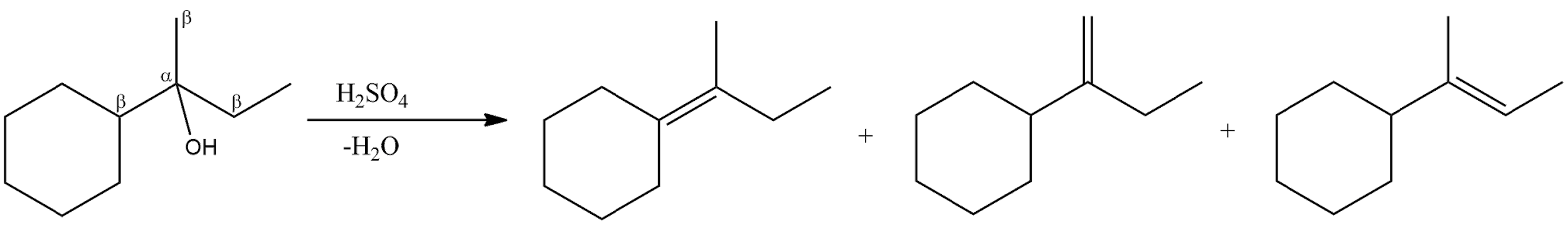
- So, in the options (A), (B) and (C) are the products of the given alcohol compound.
- Therefore, option (D) is the correct answer.
Note: Remember in dehydration reaction, there is elimination of water molecules from the compound. In the case of alcohols and halogen derivatives of alkanes, dehydration reaction will give rise to alkenes as the product by removal of adjacent hydroxyl groups and hydrogen atoms in the form of water. The double bond will be formed in between the !!α!! -carbon and the !!β!! -carbon atoms which are losing a water molecule.
