Question
Question: Which of the following is not formed by Sandmeyer reaction? A. \({C_6}{H_5}Cl\) B. \({C_6}{H_5}...
Which of the following is not formed by Sandmeyer reaction?
A. C6H5Cl
B. C6H5l
C. C6H5Br
D. C6H5CN
Solution
The Sandmeyer reaction is an extremely useful reaction for the functionalization of aromatic rings through a diazonium intermediate. For conversion of a diazonium intermediate to the corresponding chloride, bromide, or cyanide, the copper(I) salt is used. In case of Iodobenzene different reagents as KI used to obtain the product because it cannot be formed in presence of Cu(I) and also Iodine being less reactive than other halogens.
Complete step by step answer:
Sandmeyer reaction is a type of substitution reaction that is mainly used in the production of aryl halides from aryl diazonium salts. Copper (Cu) salts like chloride (Cl), bromide (Br) ions are used as catalysts in this reaction. The Sandmeyer reaction can be used to perform unique transformations on benzene notably. The transformations include hydroxylation, trifluoromethylation, carnation, and halogenation.
The Sandmeyer reaction is a very useful reaction for the functionalization of aromatic rings through a diazonium intermediate. For conversion of a diazonium intermediate to the corresponding chloride, bromide, or cyanide, the copper(I) salt is used. But, for iodination, potassium iodide is the reagent that is most frequently used.
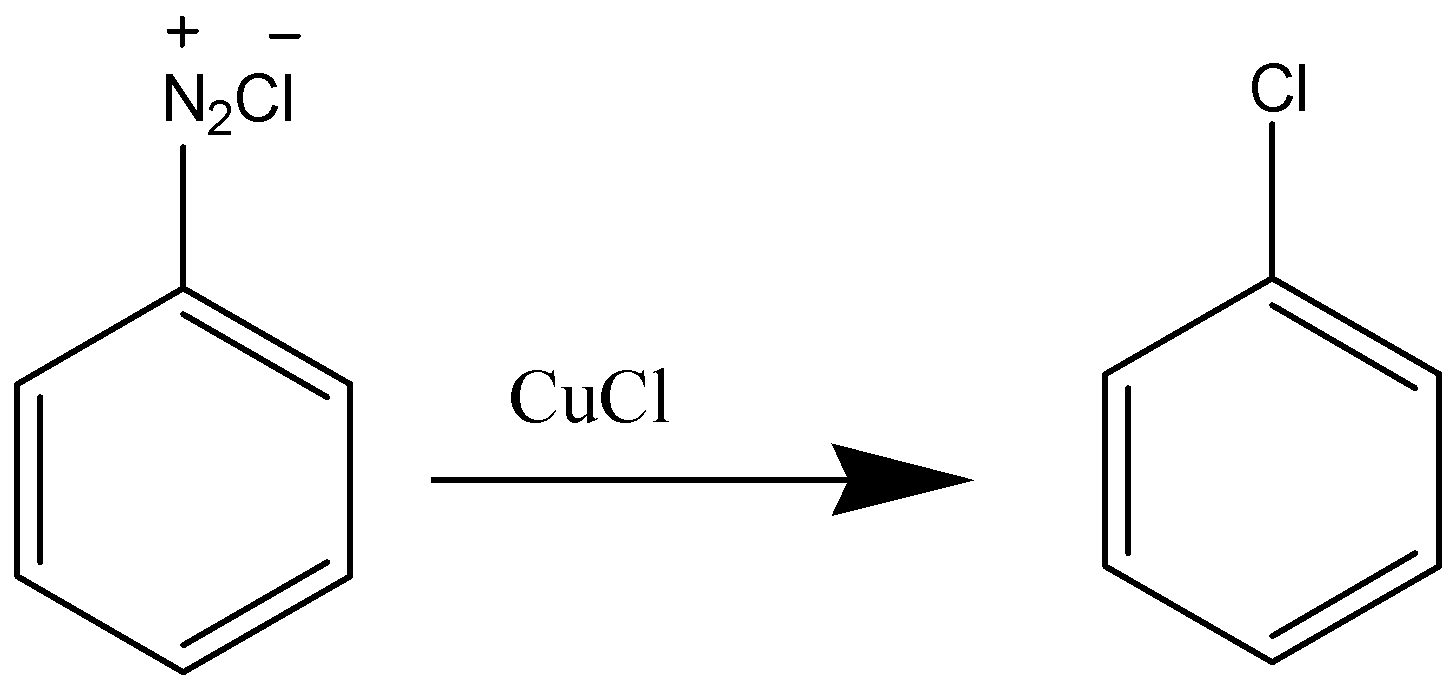
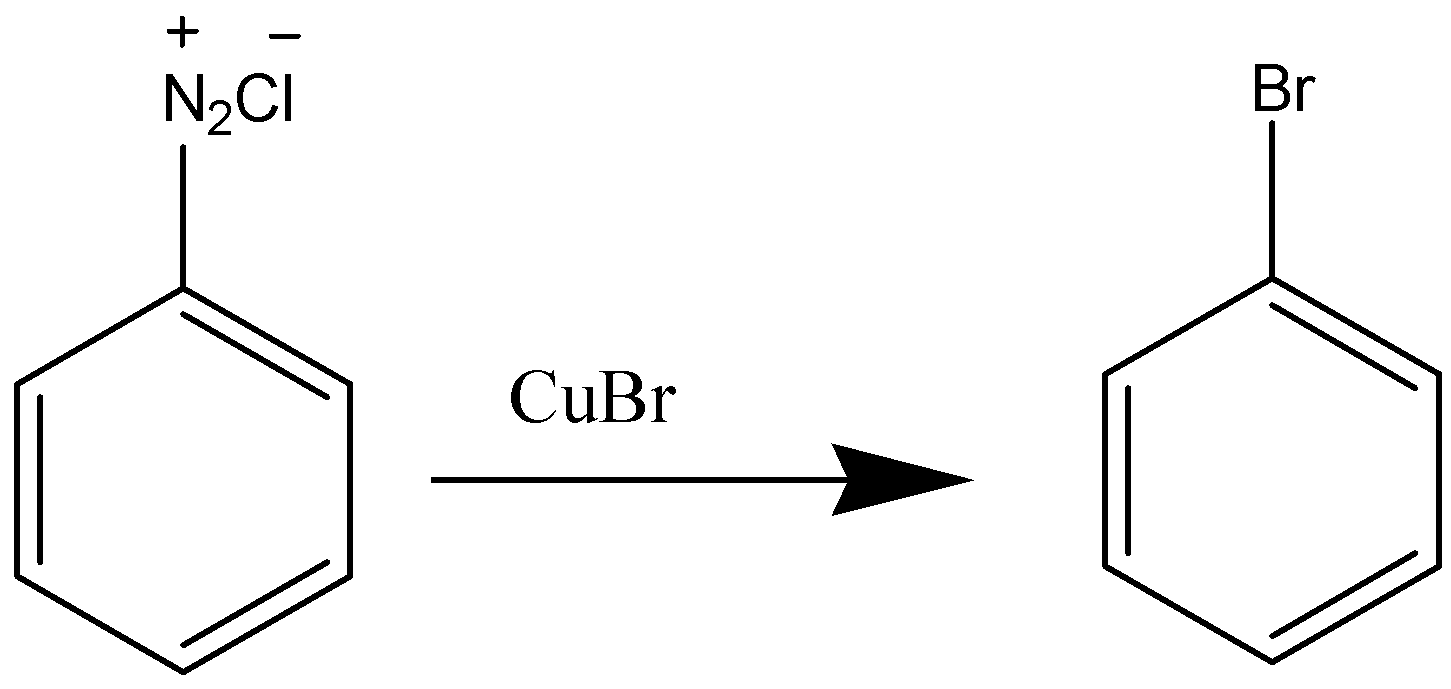

In Sandmeyer’s reaction, Iodo Benzene cannot be formed because iodine is an oxidising agent and iodine reacts with itself to form l2 and also because of its large size. In case of Iodobenzene different reagents as KI used to obtain the product because it cannot be formed in presence of Cu(I) (Iodine being less reactive than other halogens)
Therefore, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: In the mechanism of the Sandmeyer reaction, it commences with a transfer of a single electron from the copper (Cu) to the diazonium. This results in the formation of a non-participating diazo radical as well as copper (II) halide. A molecule of nitrogen gas is then released by the diazo radical to give aryl radical, which then reacts with the copper (II) halide to restore the catalyst [copper (I) halide]. Then, the final product, aryl halide is obtained after this.
