Question
Question: Which of the following is not a \[\pi - bonded\] system? A.Zeise’s salt B.Ferrocene C.Dibenzen...
Which of the following is not a π−bonded system?
A.Zeise’s salt
B.Ferrocene
C.Dibenzene Chromium
D.Tetraethyl lead
Solution
A π−bonded system must contain at least one double or triple bond in the complex. Aromatic systems, alkenes or alkynes as ligands present independently or as part of organometallic complexes contribute π−electrons present in their unhybridized p-orbitals.
Complete answer:
In order to determine whether a system contains π−electrons or not, the complete structure of the compound must be known.
1.Zeise’s salt : It is an organometallic compound containing platinum as the central metal. Platinum is bonded to three chloride ligands and one ethene ligand with an overall negative charge on the complex.
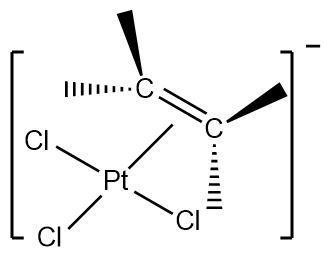
Hence, the given complex is a π−bonded system.
2.Ferrocene: It is an organometallic compound also known as a sandwiched compound as it contains an iron atom sandwiched between two cyclopentadienyl rings. Cyclopentadienyl rings are aromatic in nature containing two double bonds and a lone pair (a total of 6 π−electrons) that are delocalized throughout the ring.
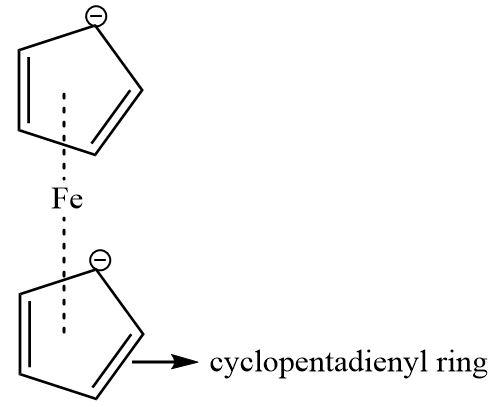
Hence, Ferrocene is a π−bonded system.
3.Dibenzene chromium: It is also an organometallic compound containing chromium metal sandwiched between two benzene rings. Here benzene rings act as ligands with hapticity six. Benzene in itself is an aromatic compound and contains six π−electrons each.
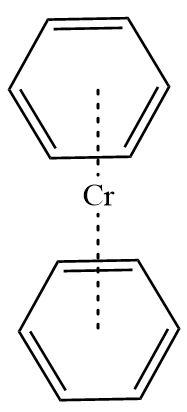
Hence, Dibenzene chromium is a π−bonded
4.Tetraethyl lead: An organometallic compound containing four ethyl groups attached to a lead atom. The ethyl groups are completely saturated and do not contain any π−electrons.
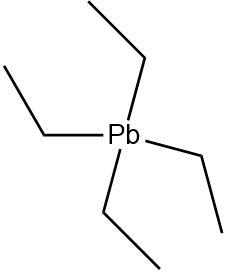
Due to the lack of double, triple bonds or aromatic systems Tetraethyl lead is not a π−bonded system.
Thus, option (D) Tetraethyl lead is not a π−bonded system.
Note:
Many organometallic compounds contain organic compounds as hapto ligands. Hapticity is the measure of the number of carbon atoms that are directly bonded to the central metal while donating its electrons.
