Question
Question: Which of the following is not a coloured cation? A) \(F{e^{ + 2}}\) B) \(C{a^{ + 2}}\) C) \(F{...
Which of the following is not a coloured cation?
A) Fe+2
B) Ca+2
C) Fe+3
D) Ni+2
Solution
We know that transitions metals are placed in d-block. The presence of unpaired electrons in d-block shows d-d transition in d-orbital emit colour. Anyway when the metal begins holding with different ligands, this changes. Because of the d-orbital and inductive impacts of the ligands on the electrons. The d-orbitals split apart and became non-degenerate (have distinct energy levels).
Complete step by step answer:
Reason of colour of ions= Compound of the s and p-block elements are colourless as white if anion is not coloured while compounds of d-block elements are coloured.
It is due to the fact that under the influence of the magnetic field of ligands (like water, ammonia etc.) d subshell is split into two groups namely t2g and eg. This is called d-d splitting.
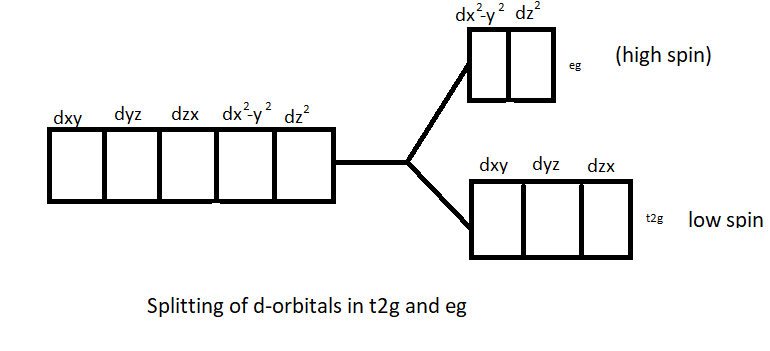
d-d transition= t2g and eg orbitals have different energies and this energy difference lies in the visible region. Thus in a d-d transition (t2g⇄eg), some wavelengths of visible region are absorbed by the ions and complementary colour of refractive wavelengths is seen.
S and p-orbital are symmetrical in geometry thus their splitting does not occur and their compounds are colourless.
The ions having d0 or d10 configuration do not show orbital splitting, hence, they are colourless. For the same reason Ca+2 ion are colourless.
Colour of metal ions are given below:
Hydrated Fe+2= green
Hydrated Fe+3= yellow
Hydrated Ni+2=green
Ca+2 Is colourless. Other cations are coloured.
Hence, option B is correct.
Additional information: This forms the basis crystal field theory (CFT). How these d-orbitals split depends on the geometry of the compound that is formed.
Note:
Transition metals are special in that the energy is different between the non-degenerate, d- orbitals corresponding to the energy of radiation of the visible light spectrum. Due to the presence of unpaired electrons in Fe+2, Fe+3 and Ni+2 ions it shows d-transition.
