Question
Question: Which of the following is/are true about the ellipse \({x^2} + 4{y^2} - 2x - 16y + 13 = 0\)? (A) T...
Which of the following is/are true about the ellipse x2+4y2−2x−16y+13=0?
(A) The latus rectum of the ellipse is 1.
(B) Distance between foci of the ellipse is 43.
(C) Sum of the focal distance of a point P (x, y) on the ellipse is 4.
(D) y=3 meets the tangents drawn at the vertices of the ellipse at point P and Q, then PQ subtends a right angle at any of its foci.
Solution
First we will convert the above equation in the standard form of ellipse so that we can find the value of a and b from the equation. Next, we need to find the eccentricity of this ellipse which is required in finding the latus rectum using the formula e=1−a2b2.
Complete answer:
In the above question, first we will convert the equation x2+4y2−2x−16y+13=0 in the standard equation of an ellipse, which is a2(x−x1)2+b2(y−y1)2=0.
Therefore,
x2+4y2−2x−16y+13=0
We can also write the above equation as,
⇒x2−2x+1+4y2−16y+16−4=0
Now, taking 4 as common
⇒(x2−2x+1)+4(y2−4y+4)−4=0
On transposing, we get
⇒(x2−2x+1)+4(y2−4y+4)=4
Now we will use the formula (a−b)2=a2+b2−2abin the above equation
⇒(x−1)2+4(y−2)2=4
Now, we will divide the whole equation by 4.
⇒4(x−1)2+1(y−2)2=1
⇒(2)2(x−1)2+(1)2(y−2)2=1
On comparing with a2(x−x1)2+b2(y−y1)2=0, we get a=2andb=1
Now,
(A) The length of latus rectum =a2b2
On substituting the values of a and b
⇒22×(1)2
⇒1
(B) e=1−a2b2
e=1−41
⇒e=43=23
Distance between foci of the ellipse =2ae=2×2×23=23
(C) Sum of the focal distance =2a=2×2=4
(D) In this part we have to prove that ify=3 meets the tangents drawn at the vertices of the ellipse at point P and Q, then PQ subtends a right angle at any of its foci. Here O denotes the focus of given ellipse.
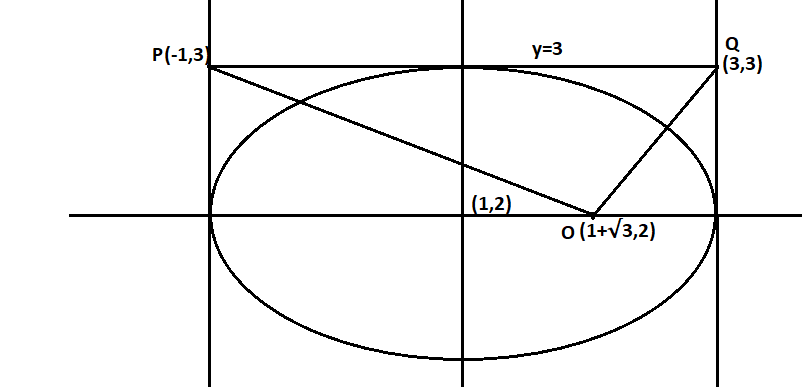
Now we use the relation m1m2=−1to prove that line OP and OQ subtend right angle at its focus. Here m1is the slope of OP and m2 is the slope of OQ.
Here, in this figure x1=1+3,y1=2,x2=−1,y2=3,x3=3,y3=3
⇒ m1=x2−x1y2−y1 and m2=x3−x1y3−y1
⇒ m1=−1−(1+3)3−2 and m2=3−(1+3)3−2
⇒ m1=−2−31 and m2=2−31
⇒ m1=−(2+3)1and m2=2−31
Now, we will multiply both the terms
m1m2=2−31×(2+3)−1
⇒m1m2=(2)2−(3)2−1
⇒m1m2=4−3−1
⇒m1m2=1−1
⇒m1m2=−1
Therefore, OP and OQ subtend the right angle at the focus.
Hence, option A, C and D are correct.
Therefore, the correct option is A, C and D
Note: All ellipses have two focal points, or foci. The sum of the distances from every point on the ellipse to the two foci is a constant. All ellipses have a centre and a major and minor axis. All ellipses have eccentricity values greater than or equal to zero, and less than one.
