Question
Question: Which of the following is/are a meso compound? THIS QUESTION HAS MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS A. ...
Which of the following is/are a meso compound?
THIS QUESTION HAS MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS
A.
B.
C.
D.
Solution
We know that a meso isomer is a stereoisomer which is not optically active. This isomer is achiral despite the presence of two or more stereogenic centres. It has a plane of symmetry and superimposable mirror image.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s first understand stereoisomers in detail. Isomers that possess different spatial atomic arrangement but same atomic connectivity are termed as stereoisomers. There are two types of stereoisomers, geometric isomers and optical isomers.
Now, we discuss the conditions required for a compound to be called a meso compound.
1)The compound must possess a plane of symmetry. A plane that bisects a molecule into two halves and these two parts are mirror images of each other is termed as a plane of symmetry.
2)The compound must have at least two chiral centres. Chiral centre is the atom in which all the four groups attached are different.
3)Also the compound must be optically inactive. An optically inactive compound possesses a plane of symmetry and centre of symmetry.
Now, we have to observe the above conditions in the given options.
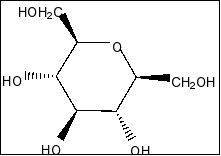
Compound in option A is
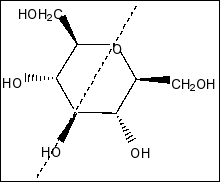
We clearly see that there is a plane of symmetry in the molecule and more than two chiral centres in the molecule. So, the compound is meso compound.
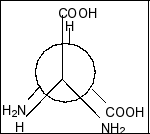
Compound in option B is,
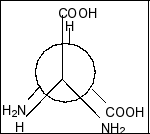
Here also, we clearly see that there is a plane of symmetry and two chiral centres. So, this compound is also a meso compound.
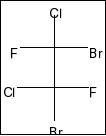
Compound in option C is,
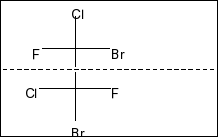
Here, also a plane of symmetry and two chiral centres in the molecule. So, it is also a meso compound.
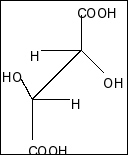
Compound in option D is,
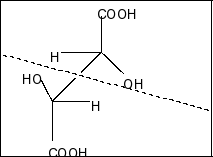
Here also a plane of symmetry and two chiral centres present. So, this compound is also a meso compound.
Hence, A, B, C and D are the correct answers.
Note:
To identify whether an atom is a chiral centre or not, we have to look at the groups bonded to it. If all the bonded groups are different it indicates that the atom is a chiral centre. If we know the number of chiral centres in a molecule, then we can calculate the number of stereoisomers of the molecule. The formula is, Numberofstereoisomer=2n, here, n represents the number of chiral centres.
