Question
Question: Which of the following had two stereogenic centers (asymmetric carbons) ? A)  ?
A) 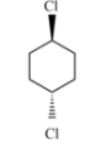
B)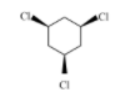
C) 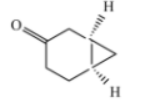
D) 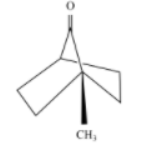
Solution
The geometrical property of a molecule or ion which cannot be superimposed on its mirror image by any combinations of rotations and translations is called chirality. A carbon atom that is bonded to four different atoms or groups loses its symmetry is referred to as asymmetric carbon.
Complete step by step solution:
The configuration of such a stereogenic center molecule with asymmetric carbon is said to be chiral and the structure will be a mirror image of the other either right-handed configuration or left-handed configuration. The non-identical mirror-image pair of stereoisomers are called enantiomers and this type of configuration isomerism is named enantiomorphism. For examining structural formulas if stereoisomers may exist to identify all stereogenic elements. A center, axis, or plane which is a focus of stereoisomerism is known as a stereogenic element such that an interchange of two groups attached to this feature leads to a stereoisomer.
Among all the given structures, option A will has two stereogenic centers which exist two asymmetric carbons (shown as * in the structure). This structure will contain stereogenic elements along the plane of two groups.
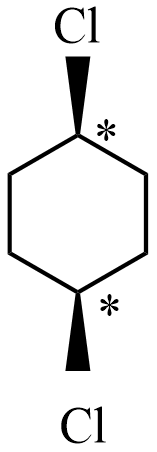
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: If a molecule exhibits an opposite R/S configuration with all chiral centers between two stereoisomers is called enantiomers. If at least one, but not all of the chiral centers are opposite R/S configuration between two stereoisomers which are diastereomers. The difference between diastereomers and stereoisomers is more than geometry.
