Question
Question: Which of the following group has the maximum hyper-conjugation effect: A. \( - C{H_3}\) B. \( ...
Which of the following group has the maximum hyper-conjugation effect:
A. −CH3
B. −CH2CH3
C. 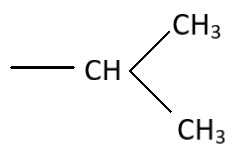
D. 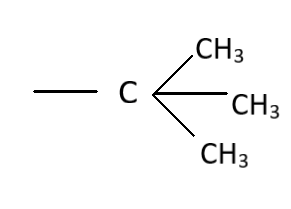
Solution
There are 1o,2o,3o carbons possible in different types of organic molecules with respect to the position in which the central carbon is present. Changes in the chemical property takes place in the different molecules based on the nature of bond formation.
Complete step by step answer:
The hyperconjugation effect occurs as a result of the delocalization of the electrons based on the sigma bonds involved in the formation of the organic molecule. The stability depends on the hyperconjugation effect of the molecules. This is because the level of stability in the organic molecule differs and hence cations stabilize according to the formation of these structures. The number of hydrogen bonds which are present in the organic compound, the higher will be the stability due to hyperconjugation. The highest number of such C−H bonds are observed in the organic compound as given in the option (D). There are three C−C sigma bonds which makes the internal carbon easier to rotate. Each of the associated carbon residues have three C−H as they are methyl linkages. Thus, a total of 9 C−H bonds are present offering the molecule having the neo butyl structure as the organic compound having hyperconjugation effect. Therefore, the correct choice based on the stability is:
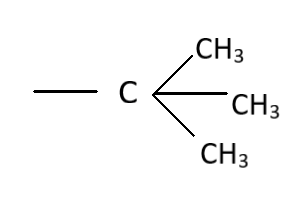
The characters of the sigma bonds between the alpha-carbon residue and the methyl groups which are associated with the internal carbon atom. Even though there is a rotatory character of internal residue, still the stability is offered as a result of the hyperconjugation. Hence the neo-structure or the one with 3o Carbon residue inside the organic molecule.
Note:
This hyper-conjugative character follows the similar nature with the stability order of the carbocation in the given organic molecules. The stability depends on the relative effect of adjacent hydrogen residues.
