Question
Question: Which of the following gases is absorbed more by activated charcoal: A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\...
Which of the following gases is absorbed more by activated charcoal:
A. CO2
B. N2
C. CH4
D. H2
Solution
Hint: In order to answer this question, we should be knowing the structures of the gases shown in the options. Knowing the structure will give us a hint about the critical temperature of the compound, and then we can figure whether it will be absorbed by charcoal or not.
Step by step answer:
Absorption of gas on the surface of activated charcoal depends on the critical temperature of a gas. Critical temperature is that temperature at which or above which the gas cannot be liquefied no matter how much pressure is increased.
Critical temperature has a direct relation to adsorption, higher the critical temperature greater will be the absorption.
Gases having higher critical temperature are easily liquefied. Hence in the liquid state they have greater force of attraction with the charcoal and therefore they are more easily adsorbed on the surface of the charcoal.
Therefore, the gas which has the highest critical temperature is Methane or CH4. Therefore, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Here are the basic descriptions of the processes that have been mentioned in the answer.
Absorption is the adhesion of atoms or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface. This process creates a film of the adsorbent on the surface of the adsorbent. This process differs from absorption, in which a fluid is dissolved by or permeates a liquid or solid respectively.
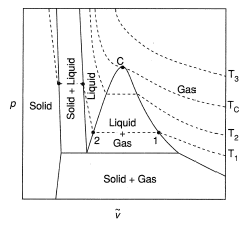
We should be knowing a bit about critical points. So we can say that in thermodynamics a critical point is the end point of a phase equilibrium curve.
The most prominent example is the liquid- vapour critical point, the end point of the pressure temperature curve that designates conditions under which a liquid and vapour can coexist.
Here is the graph of liquid - vapour critical state: