Question
Question: Which of the following does not give benzoic acid on hydrolysis? (A) Phenyl cyanide (B) Benzoyl ...
Which of the following does not give benzoic acid on hydrolysis?
(A) Phenyl cyanide
(B) Benzoyl chloride
(C) Benzyl chloride
(D) Methyl benzoate
Solution
Hint : An organic reaction which cleavage of chemical bonds takes place in an organic compound by the addition of water, is known as hydrolysis reaction. The addition of water to a compound can give an additional reaction as well as substitution reaction, depending on the type of reactant.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The molecular formula of benzoic acid is C6H5−COOH and structurally it is represented as follows:
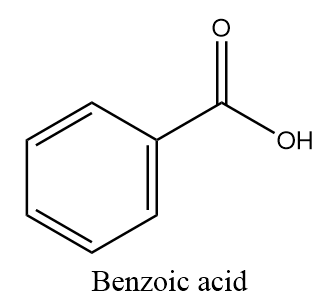
The hydrolysis reaction of the given compounds will take place as follows:
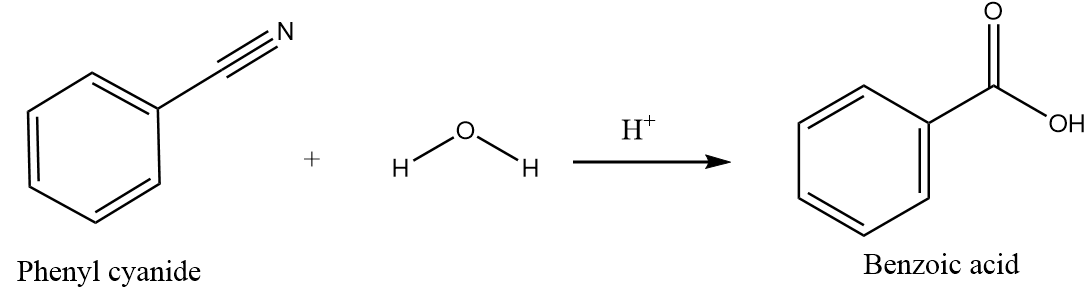
Hydrolysis of phenyl cyanide:
When phenyl cyanide undergoes hydrolysis in the acidic medium, the nucleophilic addition of water molecules takes place followed by the nucleophilic elimination reaction and forms carboxylic acids as the major product. The reaction proceeds as follows:
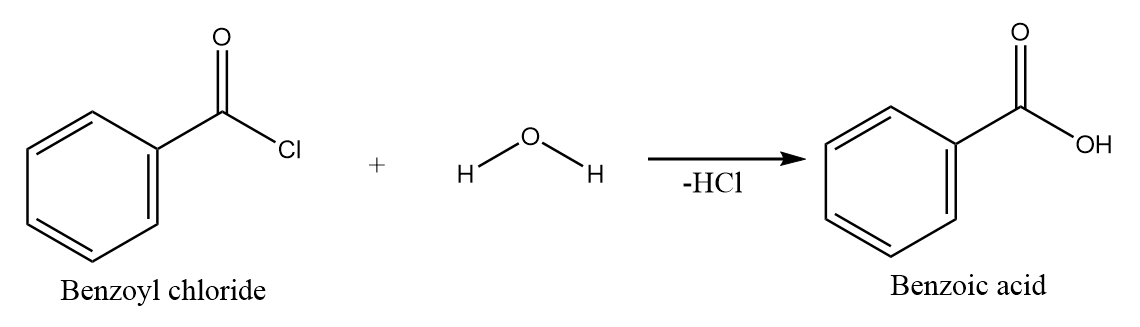
Hydrolysis of benzoyl chloride:
On hydrolysis of benzoyl chloride, the hydroxide ion attacks the carbonyl centre and removal of chloride ion takes place. Hence, benzoic acid is formed along with the removal of HCl . The reaction takes place as follows:
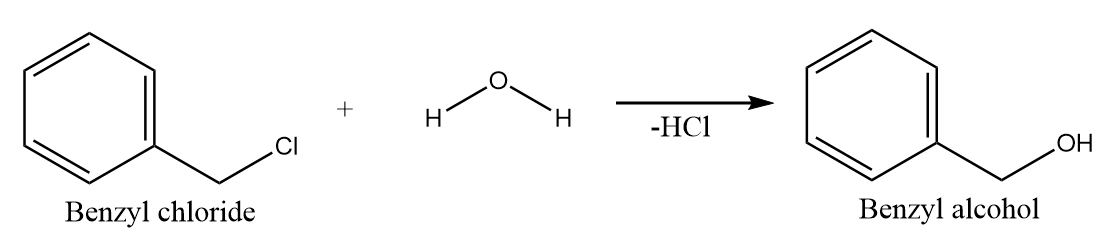
Hydrolysis of benzyl chloride:
When benzyl chloride undergoes hydrolysis reaction, then the hydroxide ion of the water molecule acts as a nucleophile and replaces the chloride ion to give a nucleophilic substitution reaction. The major product formed in the reaction is Benzyl alcohol along with the removal of HCl . The reaction proceeds as follows:
Hydrolysis of methyl benzoate:
On hydrolysis of methyl benzoate, the hydroxide ion of water molecules act as a nucleophile and replace the methoxy group to give nucleophilic substitution reaction. The major product formed in the reaction is benzoic acid along with the removal of methyl alcohol. The reaction proceeds as follows:
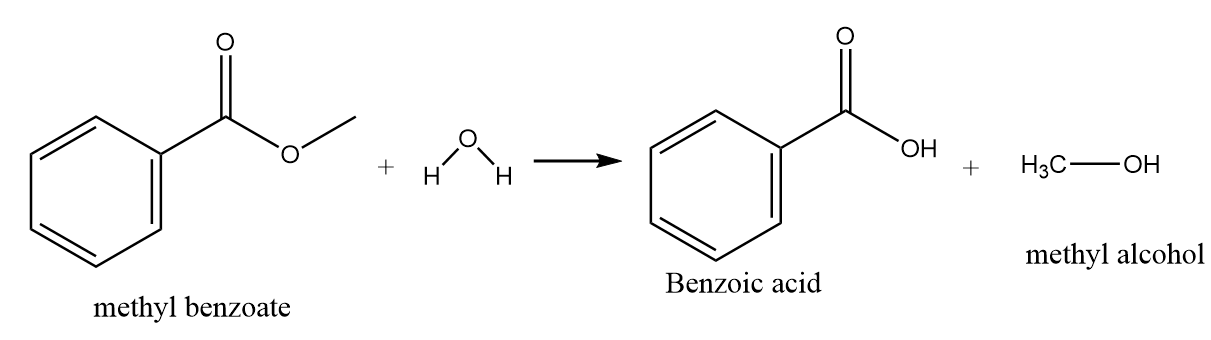
Hence, benzoic acid will not form on hydrolysis of benzyl chloride.
Therefore, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note :
It is important to note that if a carbonyl group i.e., C=O is present in the compound then in general cases, the attack of incoming nucleophile will take place at carbonyl centre only, because it is bonded to oxygen atom which is highly electronegative element and attracts electron clouds towards itself due to which the carbon atom acts as an electron deficient species.
