Question
Question: Which of the following compounds has(have) a meso isomer? A. 2,4-dibromohexane B. 2,3-dibromobut...
Which of the following compounds has(have) a meso isomer?
A. 2,4-dibromohexane
B. 2,3-dibromobutane
C. 2,4-dimethyl pentane
D. Hexane-2,5-diol
Solution
To answer this question, you should recall the concept of Stereochemistry. Stereochemistry refers to the systematic presentation or the chemistry of space i.e. it deals with the spatial arrangements of atoms and groups in a molecule.
Complete answer:
In general, a meso compound should contain two or more identical substituted stereocenters. This molecule also has an internal symmetry plane that divides the compound in half. These two halves reflect each other by the internal mirror. This results in the stereochemistry being cancelled out by the two stereocenters hence resulting in an optically inactive mixture. If A is a meso compound, it should have two or more stereocenters, an internal plane, and the stereochemistry should be R and S:
Look for an internal plane, or internal mirror, that lies in between the compound.
R cancels S out in a meso compound with two stereo centres making it optically inactive.
Using the above rules we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is 2,3-dibromobutane. The structure can be represented as:
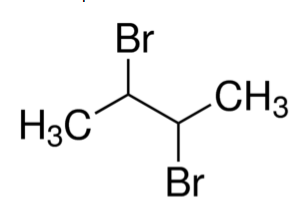
Hence, the correct answer to this question is option B.
Note: We know that isomers are defined as the molecules with the same molecular formula but possess a different arrangement of the atoms in space or different connectivity of atoms. The phenomenon in which the molecules in which the atoms that form the isomers are connected differently is known as structural isomerism. The phenomenon in which the connectivity of atoms is the same in isomers but a different spatial arrangement is a stereoisomerism. 2-Butene can exist as cis and trans isomers because of the double bond that leads to the restricted rotation. For example in 2-Butene, this results in two isomers where the cis-isomer formed have the two methyl groups on the same side and the trans-isomer formed has the two methyl groups on opposite sides. 2-methyl propene and 2-methyl-2-butene contain a double bond but the groups attached to one of the C of the double bond are the same.

