Question
Question: Which of the following compounds contains –OH functional group? A) Propanone B) Propanol C) Pr...
Which of the following compounds contains –OH functional group?
A) Propanone
B) Propanol
C) Propanoic acid
D) Propanal
Solution
To answer this question, we should have knowledge of IUPAC nomenclature. The given functional group is –OH, means it represents alcohol. And from the above options we should know that for alcohols, what are IUPAC names given as suffixes and also their structures.
Complete step by step answer:
As we are aware, the functional group –OH represents alcohol. We know the famous four functional groups are Carboxylic acid, Aldehyde, ketone, and alcohol.
There are specific prefixes also, according to the number of carbons in parent, principal or main chain. Examples like for 1 carbon word root is meth, 2 carbons- eth, 3 carbons- prop.
Thus we can see that in the above options, every option has prop as a prefix, meaning 3 carbon are present in each option.
Each of these functional groups has special representation and ends with a specific suffix.
IUPAC nomenclature tells us that, in the case of a functional group, remove last –e from the name of respective alkane, and add a proper suffix related to each functional group.
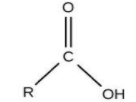
For Carboxylic acid, the group is ‘–COOH’ and the name ends with ‘–oic acid’.
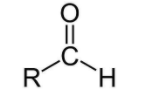
For aldehydes, the group is ‘–CHO’ and the name will end in ‘–al’.
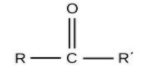
For ketones, the group is ‘–CO-‘ and the name will end with ‘–one’.
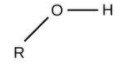
For alcohols, the group is ‘–OH’ and the name will end in ‘–ol’.
Here, the option (A) propanone ends with ‘–one’, means it is ketone.
The option (B) propanol is ending with ‘–ol’, meaning it is alcohol.
The option (C) propanoic acid is ending with ‘–oic acid’, meaning it is carboxylic acid.
The option (D) propanal is ending with ‘–al’, meaning it is aldehyde.
Thus the correct option is (B) propanol, which is alcohol with ‘–OH’ as a functional group.
Note: In the structural arrangement, we might get confused with the presence of –OH group in carboxylic acid. But we should take care that the carbon with which –OH is attached is not having any double bonded Oxygen (O) atom, then it is alcohol, if the carbon attached to –OH has, double bonded oxygen (O) atom, then it is carboxylic acid.
