Question
Question: Which of the following carboxylic acids undergoes decarboxylation easily? A) \({{\text{C}}_{\text{...
Which of the following carboxylic acids undergoes decarboxylation easily?
A) C6H5COCOOH
B) C6H5COCH2COOH
C) C6H5CHOHCOOH
D) C6H5CHNH2COOH
Solution
Decarboxylation of acid is the removal of the carboxylic group from acid. β-keto acids undergo decarboxylation very easily. Thermal decomposition of β-keto acids is easy.
Complete step by step answer:
A reaction where there is a loss of carbon dioxide is called a decarboxylation reaction.
The general decarboxylation reaction is as follows:
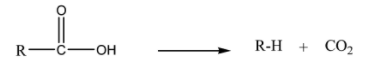
Simple carboxylic acids do not undergo decarboxylation reactions easily. Carboxylic acids having carbonyl group at β potion that is β-keto acids undergo decarboxylation very easily.
As simple carboxylic acids are stable, they do not undergo decarboxylation reaction at the mild condition. While β-keto acids are unstable they undergo decarboxylation reactions easily at mild conditions also.
Now we can draw the structures of all carboxylic acid given in options and determine the β-keto acid.
The structure of C6H5COCOOH is as follows:
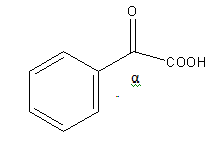
As C6H5COCOOH is not β-keto acid it will not undergo decarboxylation reaction easily. So, option (A) is incorrect.
Structure of
C6H5COCH2COOH is as follows:
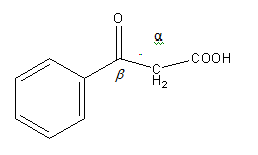
As C6H5COCH2COOH is β-keto acid it will undergo decarboxylation reaction easily. So, option (B) is correct.
Structure of C6H5CHOHCOOH is as follows:
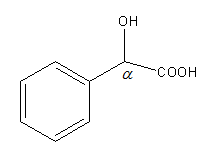
As C6H5CHOHCOOH is not β-keto acid it will not undergo decarboxylation reaction easily. So, option (C) is incorrect.
Structure of C6H5CHNH2COOH is as follows:
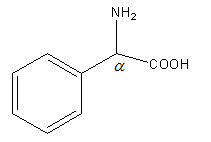
As C6H5CHNH2COOH is not β-keto acid it will not undergo decarboxylation reaction easily. So, option (D) is incorrect.
Thus, the correct option is (B) C6H5COCH2COOH.
Note: In decarboxylation reaction carboxylic acid is converted into ketone after the elimination of carbon dioxide gas. Due to the formation of a cyclic six atom transition state, β-keto acids undergo decarboxylation reaction rapidly under the mild condition as well.
