Question
Question: Which of the following can have meso isomers? (a)- \(C{{H}_{2}}(OH)CH(OH)CHO\) (b)- \(C{{H}_{2}...
Which of the following can have meso isomers?
(a)- CH2(OH)CH(OH)CHO
(b)- CH2(OH)CH(OH)CH(OH)CHO
(c)- HOOCCH(OH)CH(OH)COOH
(d)- CH2(OH)CH(OH)CH(OH)COOH
Solution
Meso isomers are those in which there are two chiral carbon atoms, but still they are not optically active because of the plane of symmetry. Plane of symmetry means the molecule, when divided into two parts then the two molecules are the same.
Complete step by step answer:
Meso compounds are those which are not optically active or show optical activity, even though there are two chiral carbon atoms. The factor due to which the meso compounds do not show optical activity is because of the presence of a plane of symmetry. Plane of symmetry means the molecule, when divided into two parts then the two molecules are the same. So first we have to check the number of chiral carbon atoms and then the plane of symmetry. And we can check the chiral carbon as the carbon atom that has all four different groups. The structure of the molecule CH2(OH)CH(OH)CHO is given below:
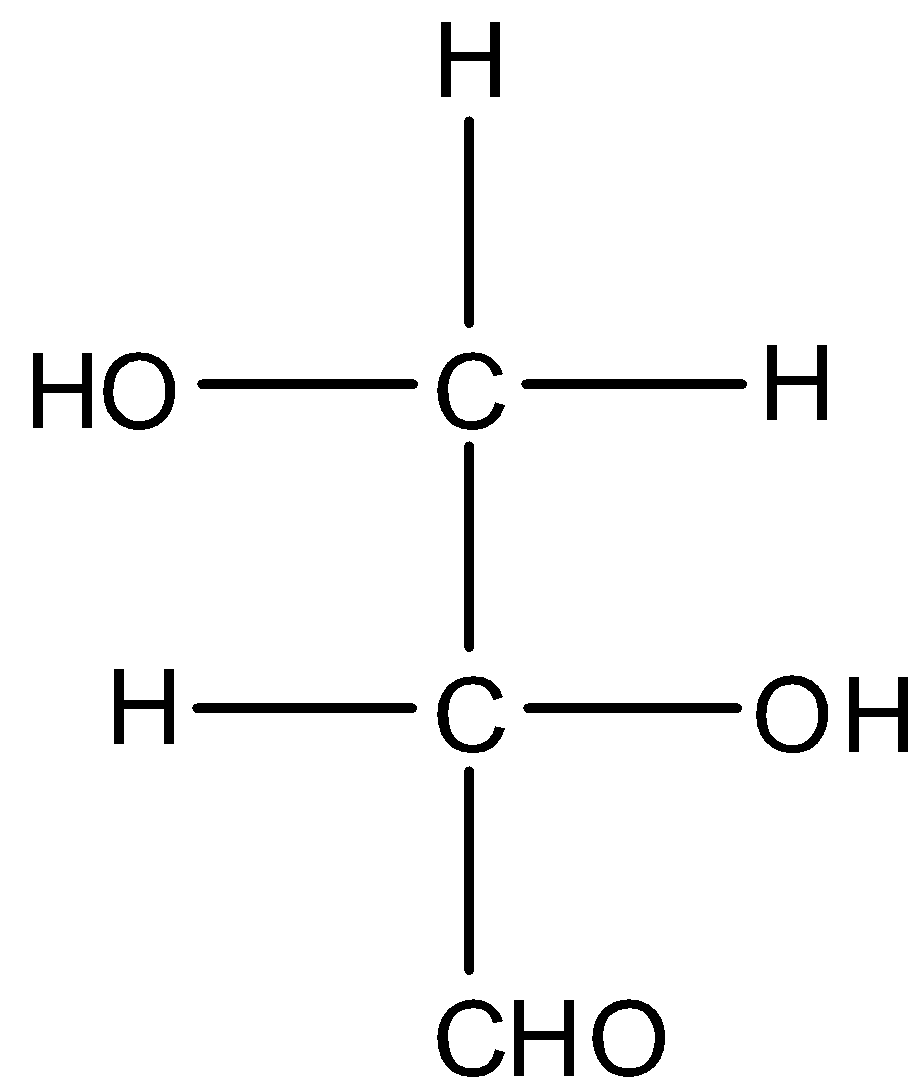
This molecule only has one chiral carbon atom, then it is not a meso compound. The structure of the molecule CH2(OH)CH(OH)CH(OH)CHO is given below:
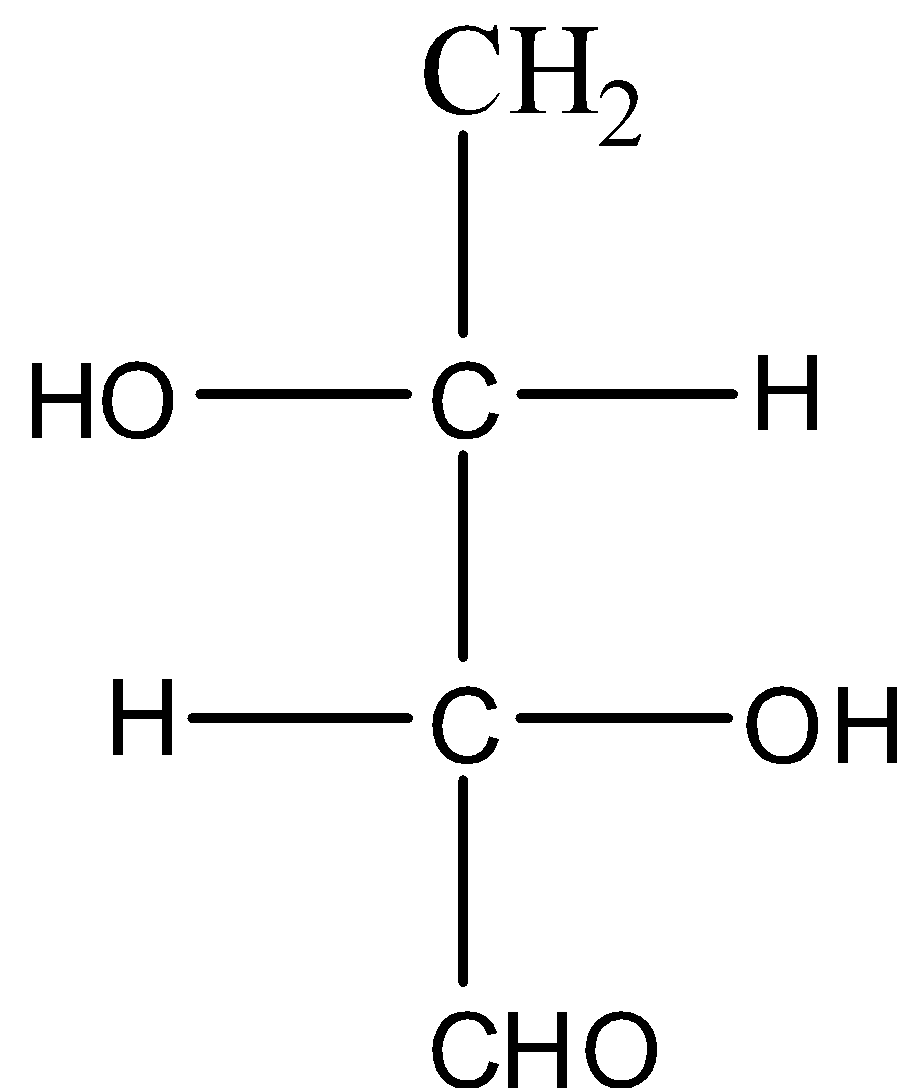
This molecule has two chiral carbon atoms but it doesn't have a plane of symmetry. So it is not a meso isomer. The structure of the molecule HOOCCH(OH)CH(OH)COOH is given below:
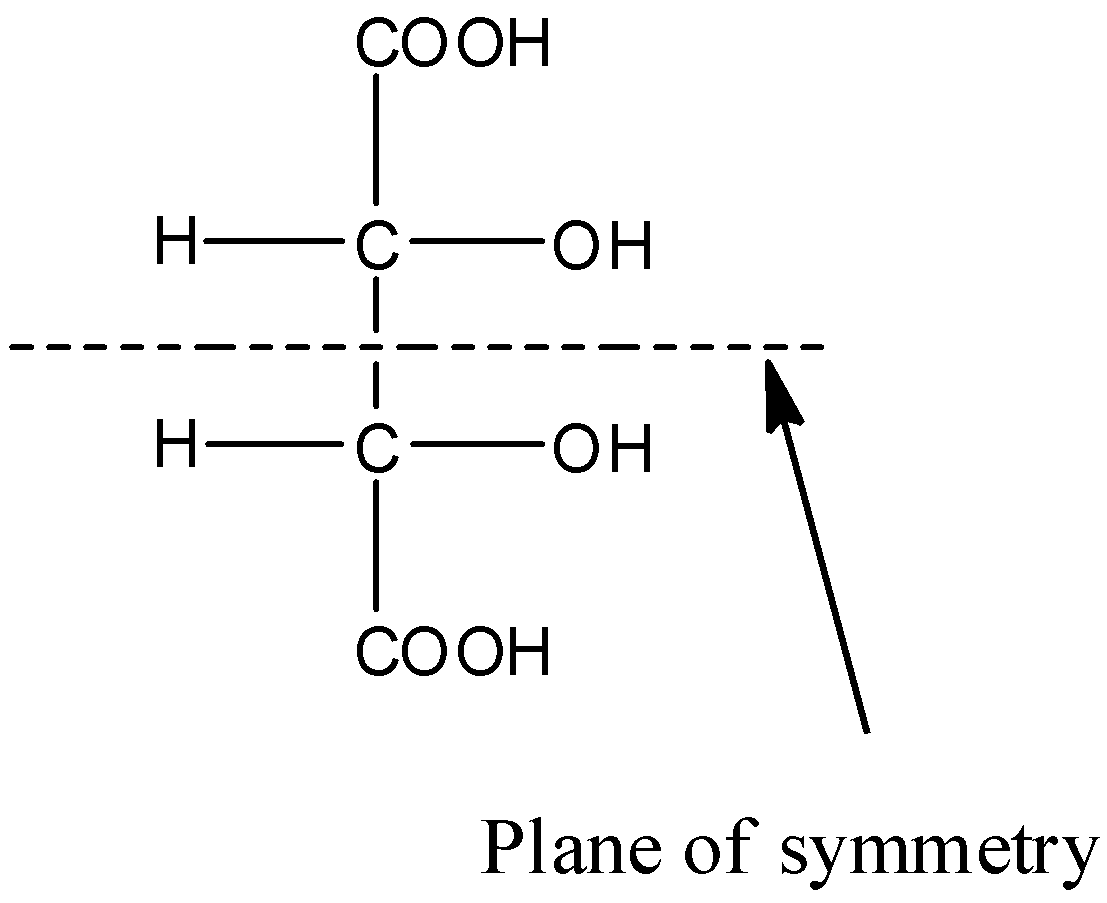
This molecule has two chiral carbon atoms and also has a plane of symmetry. So it is a meso isomer. The structure of the molecule CH2(OH)CH(OH)CH(OH)COOH is given below:
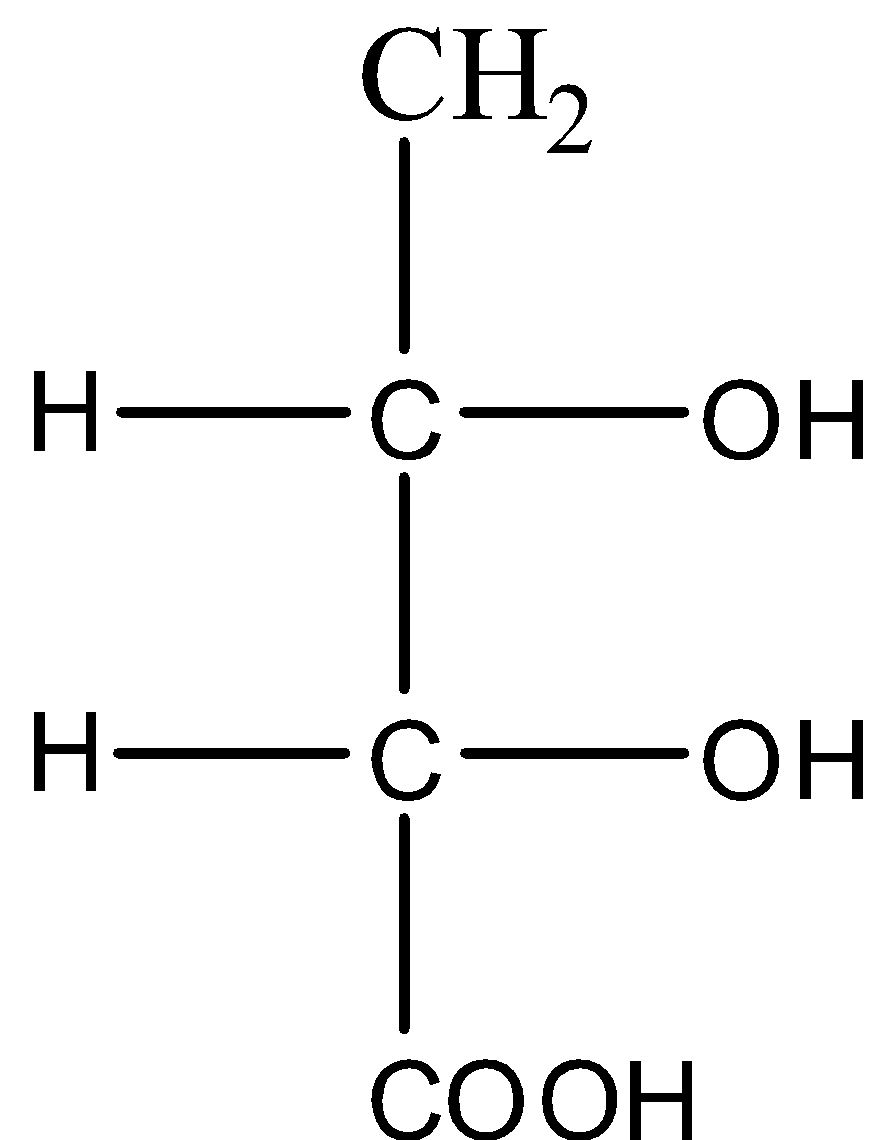
This molecule has two chiral carbon atoms but it doesn't have a plane of symmetry. So it is not a meso isomer.
Therefore, the correct answer is an option (c)- HOOCCH(OH)CH(OH)COOH.
Note: Since the meso compound has two same molecules, so when they are passed through the optical light, there is an internal compensation i.e., rotation due to one part of the molecule is canceled by the rotation due to the other part of the molecule.
