Question
Question: Which of the following can be used in the Friedel Crafts reaction to generate electrophile? This que...
Which of the following can be used in the Friedel Crafts reaction to generate electrophile? This question has multiple correct options
A.
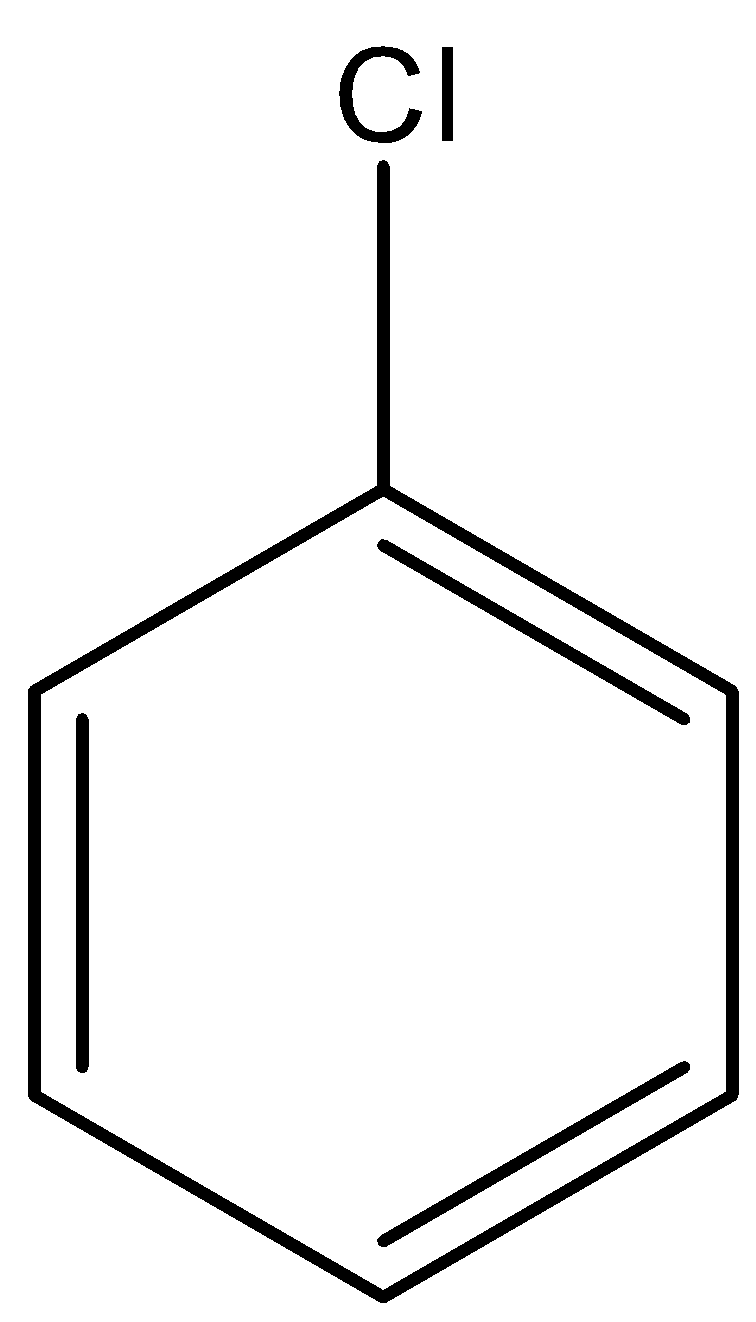
B. CH2=CH−Cl
C. CH3CH2CI sss
D. CH2=CH−CH2−CI
Solution
To convert benzene to ethylbenzene there is a very well-known reaction which is the Friedel-Craft alkylation reaction. In presence of aq. AlCl3 it reduces the nucleophilicity of the benzene ring by the formation of the cation of the benzene ring. When the acyl group is substituted into the benzene ring that reaction is also known as Friedel-Crafts acylation of Benzene.
Complete step by step answer:
Friedel-Craft reaction with aryl and vinyl halide is not possible, because the lone pair of halogen undergoes conjugation with the benzene ring and double bond respectively, and forms a partial double bond. Due to this reason, only alkyl and vinyl halide cannot be used as a halide component in a Friedel-craft reaction.
So only alkyl halides are used in Friedel Crafts reaction to generate electrophile. That the halogen group attaches with sp3 hybridized carbon can be used in Friedel Crafts reaction to generate electrophile.
So, the correct options are, C and D.
Additional information:
CH3COCl is the most reactive substance that contains an acyl group. It is commonly known as acyl chloride or acid chloride.
The benzene ring is reacted with a mixture of ethanoyl chloride CH3COCl and AlCl3 (aluminum chloride) that acts as a catalyst. The product formed is a ketone called phenylethane.
The reaction is as follows:
C6H6+CH3COCl→C6H5COCl+HCl
Or
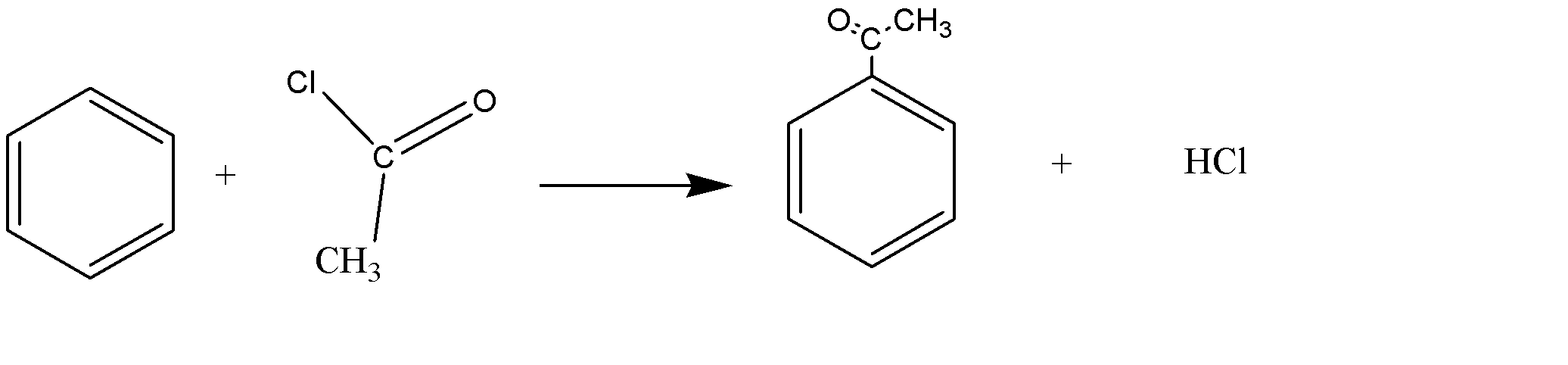
This reaction is an example of an electrophilic substitution reaction. The electrophile is CH3CO + that is produced by the reaction of ethanoyl chloride and aluminum chloride.
The reaction is as follows:
CH3COCl+AlCl3→CH3CO++AlCl4−
The electrophilic substitution mechanism is divided into 2 stages:
Stage 1 –
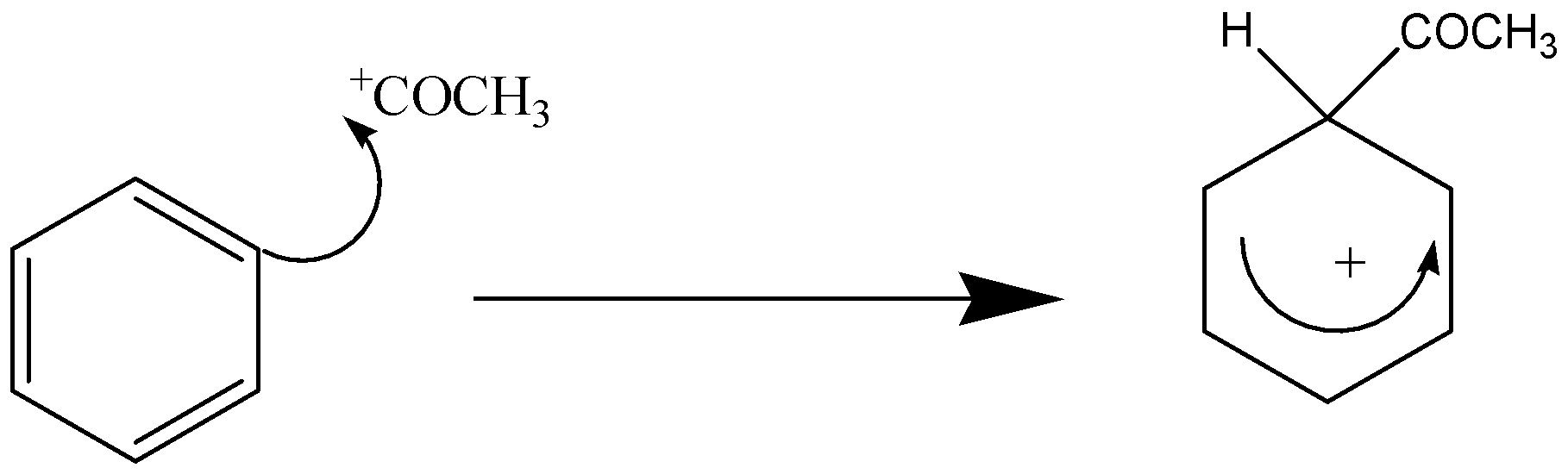
Stage 2 –
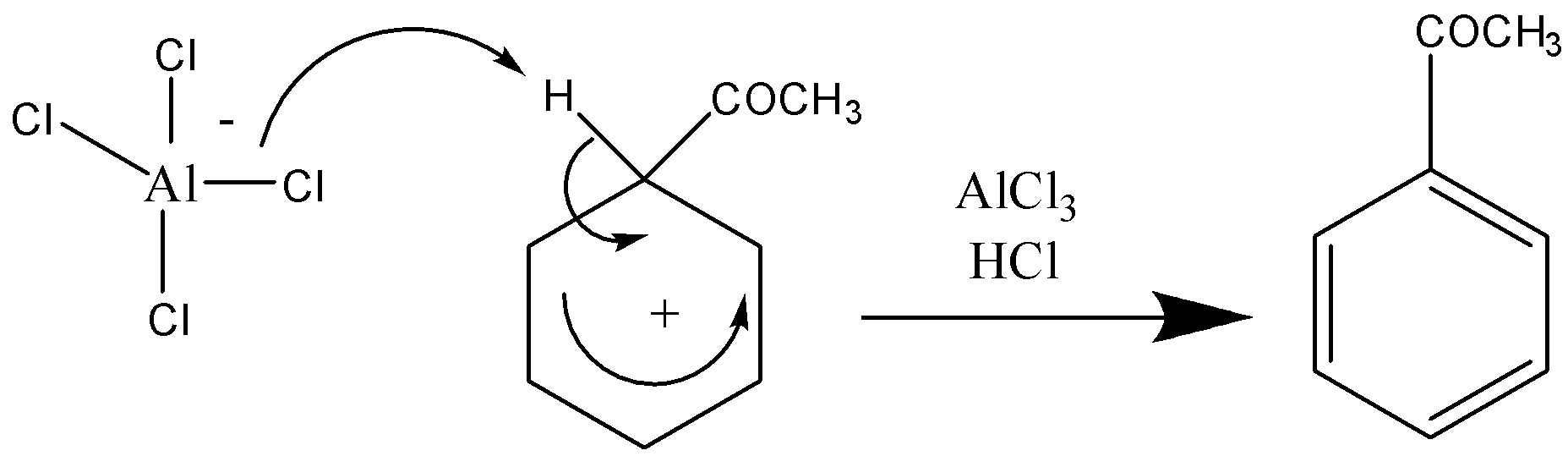
Note: A student can also get confused between electrophilic substitution and nucleophilic substitution. Electrophilic substitution involves the displacement of a functional group by an electrophile, i.e., hydrogen whereas nucleophilic substitution involves the attack of a positively charged atom by a nucleophile.
