Question
Question: Which of the following aromatic acids is the most acidic? A. 
B.
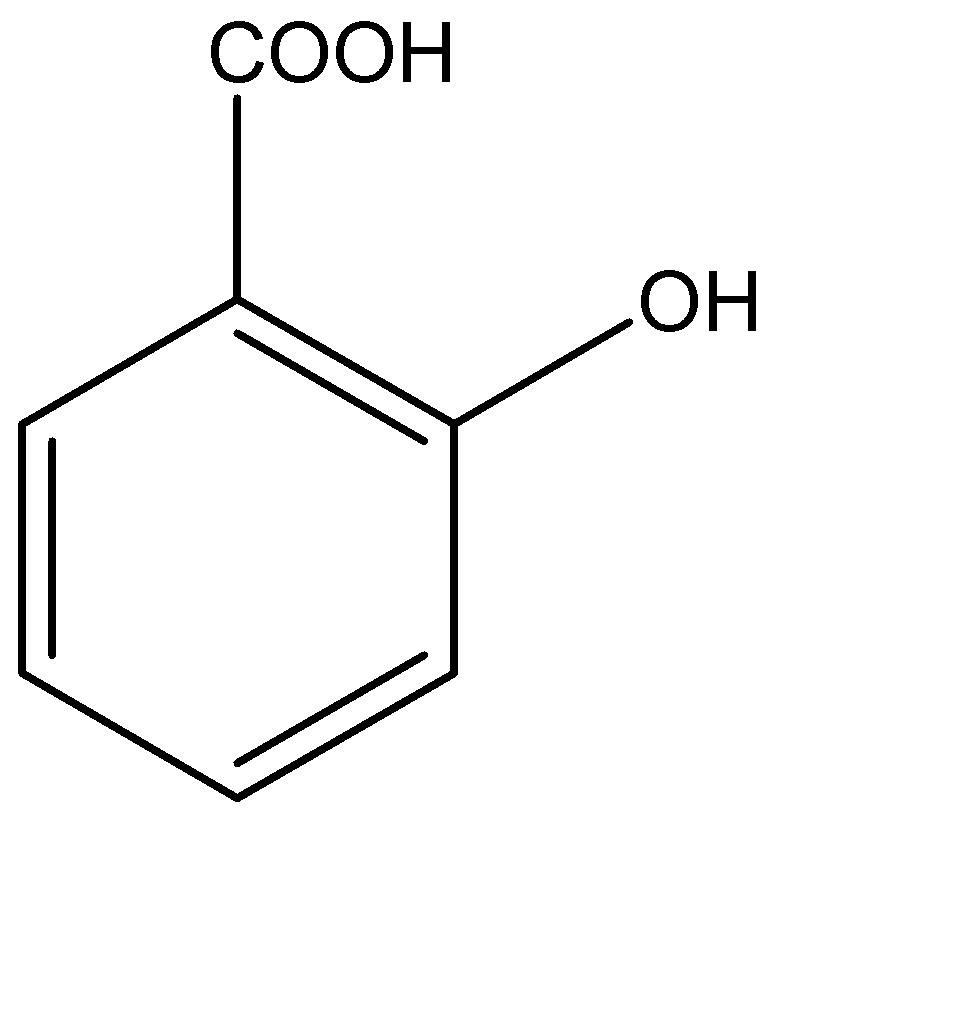
C.
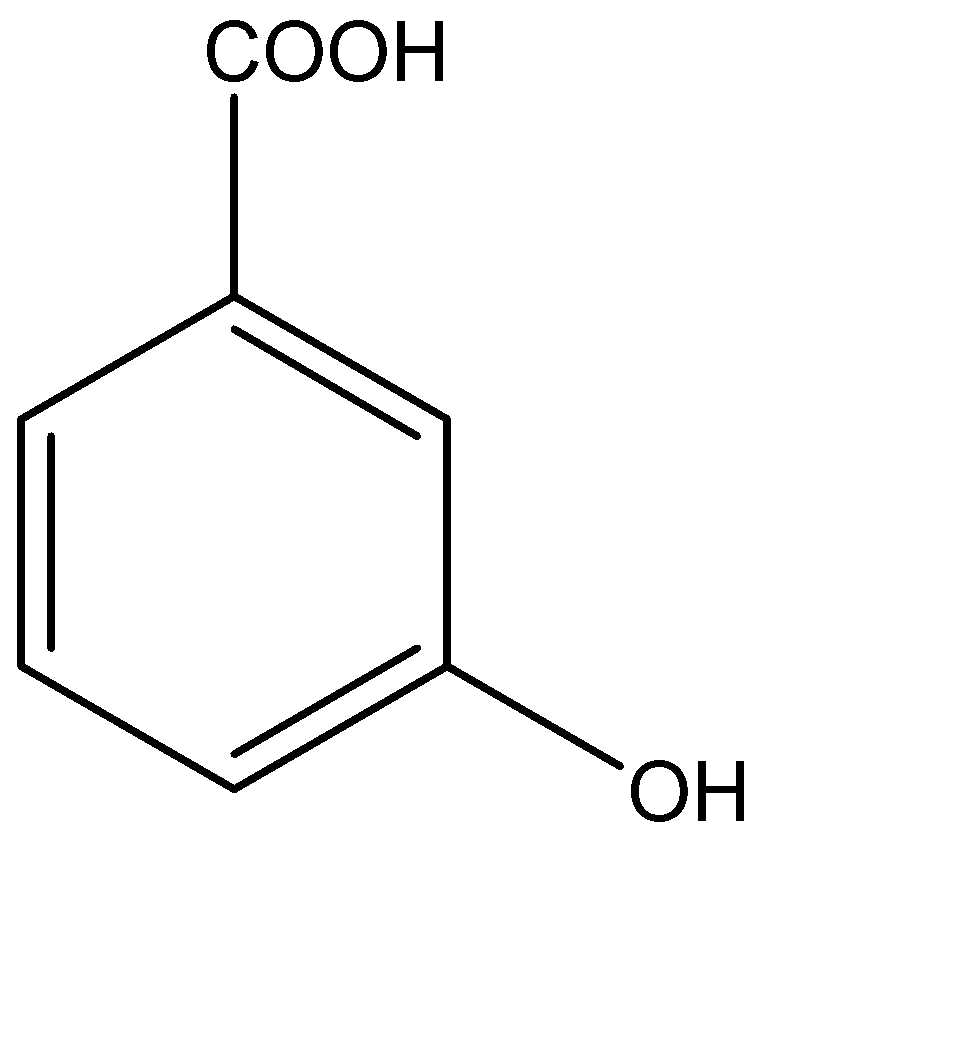
D.
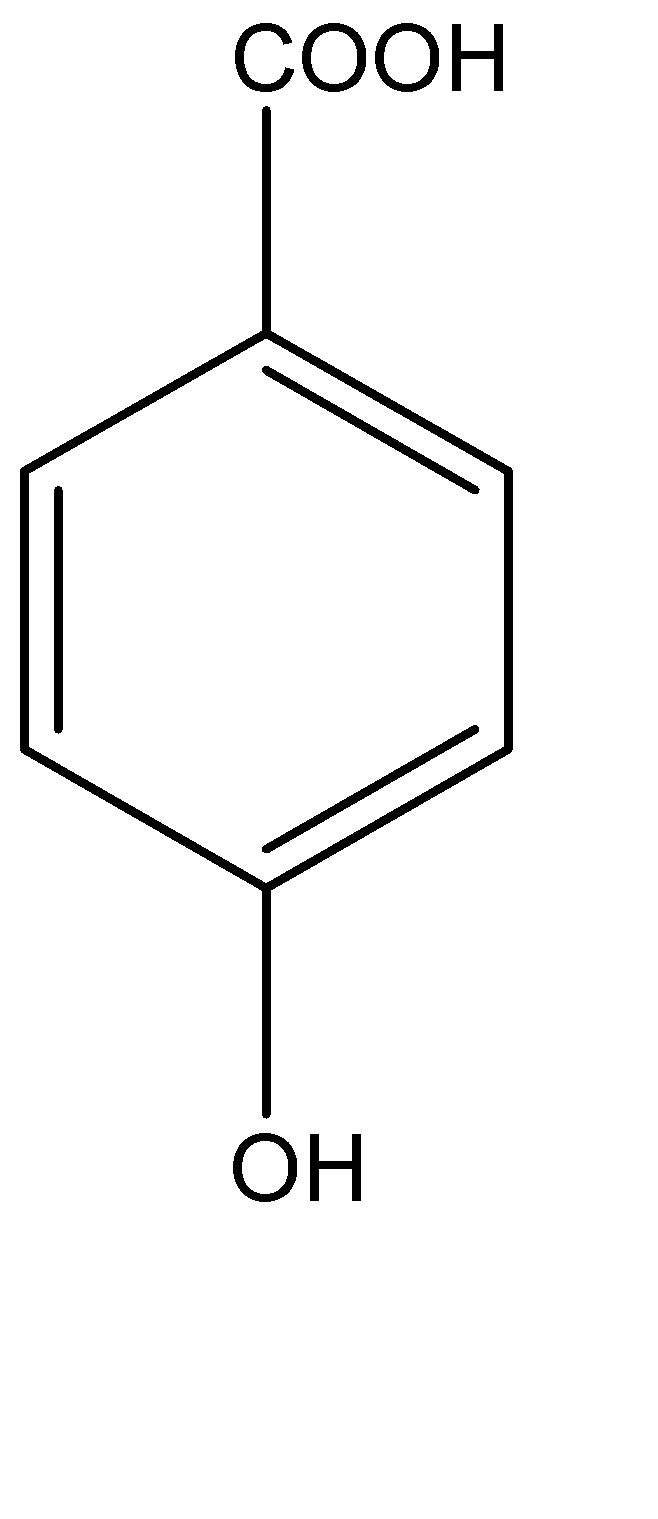
Solution
To solve this question, we must first understand what is meant by the acidic character of a compound. Then we must discuss how certain functional groups and their positions affect the acidic character of a compound, and then derive the correct answer.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
Functional groups can either be electron donating or electron withdrawing. Functional groups which are electron withdrawing show better acidic character. Also, the stability of the molecule is directly proportional to its acidic and basic character. The carboxylic group (−COOH) is an electron – withdrawing group and hence is acidic in nature. Also, the carboxylic group is an ortho, para directing group. This means that the relative yield of the ortho product and that of the para product are higher than that of the meta product. Hence, it would exhibit maximum acidic character at ortho and para positions. On the other hand, the hydroxyl group (−OH) exhibits dual character. It exhibits electron withdrawing characteristics in inductive effect, but exhibits electron donating characteristics in resonance. Since, these compounds are aromatic in nature, they exhibit resonance. Hence, the hydroxyl group is electron donating.
Out of ortho and para positions, the proximity of the ortho position of hydroxyl group to the carboxylic would ensure better and faster transfer of electrons and increase the corresponding acidic character. Hence, the most acidic aromatic compound of the following is:
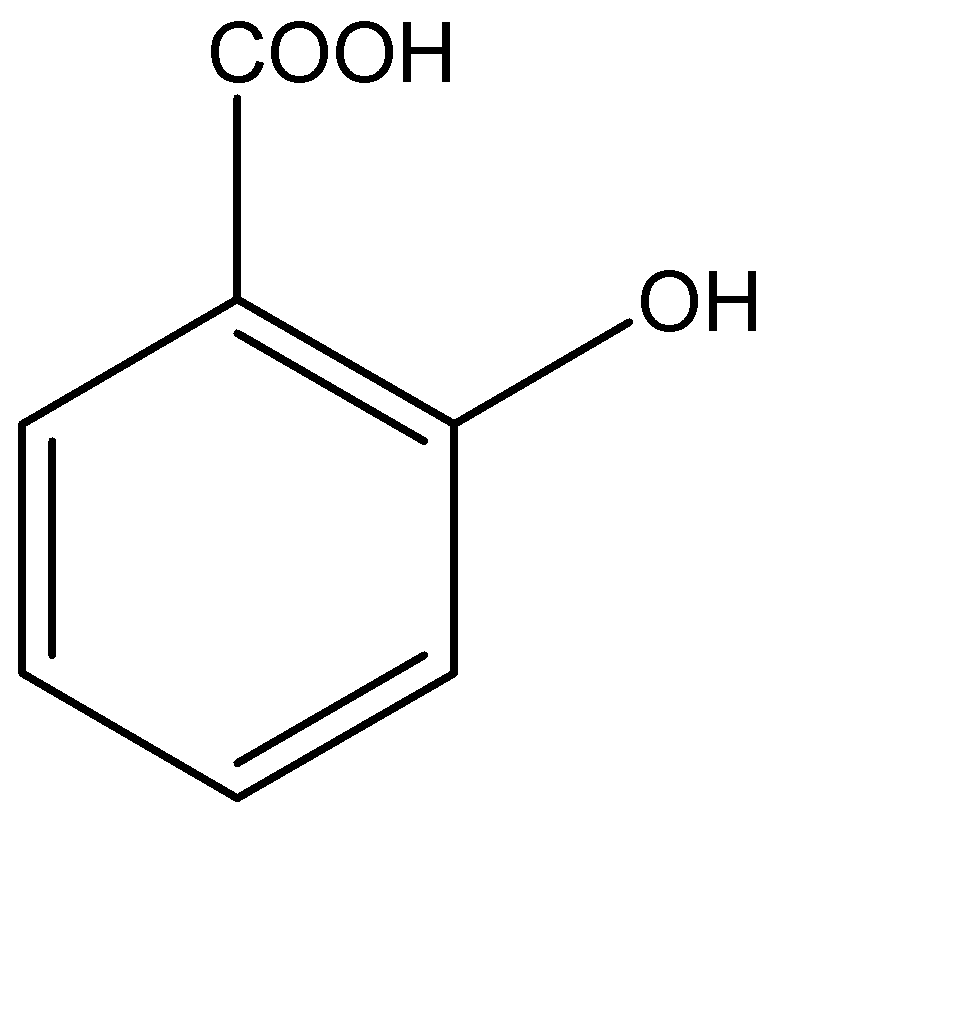
Hence, Option B is the correct option
Note: Compounds can be divided into 3 basic categories – Acidic, basic neutral. Acidic character can be understood as the characteristic that compels a molecule to attract more electrons to attain a more stable electronic configuration for the central atom. This property can be explained on the basis of electronegativity. Electronegativity can be explained as a given atom’s measure to attract shared electrons.
Now, certain functional groups are acidic in nature because of their higher electronegative character. Also, in molecules which exhibit resonance, the position of the functional determines the acidic or basic character of the compound.
