Question
Question: Which of the following alcohol is unable to turn the orange color of chromic acid to green? A. \[...
Which of the following alcohol is unable to turn the orange color of chromic acid to green?
A. 1∘ alcohol
B. 2∘ alcohol
C. 3∘ alcohol
D. Allyl alcohol
Solution
Alcohols are those organic molecules that are formed by linking −OH group to any alkyl or aryl parent chain. This −OH substituent is known as the alcoholic functional group. To put this in simpler terms, alcohols are a homologous series which contain the −OH group. This −OH group is also commonly known as the hydroxyl group.
Complete step by step answer:
Depending on the number of the alkyl group attached with the alpha carbon of the alcohol, it can be 1∘ alcohol, 2∘ alcohol, and 3∘ alcohol. This is also known as primary alcohol, secondary alcohol, tertiary alcohol respectively.
| Molecular structure | no. of alpha hydrogens
---|---|---
1∘ alcohol| 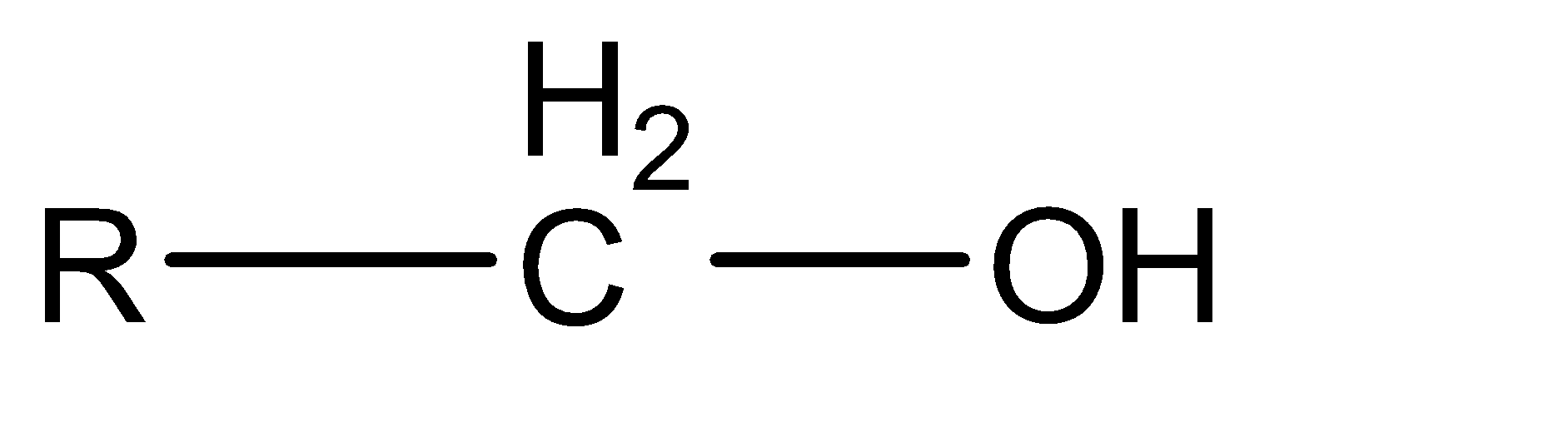 | 2
| 2
2∘ alcohol| 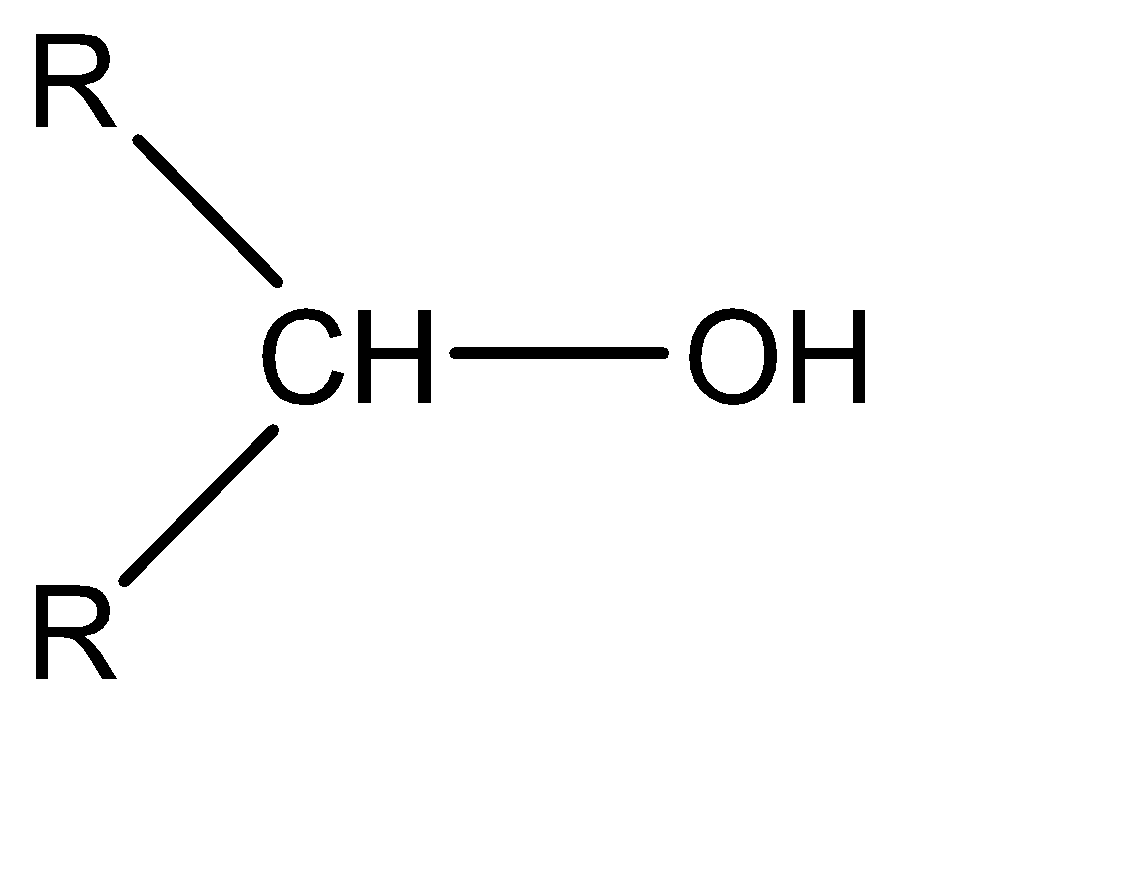 | 1
| 1
3∘ alcohol| 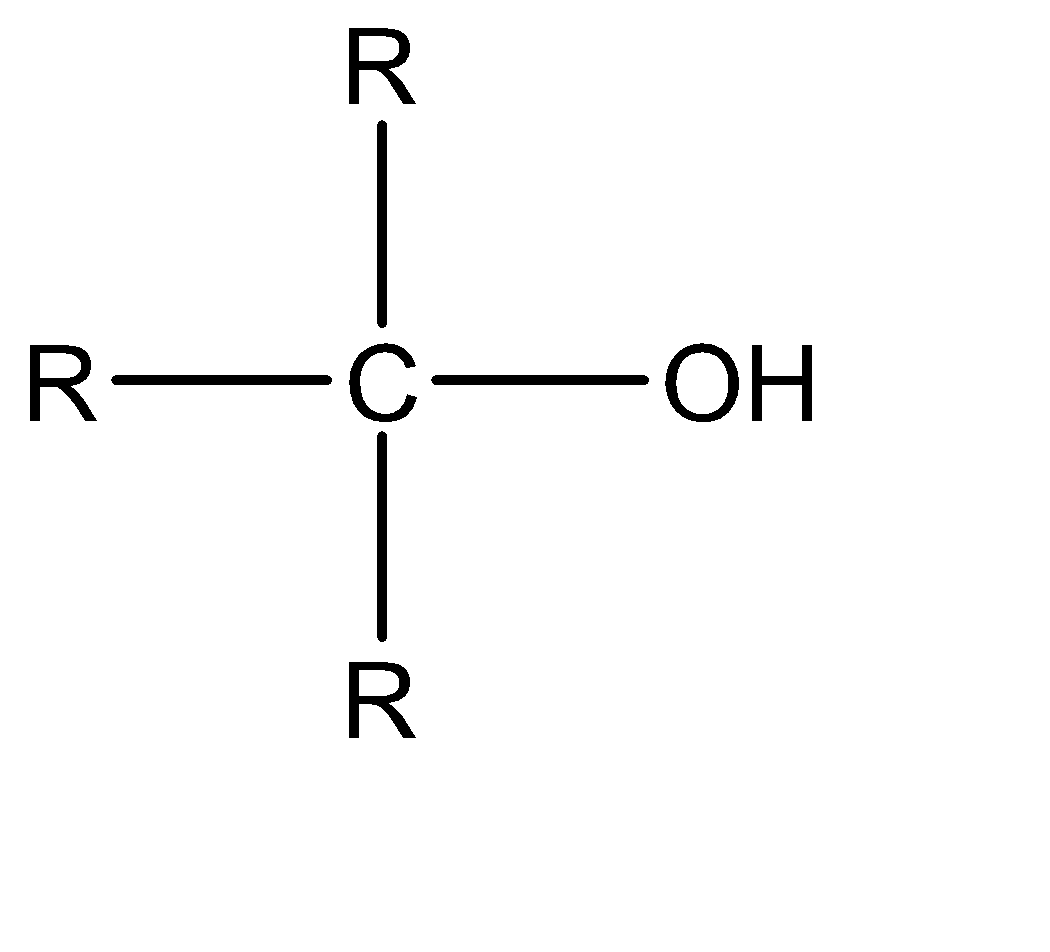 | 0
| 0
The formula of chromic acid is H2Cr2O7 . It is an oxidizing agent. It oxidizes alcohol into aldehyde or ketone and then into a carboxylic acid. In this case alpha hydrogen at the alpha carbon. but in the case of tertiary alcohol there is no alpha hydrogen present, so oxidation is not possible. Instead of oxidation elimination takes place as follows,
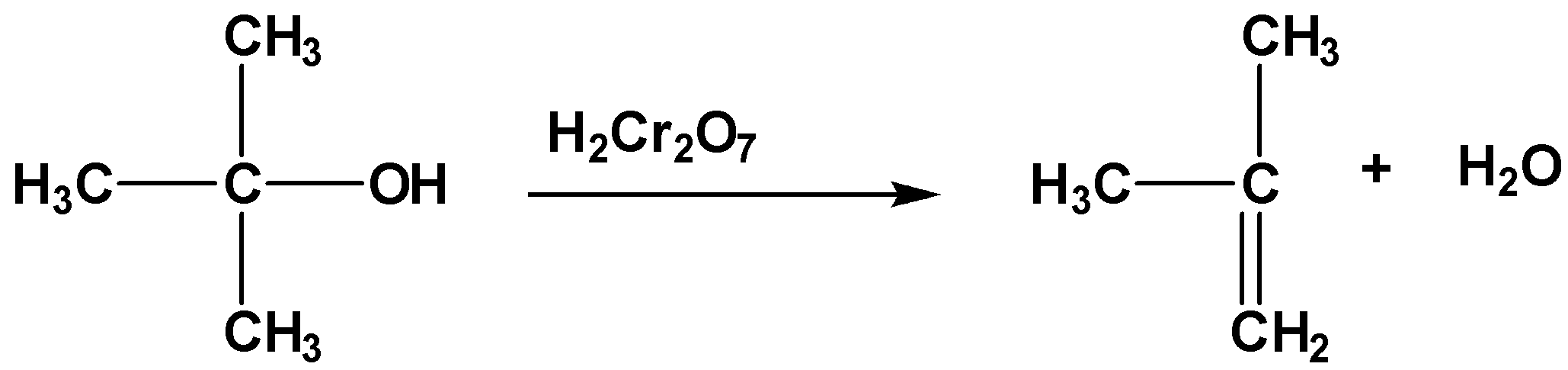
Therefore, 3∘ alcohol is unable to turn the orange color of chromic acid to green.
So, the correct option is C.
Additional information:
Alcohols react with active metals such as sodium, potassium, etc. to yield corresponding alkoxides. Alcohol has a hydrogen atom attached to the oxygen atom. Such compounds which contain hydrogen bonded to high electronegative elements like oxygen are acidic in nature. Therefore, alcohols are acids, although their acidic strength is very less. So, alcohol does not take part in reactions in which acid is already present.
Sodium metal reacts with alcohol to release hydrogen gas. The order of reactivity depends on the acidic strength of the types of alcohol i.e. primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols. Acids that have higher acidic strength react with sodium faster as compared to weaker acids.
In tertiary alcohols, alkyl groups supply the electron density towards the oxygen of alcohol, this reduces the acidic strength of alcohol. Therefore, as the alkyl groups on carbon connected to the alcohol functional group increases, thereby decreasing the acidic strength of alcohol.
From this, we conclude that the reactivity of alcohol with sodium will be primary > secondary > tertiary.
Note: The acidic character of alcohol in alkyl alcohols can be determined by understanding the strength of the conjugate base of the given acid. A conjugate base can be understood as an intermediate product that is formed when an acid tends to gain electrons or lose hydrogen ions (protons). The stronger the acidic character of a species lower would be the strength of the base.
Hence the acidic character of 1∘ alcohol is the greatest while the acidic character of 3∘ alcohol is the smallest.
