Question
Question: Which of the following acids on decarboxylation gives isobutane? A) 2,2-Dimethyl Butanoic acid B...
Which of the following acids on decarboxylation gives isobutane?
A) 2,2-Dimethyl Butanoic acid
B) 2,2-Dimethyl Propanoic acid
C) 3-methyl pentanoic acid
D) 2-methyl butanoic acid
Solution
Decarboxylation reaction is the reaction which involves elimination of carboxyl group and liberating carbon dioxide. Decarboxylation mostly occurs in carboxylic acids, which erases the carbon atom from the chain of carbons. Carboxylation is a reversible process, in which carbon dioxide is added. The enzymes that catalyze decarboxylation are known as decarboxylases.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The general representation of decarboxylation reaction can be given as:
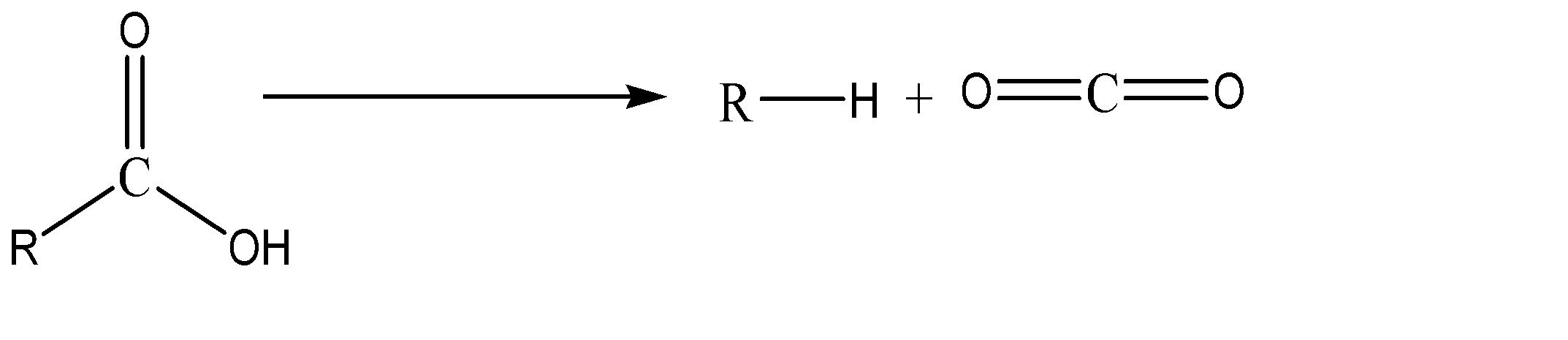
Decarboxylation refers to replacement of a carbonyl group with a hydrogen atom. This is one of the oldest known reactions and is the process assumed to accompany pyrolysis and destructive distillation. This process is mainly carried out in the presence of NaOH/CaO and heat. One by one we’ll analyse each given option to know the product.
A) 2,2-Dimethyl Butanoic acid, on removal of carbonyl group gives 2,2-dimethylbutane. It is also known as neo isopentane. The reaction can be given as:
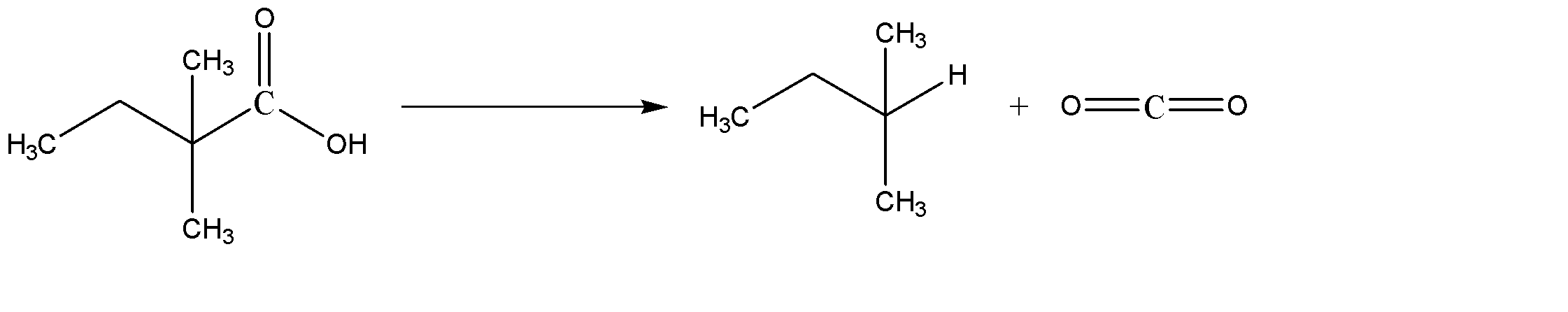
Hence Option A is incorrect
B) 2,2-Dimethylpropanoic acid on decarboxylation gives 2 methylpropane, also known as isobutane. The reaction is given below:
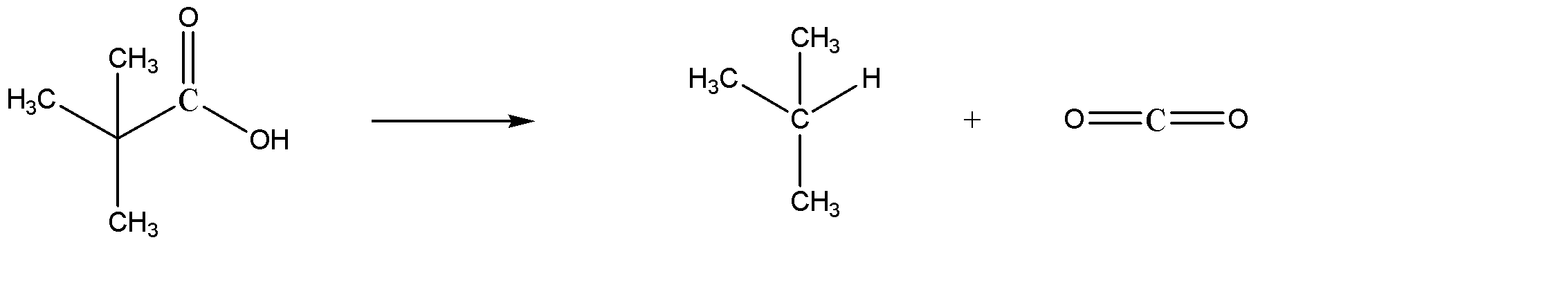
This is the desired answer. Hence, Option B is the correct answer.
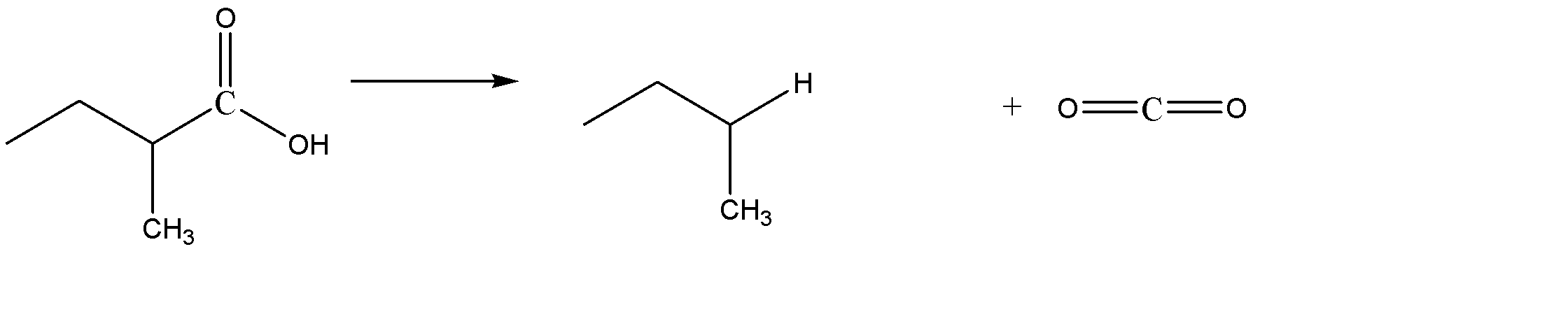
C) 3-methyl pentanoic acid on decarboxylation gives 2-methyl butane. The reaction is given below. Hence Option C is also incorrect
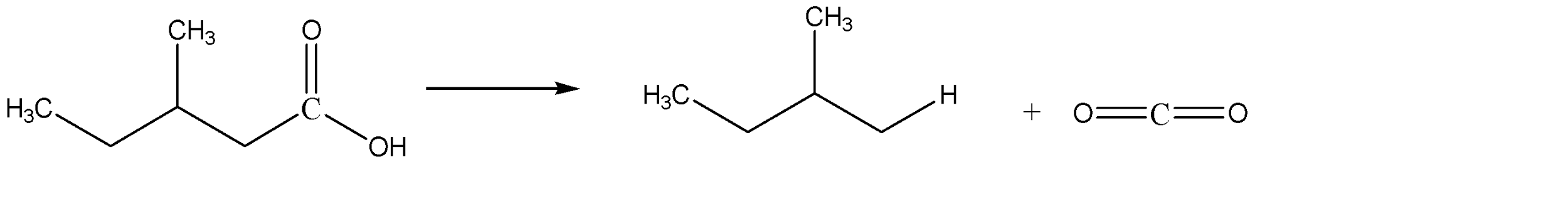
D) 2-methyl butanoic acid on decarboxylation gives n-butane. The reaction is shown below. Option D is incorrect
Note:
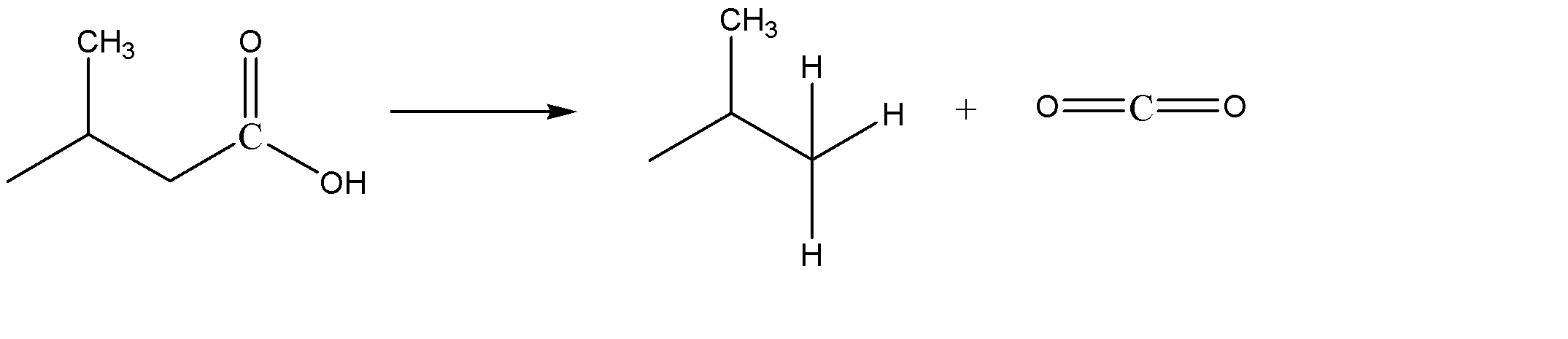
Another way or alternate way for the production of isobutane by decarboxylation is the decarboxylation of 3-methyl butanoic acid in the presence of CaO/NaOH and heat. This gives us isobutane as the product.