Question
Question: Which of the elements is a component of cytochrome oxidase? A. Copper B. Iron C. Mercury D....
Which of the elements is a component of cytochrome oxidase?
A. Copper
B. Iron
C. Mercury
D. Cobalt
Solution
The enzyme cytochrome oxidase or complex IV is a large protein complex found in bacteria and eukaryotic mitochondria. This will be the last enzyme in the cellular transportation chain of the respiratory electron positioned in the membrane. It earns an electron out of each of four molecules of cytochrome C and converts it to one molecule of dioxygen, adding the molecular oxygen to two water molecules.
Complete answer:
Cytochrome C oxidase consists of 13 polypeptide subunits. It includes 3 copper ions that really are essential for its functioning. It also comprises zinc, magnesium, and two heme groups. Copper chaperones are essential for the assembling of the cytochrome C oxidase network, and abnormalities in the genes encoding such chaperones lead to multiple pathologies. The absence of cytochrome oxidase activity is likely to be fatal. Copper is an important micronutrient used by cytochrome c oxidase (Cox) as a metal cofactor. Cox’s key complex includes a copper atom which is needed for its catalytic action. Complications in biogenesis and copper entry into cytochrome C correspond to mitochondrial human diseases.
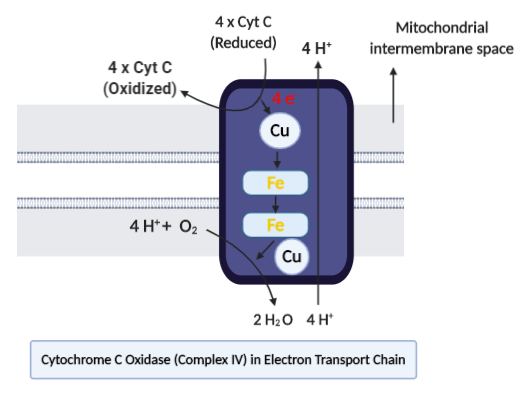
So, the correct answer is (A).
Additional information:
COX takes place in three conformational states: entirely oxidized, slightly reduced, and completely reduced. Each inhibitor does have a strong affinity to some other state. Both heme a3 and CuB nuclear centers are oxidized in the pulsed state; that's the confirmation of the enzyme which has the maximum activity. A two-electron decrease begins a conformational shift which allows oxygen to adhere to the partly-reduced enzyme just at the binding site. Four electrons bound to COX to reduce the enzyme fully. Its complete reduced state, consisting of a reducing Fe2+ in the cytochrome a3 heme and a reducing CuB+ binuclear core, is assumed to be the inactive or resting state of the enzyme.
Note: The above enzyme cox catalyzes the movement of electrons between two substrates, notably Ferro cytochrome C and molecular oxygen. Much of the redox energy involved in this mechanism is being used by the enzyme to move protons from the aqueous environment to the mitochondrial region of the intermembrane. Thus, cytochrome C oxidase is a redox-linked proton engine that integrates redox energy to proton transportation.
