Question
Question: Which of the compounds will give \[{S_n}1\] reaction? a.
b.CH3−Cl
c.CH3−CH2−Br
d.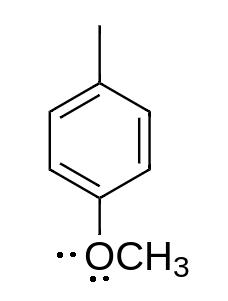
Solution
Basically there are two types of nucleophilic substitution reactions, that is, Sn1 and Sn2 reaction. Here we are asked about the Sn1 reaction, so this reaction is a unimolecular reaction and the rate of this reaction is dependent on the concentration of only one reactant.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Nucleophilic substitution reactions are those reactions in which a nucleophile which is electron-rich, attacks electrophile which is positively charged, in order to replace the leaving group. There are two types of nucleophilic reactions, that is, Sn1 and Sn2 reactions. So, Sn1 reaction is known as a unimolecular reaction, so its rate is dependent upon the concentration of only one reactant. This is a two-step reaction. Whereas Sn2 reaction is a one-step process and is bi-molecular, so its rate is dependent upon both the concentration present in the reaction.
In Sn1 reaction, tertiary carbocations are considered to be most stable, therefore tertiary carbocations are most reactive towards Sn1 reaction as compared to primary and secondary. As more is the stability of carbocation, more is the reactivity.
So, as per the stability of the carbocation, 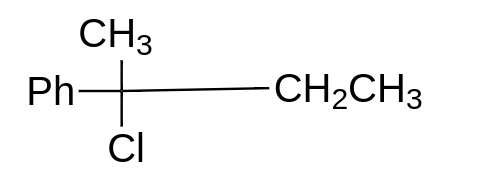
option (A) will give Sn1 reaction, because here, the formation of stable tertiary carbocation will take place, so this will give us Sn1 reaction. This molecule will always go for Sn1 reaction.
Therefore, the correct option is option (A).
Note :
Since, we know that Sn1 is a unimolecular reaction, so its rate will be dependent upon halo alkenes only not on nucleophiles. There are several other factors on which Sn1 reaction depends, such as polar protic solvent is required here in this, the better-leaving group should be there, that increases the rate of the reaction, weak nucleophiles are preferred.
