Question
Question: Which law of Mendel is also known as the “Law of purity of gametes”? A. Law of dominance B. Law ...
Which law of Mendel is also known as the “Law of purity of gametes”?
A. Law of dominance
B. Law of independent assortment
C. Law of segregation
D. Law of gravitation
E. None of these
Solution
Gregor Mendel gave the three laws of inheritance that guide the gamete transfer. The law of purity of gametes is the second law given by Mendel. It describes the individuality of gametes and how they transfer from parents to offspring.
Complete answer:
Mendel is called the founder and the father of genetics he unlocked the mystery of gametes and inheritance. His experiments on pea plants are famous tools of genetics and he observed the inheritance pattern in them in consecutive generations. These observations and investigations led to the formation of three laws of inheritance as stated by Mendel. These laws are also called Mendel’s law of inheritance.
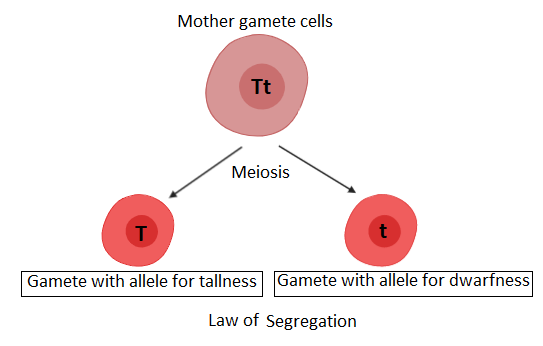
The three laws of inheritance are named: the law of segregation, the law of independent assortment, and the law of dominance. The law of segregation is also referred to as the law of virtue of gamete or the rule of isolation of gametes. At the time of gamete formation, pairs of genes separate and segregate to individual gamete so that each gamete has only one allele for a gene. Alleles are regulating agents of traits or characters. Each gamete carries a single allele. For example, if the gene for height is Tt, then T is the allele for tallness and t is the allele for dwarfness. When the gamete formation occurs each of the gametes will have either T or t. so, this law ensures the purity of gametes as only one allele will be present in one gamete.
So, the right answer is option C.
Note: The law of segregation is based on four basic concepts as observed by Mendel. The first concept is based on the existence of multiple forms of an allele. The second concept is based on meiosis that the allele pairs separate to leave a single allele for each gamete. The third concept is based on the fact that each organism gets two alleles for every trait. The fourth concept is that the two alleles of a gene are different. That is either dominant or recessive.
