Question
Question: Which is the best reagent to convert cyclohexanol into cyclohexene? A. \(Conc.HCl\) B. \(Conc.HB...
Which is the best reagent to convert cyclohexanol into cyclohexene?
A. Conc.HCl
B. Conc.HBr
C. Conc.H3PO4
D. HCl+ZnCl2
Solution
To find the answer of this question, remember by using an acid catalyst (such as strong concentrated acids, like sulphuric acid) as a reagent, an alcohol can be converted to an alkene. So, try to look at each option and choose the option which suits the criteria.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know, alcohol upon reaction with protic acids or acid catalysts (such as sulphuric acid or phosphoric acid) tends to lose a molecule of water and further form alkenes. These types of reactions are called dehydrogenation or dehydration of alcohols. It is an example of an elimination reaction.
Dehydration of alcohols follows a three-step mechanism:
-Formation of protonated alcohol,
-Formation of a carbocation, and
-Formation of alkenes.
So, here in the given question, let us see which option suits as a strong concentric acid which will act as a catalyst in the reaction of converting the cyclohexanol (which is an aromatic alcohol) to cyclohexene (which is an aromatic alkene).
So, here looking at each option, the option with Conc.H3PO4 is found to be a protic and a strong acid. This acid is generally used in the dehydration reaction of alcohols. Here, the acid protonated the −OHgroup present in the cyclohexanol because −OH is a strong base making it a poor leaving group. Once the hydroxyl group has been protonated to H2O, it now leaves and the nucleophile will obstruct beta hydrogen to form a carbon double bond or an alkene i.e. cyclohexene.
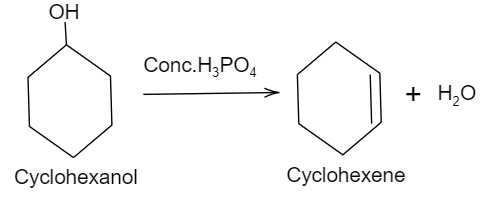
Concentrated phosphoric acid is a good dehydrating agent which converts an alcohol to an alkene by promoting the reaction but not consuming it while other options given are all nucleophiles, which will convert alcohols to alkyl halides.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Phosphoric acid is also called as orthoboric acid and is a weak acid with the chemical formula H3PO4. The most common form of this acid is in 85% liquid solution and these solutions are colourless, odourless and non-volatile in nature.
