Question
Question: Which is a diad form of tautomerism? A. 
B.
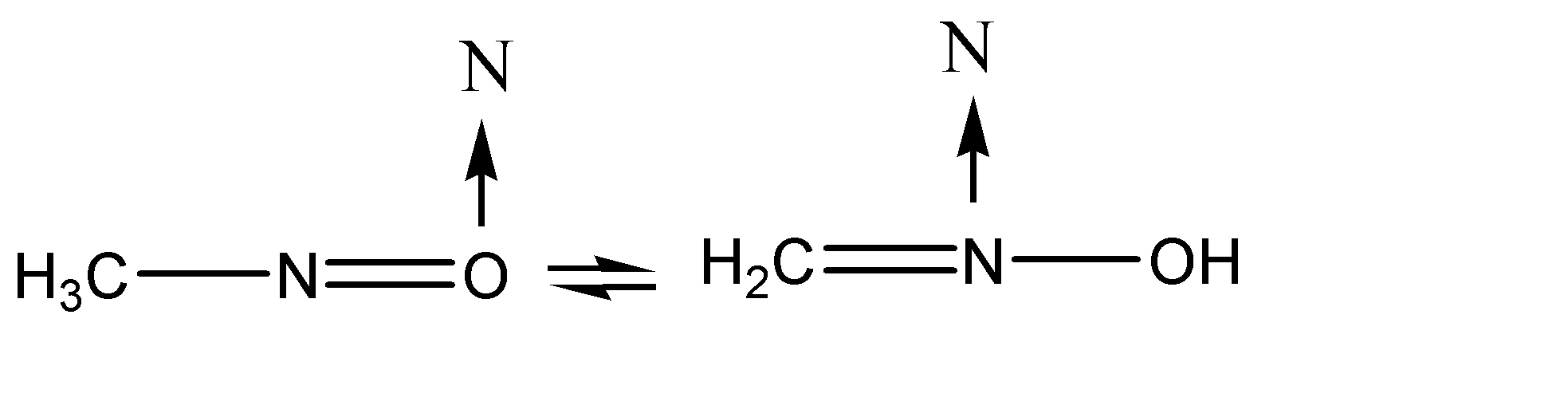
C.
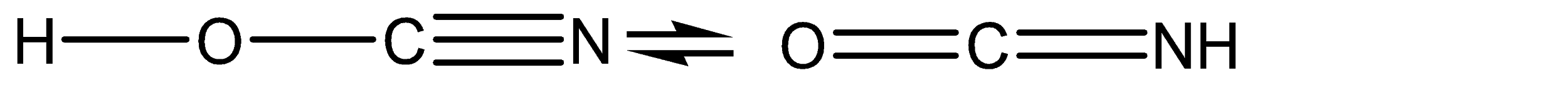
D.All of these
Solution
Tautomerism can be explained as a type of isomerism that is exhibited by different compounds which involves only the change in the positions of protons and electrons, rather than the entire molecular structure. This means that positions of the constituent atoms are unaltered but the orientations of the electrons and protons are shifting.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
The major condition for any compound to exhibit tautomerism is that it should have at least one alpha hydrogen atom. In tautomerism, molecules with the same molecular formula interconvert rapidly. Hence, these molecules also exhibit dynamic equilibrium with each other. Also, tautomerism can be exhibited by any functional group as long as the parent chain has at least one alpha hydrogen. In tautomerism, one of the two isomers formed is more stable than the other.
Now, the Diad system can be understood as migration of charge or electrons from the atom at position 01 to the atom at position 02, in the given tautomer. For a system to be identified as a diad system, it must have at least one pi bond between the first and the second atoms to transfer the charge of electrons between them. Let us now discuss the options given to us:
A.
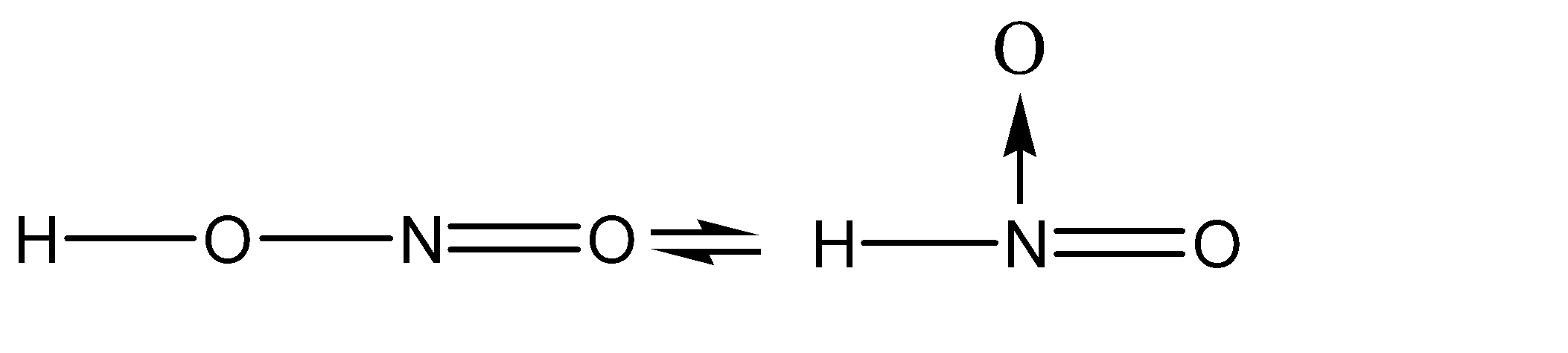
Transfer of charge is taking place between the atoms at position 01 and position 02.
B.
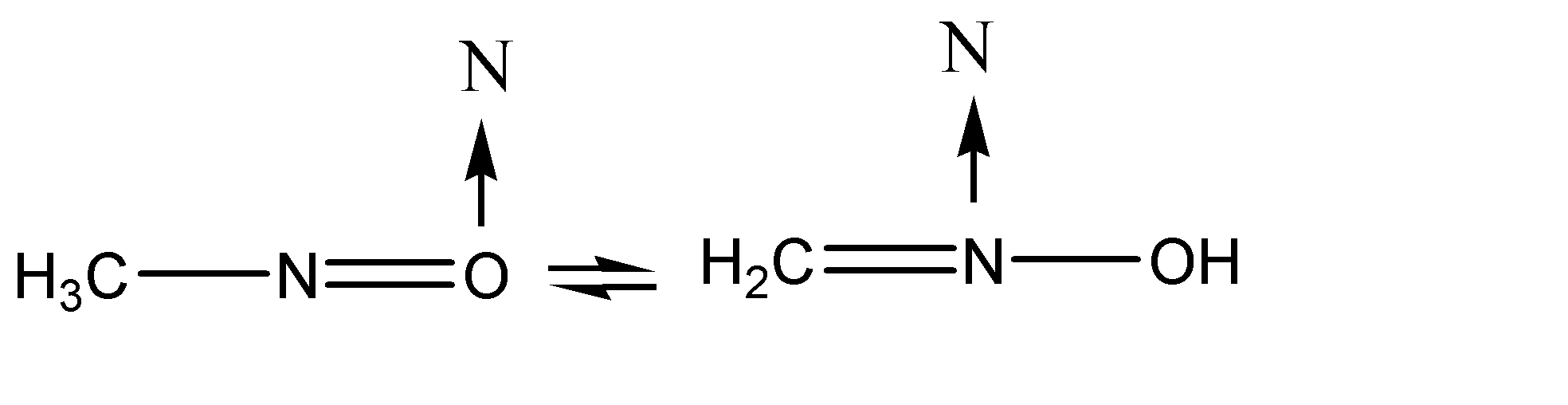
Transfer of charge is taking place between the atoms at position 02 and position 03.
C.
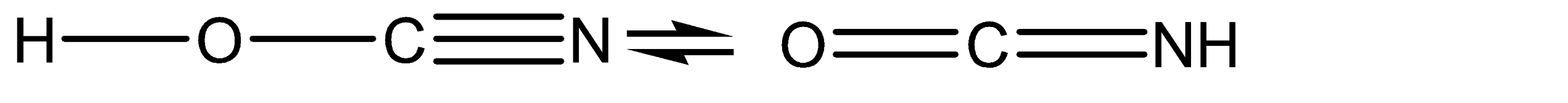
Transfer of charge is taking place between the atoms at position 02 and position 03.
Hence, Option A is the correct option
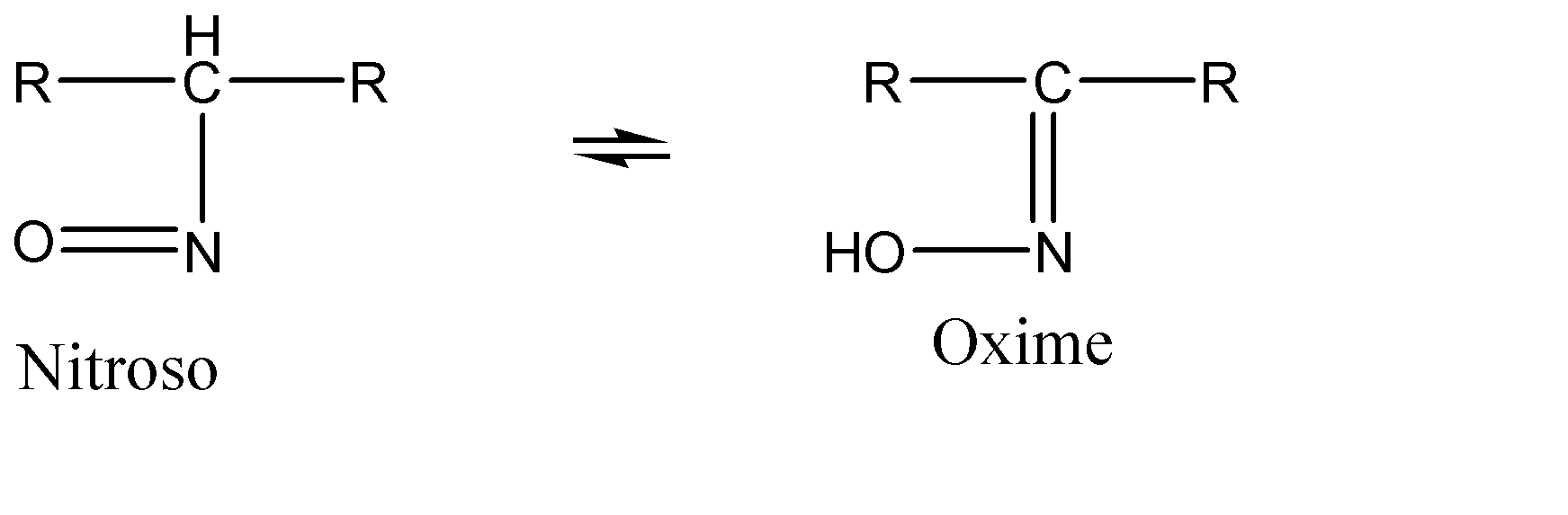
Note: Similar to a Diad system, there exists a system known as a Triad system. In a triad system, there is a shift of electrons or charge between the position 01 and position 03. One such example of a triad system is Oxime – nitroso: