Question
Question: Which hybridization results in non-planar orbitals? (A)- \(sp\) (B)- \(s{{p}^{2}}\) (C)- \(s...
Which hybridization results in non-planar orbitals?
(A)- sp
(B)- sp2
(C)- sp3
(D)- dsp2
Solution
Hybridization is the mixing of atomic orbitals of comparable energies belonging to the same shell, to form new orbitals of equal energy and shape. Angle between the four hybrid orbitals in sp3-hybridization is 109o28′.
Complete answer:
The shapes of molecules can be determined from the type hybridization the molecule is undergoing. Let us now discuss the shapes of the hybrid orbitals resulting from the above given hybridizations.
sp-hybridization
One s and one p orbital of the same shell of an atom combine or hybridize together to form two identical hybrid orbitals. The new hybrid orbitals formed due to hybridization of s and p orbitals are called sp hybrid orbitals.
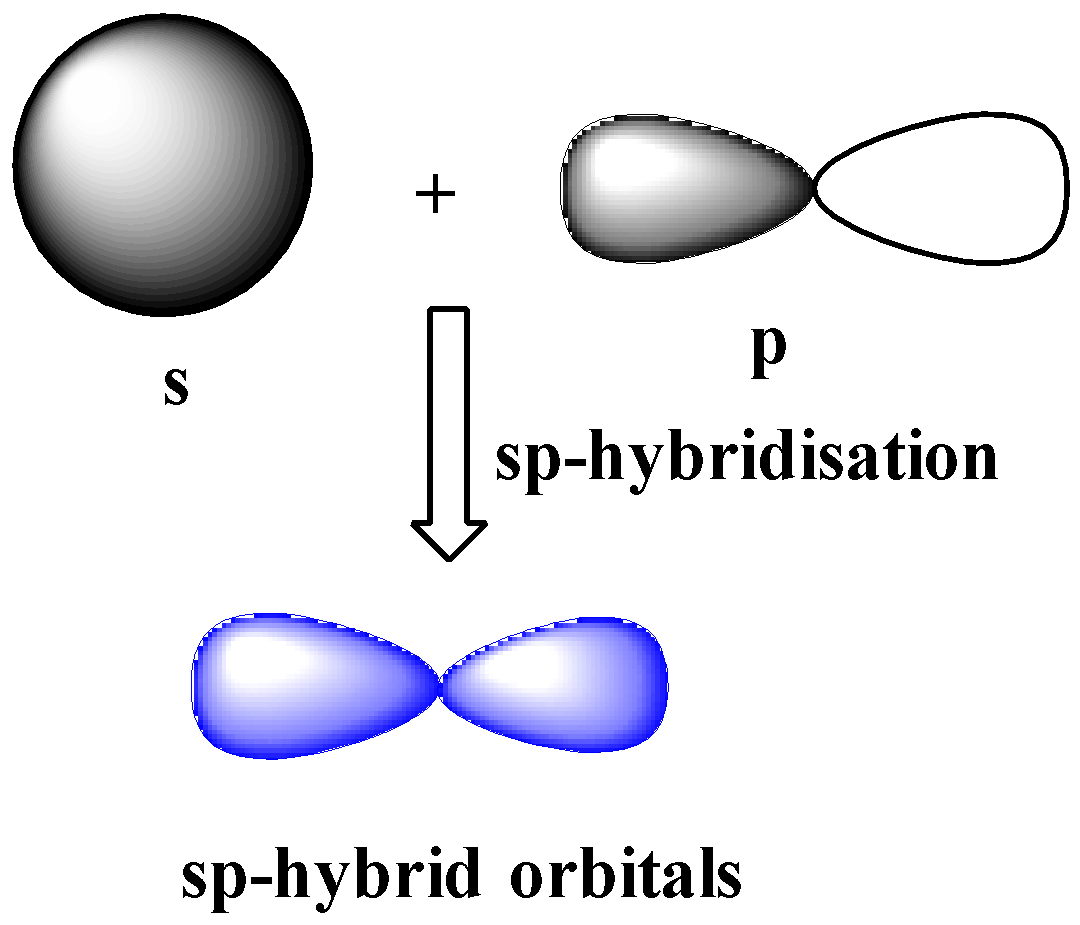
The new hybrid orbitals formed due to hybridization of s and p orbitals are called sp hybrid orbitals. These orbitals have 180o angle between then and are collinear.
sp2-hybridization
When one s and two p orbitals of the same shell mix together to form three orbitals of equal energy and identical shape, the hybridization is sp2 hybridization. The three hybrid orbitals make 120o with one another and are in the same plane. sp2 hybridization leads to trigonal planar geometry.
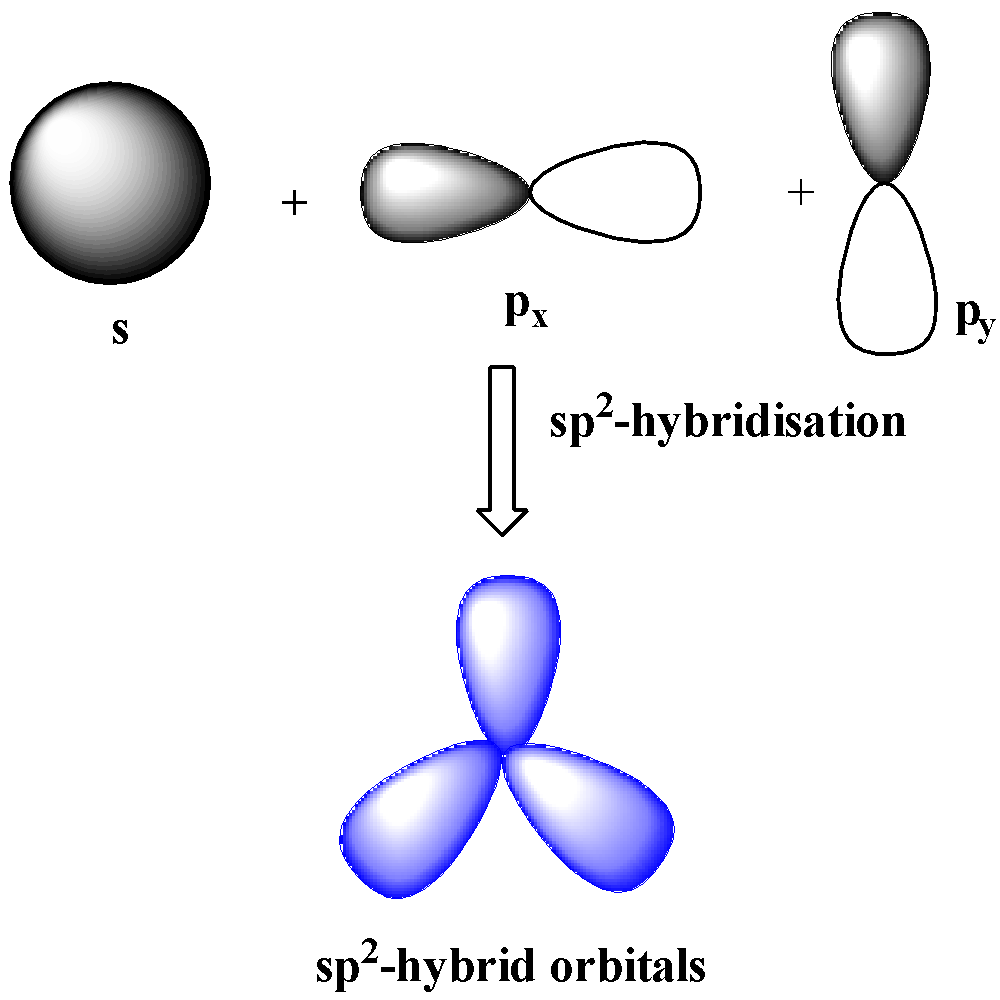
sp3-hybridization
One s and three p-orbitals belong to the same shell mix together to four new equivalent orbitals.
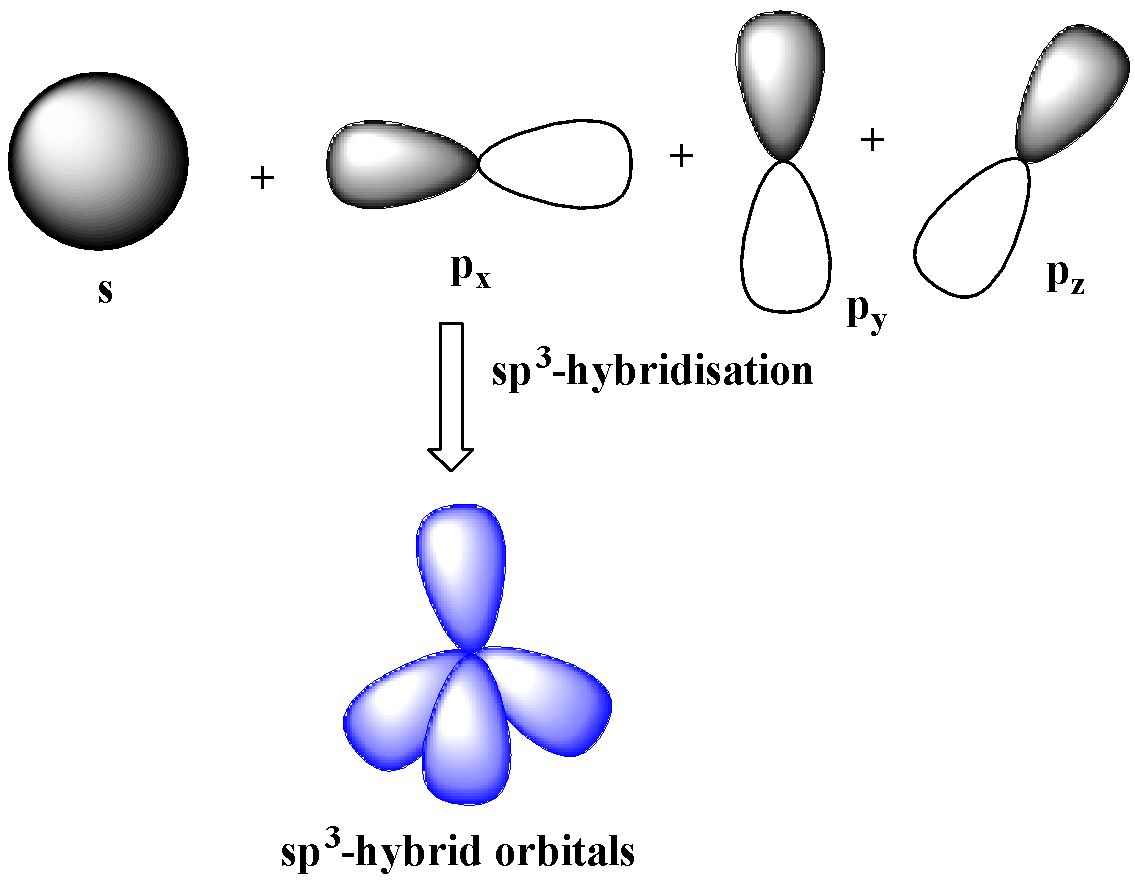

These orbitals rearranged in a regular tetrahedron making an angle of 109.5o with one another. Therefore, these orbitals are non-planar.
dsp2-hybridization
In this type of hybridization, one d (dx2−y2) orbital of lower shell and one s and p orbital of the next shell mix together to form four orbitals of identical shapes and equal energy.
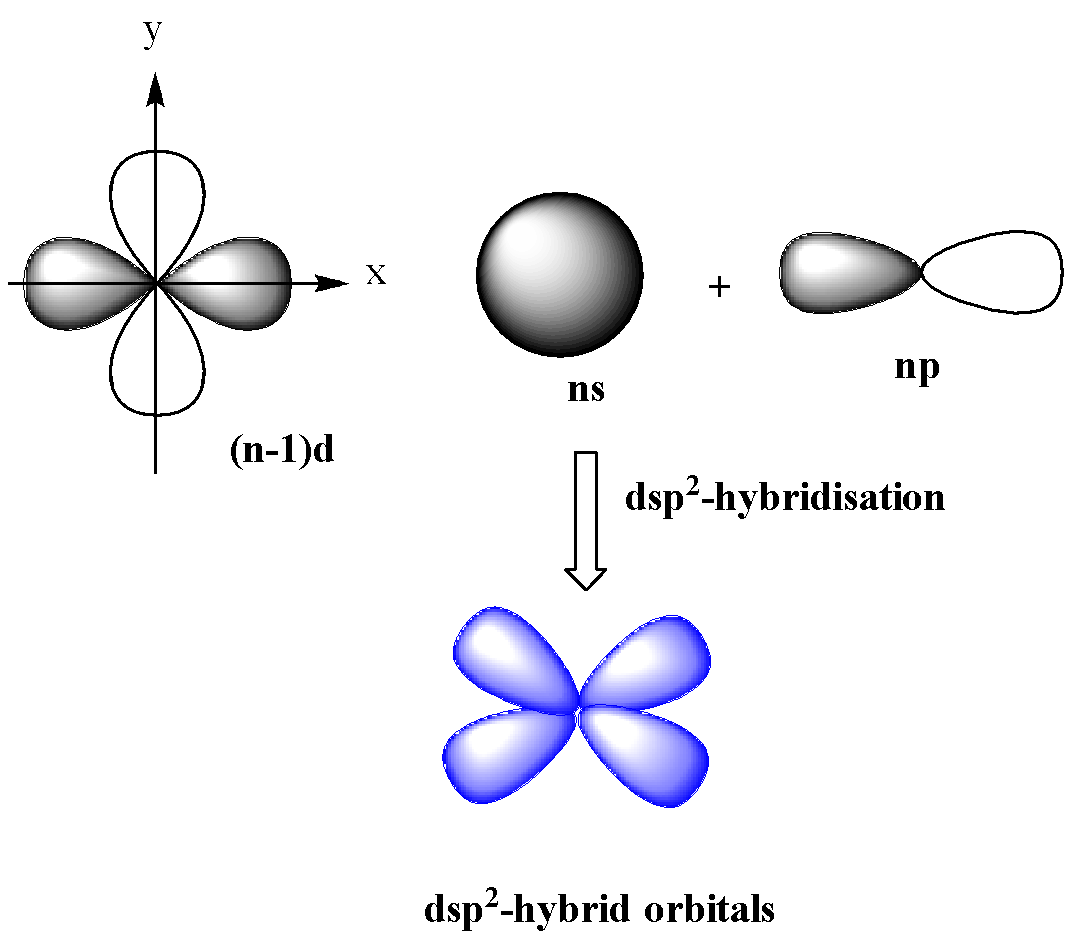
These orbitals are in the same plane having an angle of 90o with one another. dsp2-hybridization gives square planar geometry.
Based on the above discussion, we can see that sp3-hybridization leads to non-planar orbitals.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Do not confuse yourself between dsp2 and sp3. Both involve the hybridization of four orbitals. But the orbitals involved in hybridization are different in the two cases. sp3 leads to non-planar tetrahedral geometry whereas dsp2 leads to square planar geometry.
